Azure Storage
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Benefits of Azure Storage
-
Durability and Availability
- Built-in redundancy ensures data safety during hardware failures.
- Cross-data center and cross-region replication protect against disasters or local failures.
-
Security and Access Control
- Automatic encryption for all stored data ensures inherent security.
- Fine-grained control over data access is maintained.
-
Scalability and Accessibility
- Designed to be massively scalable to meet diverse data storage requirements.
- Access data globally over HTTP or HTTPS with support for various client libraries and languages.
- Multiple access methods include .NET, Java, Python, PHP, PowerShell, Azure CLI, Azure portal, and Azure Storage Explorer.
Core Azure Storage Services
-
Azure Blobs
- Provides object storage for unstructured data (e.g., text, binary data).
-
Azure Managed Disks
- Block-level storage volumes managed by Azure for virtual machines.
- Types include ultra disks, premium SSD disks, standard SSD disks, and standard HDD disks.
-
Azure Files
- Fully managed file share system accessible via the SMB protocol.
- Supports mounting from Windows, Linux, and MacOS machines, on-prem and in the cloud.
-
Azure Queue Storage
- Designed for storing and managing large numbers of messages in distributed applications.
-
Azure Table Storage
- Ideal for structured NoSQL data with a key/attribute store and a schema-less design.
Storage Account types
-
General-Purpose V2 Account
- Basic storage account suitable for hosting blobs, files, queues, and tables.
- Recommended for most scenarios requiring Azure storage.
-
General-Purpose V1 Account
- Legacy account hosting blobs, files, queues, and tables.
- Similar functionality to V2 accounts, but Microsoft recommends using V2 for future-proofing.
-
Block Blob Storage Account
- Offers premium performance for block blobs and append blobs.
- Ideal for high transaction rates and scenarios requiring low storage latency.
-
File Storage Account
- Exclusive files-only storage account.
- Recommended for enterprise and high-performing applications.
-
Blob Storage Account
- Legacy account used for blob-only storage.
- Microsoft recommends using general-purpose V2 accounts instead.
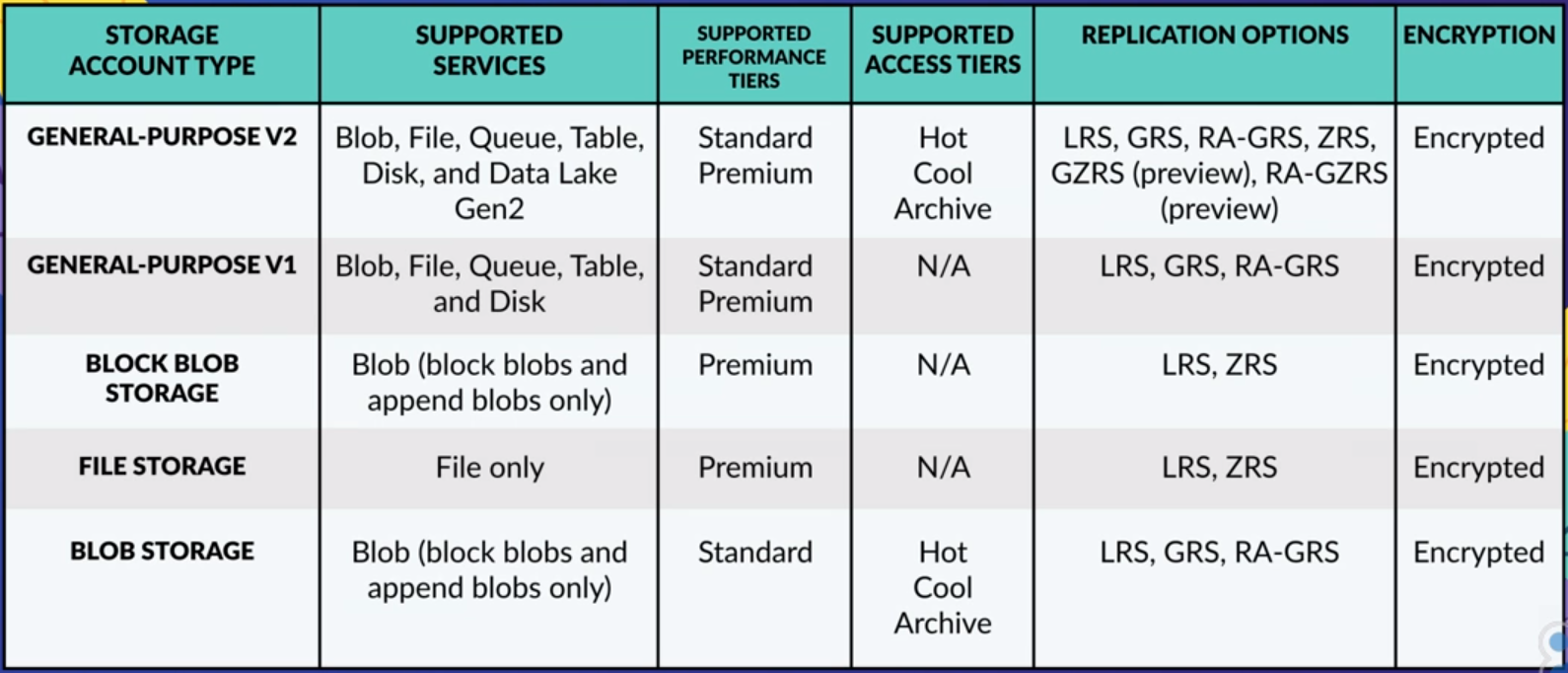
Key Features
- All storage account types are encrypted using Storage Service Encryption (SSE) for data at rest.
- Archive storage and blob-level tiering support only block blobs.
- Zone-Redundant Storage (ZRS) and Geo Zone-Redundant Storage (GZRS) are available for standard general-purpose V2 accounts, block blob accounts, and file storage accounts in certain regions.
