Azure Table Storage
Updated Nov 16, 2020 ·
NOTES
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Overview
Azure Table Storage is a NoSQL datastore, providing a schema-less and flexible approach to storing structured non-relational data.
- Ideal for storing structured non-relational data.
- Key/attribute store with a schema-less design, allowing flexibility in data storage without rigid schema requirements.
- Commonly used for flexible databases, such as user data in web applications, address books, or device information.
- Suited for scenarios with large amounts of structured data, especially when complex joins, foreign keys, or stored procedures are not necessary.
- Useful for scenarios involving large datasets that require fast access without the need for complex relational features.
Components
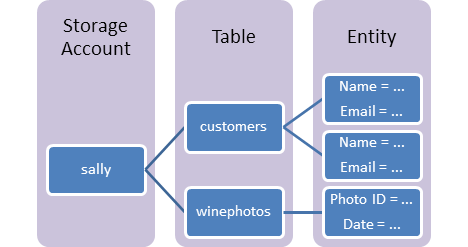
- URL Format for Access:
- Format:
http://<storage account>.table.core.windows.net/<table> - Unique URL with storage account name and table name.
- Format:
- Storage Account:
- All access to Azure storage, including table storage, is via a storage account.
- Table:
- A collection of entities; unlike relational databases, tables do not enforce a strict schema.
- Entity:
- Comparable to a traditional database row.
- Essentially, a set of properties.
- Each entity can be up to 1 MB in size.
- Properties:
- Name-value pairs.
- Up to 252 properties per entity.
- Three system properties:
- partition key
- row key
- timestamp
Key Relationships
-
Hierarchy: Storage account > Tables > Entities > Properties.
-
Access: The URL serves as the means to access the entire structure.