Retraining the Model
Updated May 12, 2023 ·
Overview
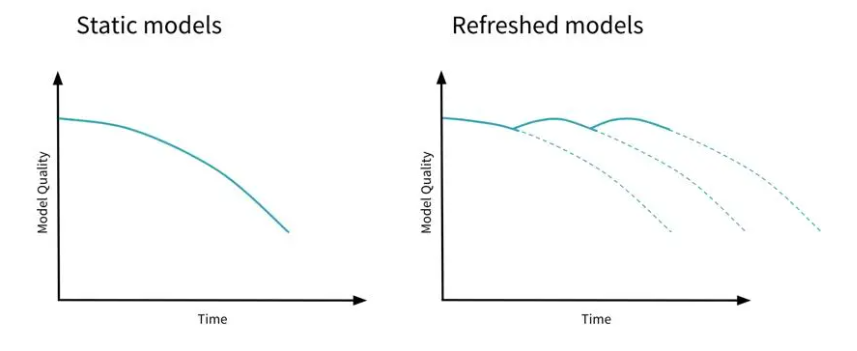
Retraining is essential to keep the model updated and accurate as data changes over time.
-
Changes in data over time
- Data naturally changes, affecting model accuracy.
- Refreshing data helps adjust the model to new patterns.
-
Drift in data
- Changes in data or relationships can affect model predictions.
Types of Drift
There are two main types of drifts:
-
Data drift
- Change in the input data (e.g., new customer demographics).
- May affect performance, but not always.
-
Concept drift
- Change in how input data relates to the target variable.
- Can reduce model accuracy if patterns change.
How Often to Retrain?
Retraining frequency depends on multiple factors.
-
Business environment
- Fast-changing industries need more frequent retraining.
- Market condition changess may need quicker adjustments.
-
Cost of retraining
- Requires resources and money, especially for complex models.
- High costs need to be weighed against model performance gains.
-
Business requirements
- High accuracy standards may necessitate more frequent updates.
- If performance drops below thresholds, retraining is needed.
Retraining Methods
When retraining, you can choose how to update the model.
-
Separate model for new data
- Train a new model only on the latest data.
- Good for handling shifting data but may miss older trends.
-
Combine new and old data
- Merge both data sets to create a new model.
- Maintain context with past data while adapting to changes.
Automatic Retraining
Retraining can be automated based on drift detection.
- Set thresholds for data or concept drift to trigger retraining.
- Reduces manual intervention by adjusting the model when needed.
- Useful in systems with frequent updates and fast-changing environments.