The Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning and Task Creation
During sprint planning, your team will populate the Scrum board with tasks necessary for the upcoming sprint. This session sets the stage for organized, prioritized work that aligns with your project goals.
- Purpose: Establish a clear plan for the sprint's tasks to ensure everyone understands their responsibilities and goals.
- Facilitation: Led by your Scrum Master or Disciplined Agile Lean Scrum Master, this meeting focuses on sequencing work for maximum value delivery.
Key Questions
- Has the team worked with the Scrum Master to prioritize sprint tasks?
- Are the story point estimates for each user story agreed upon by the team?
- Does each team member understand their tasks for the upcoming sprint?
- Is the workload aligned realistically with the team’s capacity?
Stages of Sprint Planning
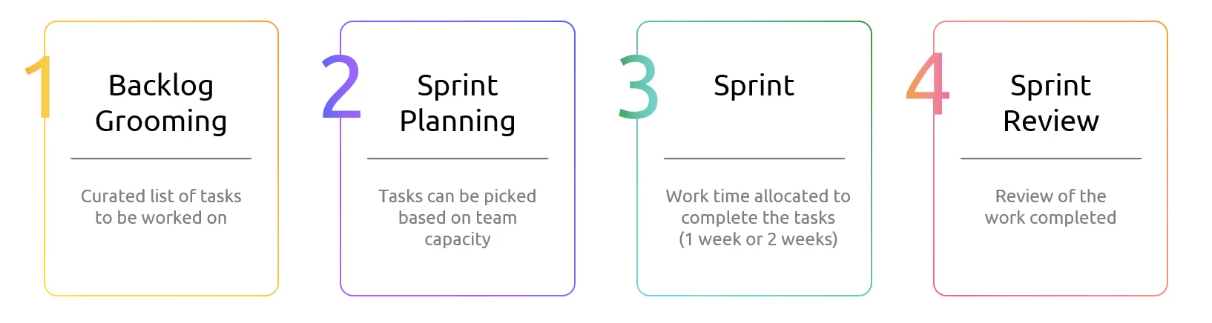
Initiating the Sprint
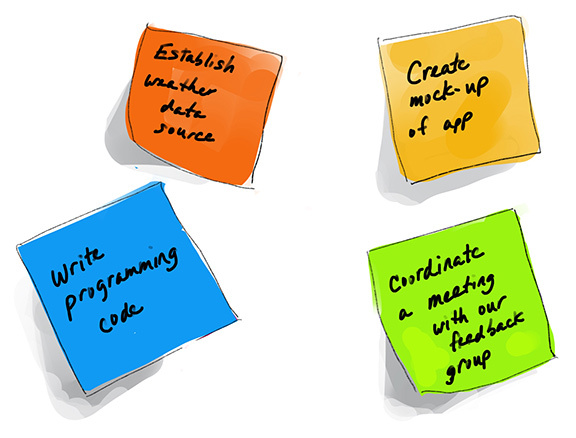
In sprint planning, user stories are decomposed into tasks, each written on a sticky note. The team assigns story points to tasks using the Fibonacci sequence to estimate effort.
Example User Story:
“As a gardener, I want a device that measures and corrects sun levels, so that I don’t have to worry about my plants getting fried by the sun.”
Tasks Derived from User Story:
- Coordinate a meeting with our feedback group.
- Create mock-up of app interface.
- Write programming code to trigger the sun shade when necessary.
- Establish weather data source.
These tasks are visualized on your Scrum board.
Using the Fibonacci Sequence for Task Points
Tasks are assigned points (1, 3, 5, 8, 13) based on their complexity, not time. This sequence helps prioritize tasks relative to one another across the project.
Example 1:
- Task: Coordinate a meeting with our feedback group.
- Acceptance criteria: A meeting is scheduled with 95% attendee confirmation.
- Story point: 1 (indicating minimal effort required)
Example 2:
- Task: Create a mock-up of a user interface.
- Acceptance criteria: Mock-up is high-fidelity and functional on mobile.
- Story point: 5 (indicating moderate effort required)
Example 3:
- Task: Write programming code to trigger the sun shade.
- Acceptance criteria: Shade activates based on sunlight intensity.
- Story point: 13 (indicating substantial effort required)
Each task must have defined acceptance criteria before being added to the sprint backlog, ensuring clarity and alignment with project goals.