- Premium performance for general-purpose V2 and general-purpose V1 accounts is available for disk storage and page blobs. For block blobs and append blobs, it's exclusive to block blob accounts. Files-only storage accounts support premium performance for files.
Important Points
- Archive storage and blob-level tiering support only block blobs.
- ZRS and GZRS are available only for standard general-purpose V2 accounts, block blob accounts, and file storage accounts in certain regions.
- Premium performance for general-purpose V2 and general-purpose V1 accounts is only for disk storage and page blobs. Block blob accounts support premium performance for block blobs and append blobs, and files-only storage accounts support premium performance for files.
Detailed information on the different storage accounts available at: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-account-overview.
Performance Levels
Aside from the redundancy level and the default access tier, there’s yet another option you need to set when you create a storage account: the performance level.
-
Standard (Default)
- Account Type: General-purpose v2 account.
- Recommendation: Suitable for most cases.
-
Premium
- Account Type: Higher-performance option.
- Consideration: More expensive and limits redundancy options.
- Usage: Recommended only if significantly faster performance is necessary.
Data Transfer into Azure Storage
-
Azure Portal
- Use: For uploading a small number of files from the desktop.
- Capability: Allows file upload and download directly through the portal.
-
AzCopy (Command-Line Utility)
- Use: For faster upload/download, especially for a large number of files.
- Capability: Supports file and folder copying, including cross-cloud transfers.
-
Azure Storage Explorer (Graphical User Interface)
- Use: For managing files, changing access tiers, and copying files using a graphical interface.
- Capability: Provides file management features beyond simple copying.
-
Azure File Sync
- Use: Specialized use case for creating a local cache of Azure Files on Windows servers.
- Capability: Enhances access speed to an Azure file share in an on-premises environment.
Migration Tools
-
Azure Migrate
- Use: Comprehensive tool for discovering, assessing, and migrating on-premises servers, web apps, and databases to Azure.
- Process: Discovers on-premises resources, assesses size and cost of equivalent Azure services, facilitates migration.
-
Azure Data Box
-
Use: For sending a large amount of data during migration.
-
Process: Microsoft ships a Data Box storage device, data is copied to the device, shipped back to Microsoft, and data is transferred to the Azure storage account.
-
Consideration: Typically used for data transfers exceeding 40 terabytes due to time and expense involved.
-