SSH-Based Logins
SSH key-based login is a method to securely connect to remote systems without using a password. Instead, it uses a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key, kept on your local machine, and a public key, placed on the remote server. This enhances security by eliminating the need for password-based authentication.
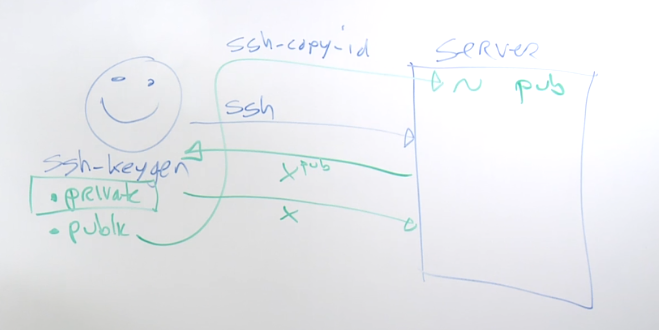
Setting up SSH Key-Based Login
To set up SSH key-based login, follow these steps:
-
Generate SSH Key Pair:
ssh-keygen -t rsa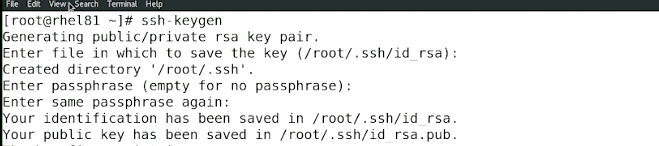
-
Copy Public Key to Remote Server:
ssh-copy-id user@remote_server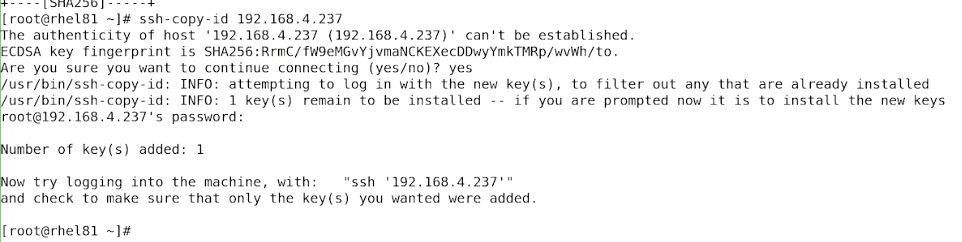
If the
ssh-copy-idcommand doesn't work, manually copy the public key to the remote server. -
Test SSH Key-Based Login:
ssh user@remote_server
-
Cache the SSH Key:
ssh-add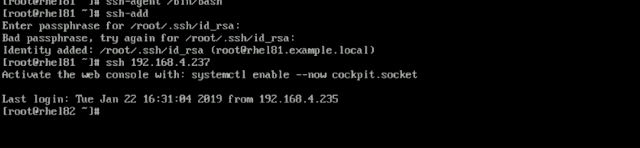
Example Scenario
In this example, I'll connect my local VM from VirtualBox to my EC2 instance.
-
EC2 instance - tst-rhel-a1
-
Local VM - tst-rhel-local
On my local VM, I generated the key and tried to copy it to my remote EC2 instance.
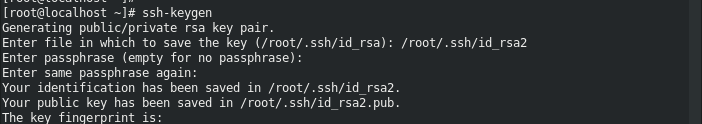
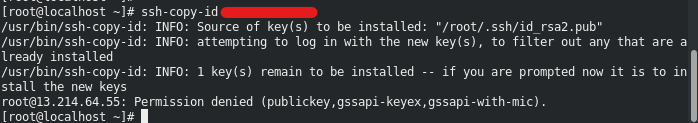
If automatic copying fails, manually copy the contents of the RSA public key of the local VM:
-
Locate and Display Public Key:
[root@localhost ~]# ll .ssh/
total 12
-rw-------. 1 root root 2655 Jan 3 22:01 id_rsa
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 580 Jan 3 22:01 id_rsa.pub
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 174 Jan 3 22:03 known_hosts
[root@localhost ~]# cat .ssh/id_rsa.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3Nza... root@tst-rhel-local -
Paste Public Key into
authorized_keyson Remote Server:$ vim .ssh/authorized_keys
ssh-rsa AAAAB3Nza... root@tst-rhel-local -
Connect to Remote Server:
ssh user@remote_server
Changing Common SSH Server Options
To enhance security and configure SSH server settings, edit the sshd_config file:
-
View SSH Configuration Files:
$ ll /etc/ssh/ssh*
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1770 Jul 12 08:41 /etc/ssh/ssh_config
-rw-------. 1 root root 4268 Jan 2 13:58 /etc/ssh/sshd_configNote:
- Server options are set in
/etc/ssh/sshd_config. - Client options are set in
/etc/ssh/ssh_config.
- Server options are set in
-
Edit
sshd_configFile:$ sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config -
Important Parameters:
# If server is internet-facing, good to set this to NO
PermitRootLogin yes
# You can also specify the users that are allowed to login
AllowUsers johnsmith janedoe
# If you want to disable passwords and allow only keypair you can set this to NO. Note that this is convenient.
PasswordAuthentication no -
Apply Changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
Changing the SSH Port
Enhance security by changing the default SSH port from 22 to another port:
-
Edit
sshd_configFile:$ sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell
# SELinux about this change.
# semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER
#
#Port 22
Port 2222 -
Allow New Port in Firewall and SELinux:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=2222/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=2222/tcp --permanent
$ sudo semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 2222 -
Restart SSH Service:
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd