Azure Traffic Manager
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Overview
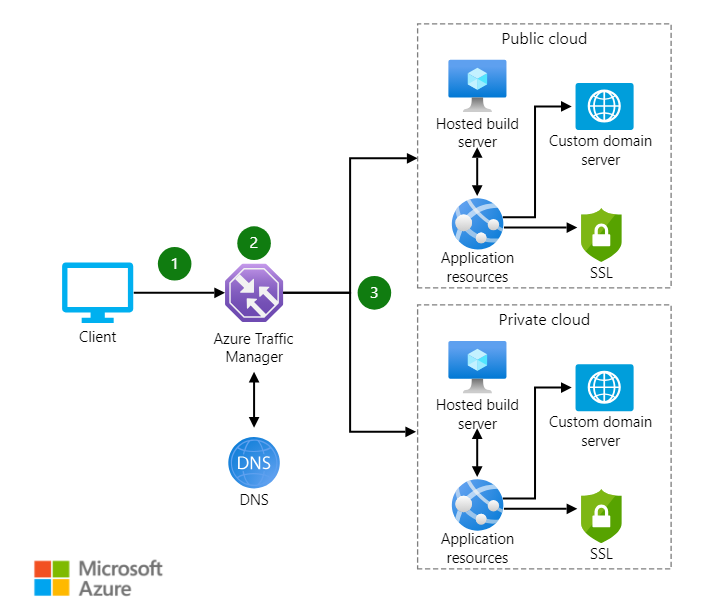
Unlike other load balancer offerings, Azure Traffic Manager is a DNS-specific load balancing solution used to distribute traffic to services across different global Azure regions.
 |
|---|
Through this mechanism, Azure Traffic Manager enhances application availability and responsiveness for users in various geographical locations.
Key Features
Azure Traffic Manager offers a range of capabilities to optimize traffic distribution and enhance service accessibility:
-
Global Load Balancing
- Distributes traffic globally to services across Azure regions.
- Ensures European users access the application from the nearest endpoint, while North American users connect to the closest service endpoint.
-
DNS-Based Traffic Routing
- Leverages DNS to direct access requests to the service endpoint with the least latency, considering configured routing methods and endpoint health.
- Supports Internet-facing services both inside and outside Azure.
-
Routing Methods
- Priority
- Sends all traffic to a primary service endpoint, with backup endpoints available.
- Weighted
- Splits traffic across multiple endpoints based on defined weights.
- Performance
- Routes users to the closest endpoint, reducing latency.
- Geographic
- Forces users to the closest endpoint based on their geographic location.
- Multivalue
- For Traffic Manager profiles with IPv4 or IPv6 addresses as endpoints.
- Subnet
- Maps specific user IP address ranges to specific endpoints.
- Priority
-
Traffic Manager as a Traffic Cop
- Not a proxy or gateway.
- Directs clients to endpoints; traffic passes directly between clients and endpoints.
