Aggregations
Overview
Elasticsearch is more than a search engine. It can analyze and organize numerical data, offering fast and efficient metrics analysis.
Elasticsearch aggregations can sometimes replace tools like Hadoop and Spark. While Hadoop or Spark may take minutes or hours to run queries, Elasticsearch often provides results in seconds.
Aggregation Types
Bucket Aggregation
Bucket aggregation groups documents into buckets based on specific criteria, similar to the SQL GROUP BY clause. These buckets can be defined by terms, ranges, or intervals, such as grouping by sector or creating date histograms.
- Groups documents into buckets based on matching criteria
- Options include single terms, ranges, or date histograms
- Allows splitting data into meaningful categories
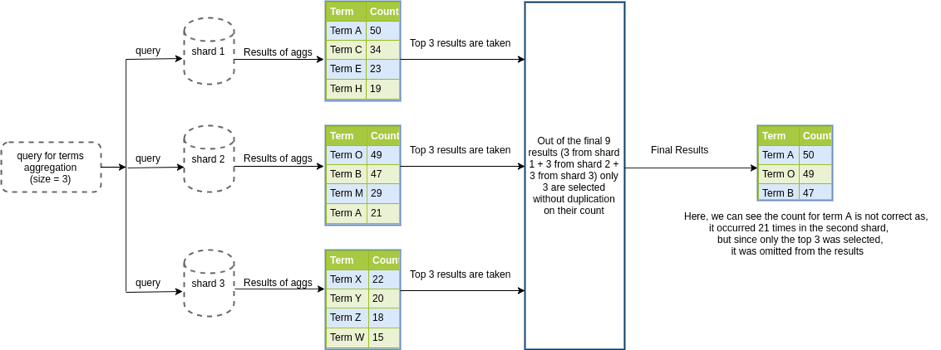
While powerful, too many buckets can overwhelm the coordinating node responsible for reducing results. To mitigate this, limit the number of buckets per shard or consider partitioning to balance performance and accuracy.
The image below illustrates the problem with generating too many buckets:
Metric Aggregation
Metric aggregation calculates values for specific fields, either within buckets or across all documents. These values include predefined metrics like maximum, minimum, and average, or custom calculations using scripts.
- Calculates values like max, min, or average for fields
- Can be applied to specific buckets or all data
- Supports custom scripts for advanced calculations
Metric aggregation helps analyze and summarize data efficiently, providing insights into patterns and trends.
Pipeline Aggregation
Pipeline aggregation processes and calculates metrics based on the output of other aggregations. These can be used to further refine or transform data, such as calculating cumulative sums or moving averages.
- Works on the results of other aggregations
- Useful for advanced calculations like cumulative sums or moving averages
- Enhances insights by refining existing aggregation results
Pipeline aggregation enables complex analysis by chaining and transforming results from other operations.
Aggregation Syntax
The basic aggregation syntax is:
"aggs": {
"name_of_aggregation": {
"type_of_aggregation": {
"field": "document_field_name"
}
}
}
Where:
- aggs: Specifies that an aggregation is being used.
- name_of_aggregation: User-defined name for the aggregation.
- type_of_aggregation: The aggregation type (e.g., terms, sum).
- field: Indicates the target field.
- document_field_name: The column name of the document to aggregate.