Azure LoadBalancers
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Load Balancing
In the realm of networking, "load balancing" is the art of efficiently distributing incoming network traffic across multiple backend resources. It ensures that no single server becomes overwhelmed, maintaining performance and reliability.
- Typically, these resources are virtual machines organized in a "backend pool" or instances in a virtual machine scale set.
- Operates at the Transport Layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model.
- Serves as the single access point for applications running on virtual machines (VMs) or scale sets.
- Distributes incoming traffic across the deployed backend VMs or resources.
Use Cases
Load balancing serves several critical functions, enhancing both performance and reliability.
-
Availability Enhancement
- Increase application availability by distributing traffic across multiple VMs and zones.
-
Outbound Connectivity
- Provide outbound Internet connectivity for VMs without assigning individual public IP addresses.
Types of Azure Load Balancers
Azure offers different types of load balancers to suit various needs.
-
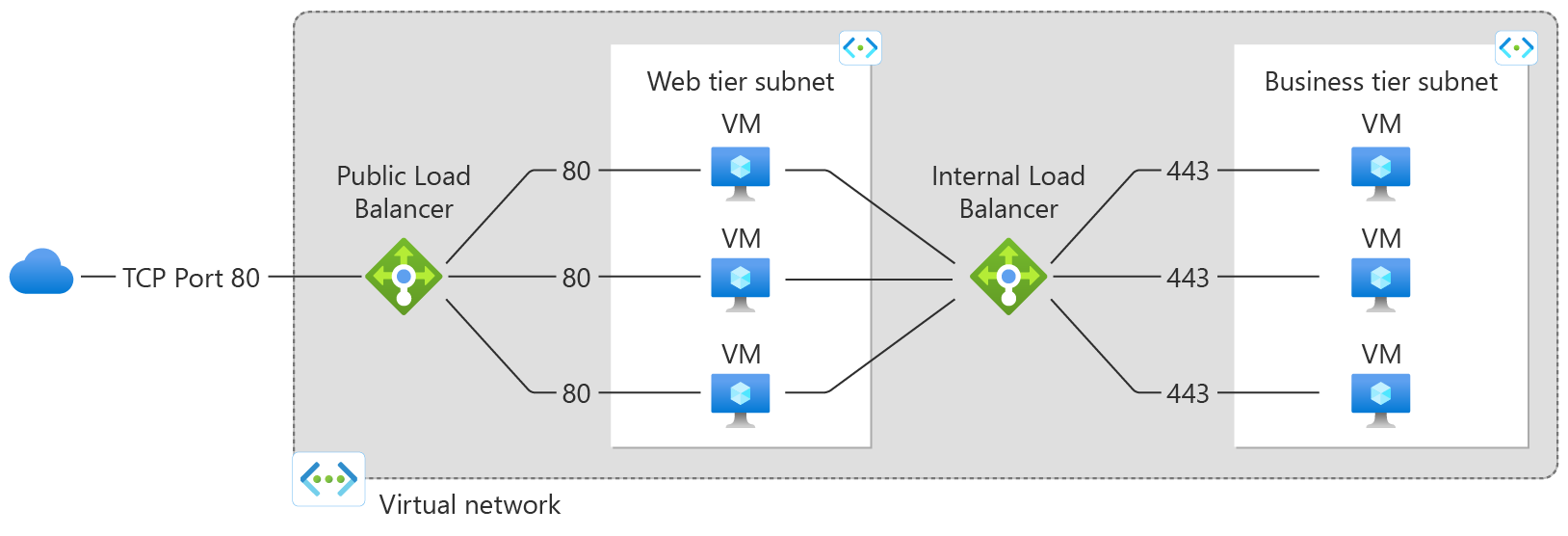
Public Load Balancer
- Distributes Internet traffic to VMs.
- Requires a public IP address on the frontend.
- Provides outbound Internet connections for VMs within the virtual network.
-
Internal Load Balancer (Private Load Balancer)
- Utilizes only private IP addresses on the frontend.
- Designed for load balancing within the virtual network or from an on-premises network connected via VPN or ExpressRoute.
Common Use Cases
Azure load balancers are used in various scenarios to optimize application performance and reliability.
 |
|---|
Load Balancer SKUs
Azure offers two primary SKUs for load balancers, each with distinct features.
-
Basic Load Balancer
- Supports up to 300 instances.
- No support for availability zones.
- Open to the Internet by default.
-
Standard Load Balancer
- Supports up to 1000 instances.
- Provides support for availability zones.
- Offers zone-redundant and zonal frontends for inbound and outbound traffic.
- Adheres to the zero-trust model, enhancing security.
- Integrated into the virtual network; inbound traffic requires explicit permission via network security groups.
Microsoft's Recommendation: Microsoft recommends using Standard Load Balancers whenever possible due to their built-in security features and extended capabilities, providing a robust solution for diverse scenarios.