Typical Client-Endpoint Connection
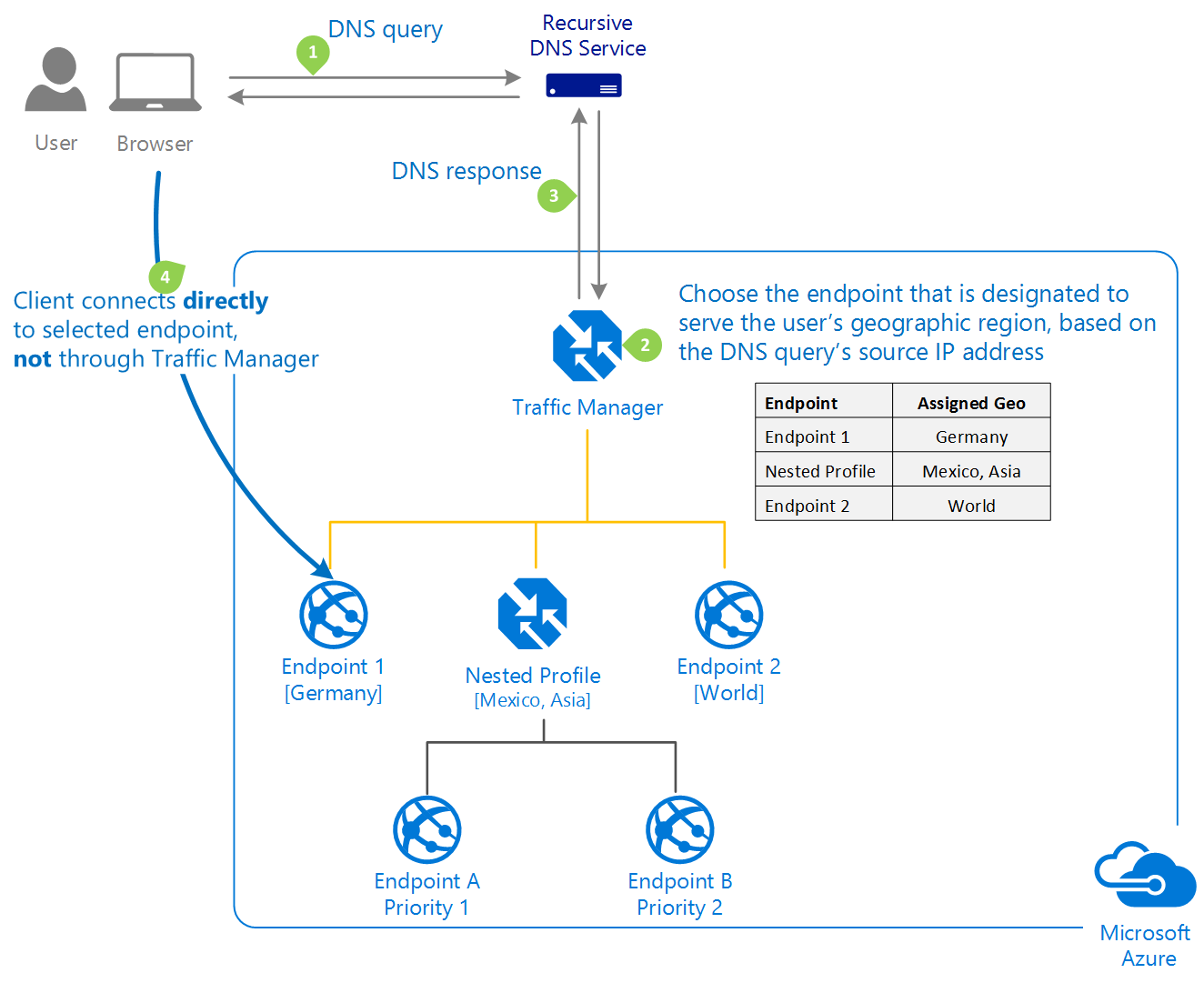
The following diagram illustrates how a client connects to an endpoint via Traffic Manager:
 |
|---|
-
DNS Query
- Client initiates a DNS query for the application.
-
DNS Service reaches out Name Servers
- DNS service reaches out to the name servers for the domain hosting the application.
- Those name servers return the CNAME record that points to the Traffic Manager implementation for the app.
- The root domain will always be trafficmanager.net for Traffic Manager implementations.
- After finding the name servers for the trafficmanager.net domain, the client’s DNS service sends a request for the DNS name.
-
DNS Reaches out Traffice Manager
- The client’s DNS service finds the name servers for the trafficmanager.net domain.
- These servers are provided by the Traffic Manager service itself.
-
Endpoint Determination
- Name servers determine the correct endpoint based on configured settings.
-
CNAME Record Return
- Traffic Manager returns the CNAME record of the proper endpoint to the client’s DNS service.
-
Endpoint Resolution
- Client's DNS service resolves the endpoint DNS name (e.g.,
bluewidget-us.cloudapp.net).
- Client's DNS service resolves the endpoint DNS name (e.g.,
-
Connection Establishment
- Client connects directly to the resolved endpoint.
For more information: Azure Traffic Manager Documentation.