Starter Notes
Overview
Ruby on Rails (or Rails) is a framework to build web applications. You can use it to create simple sites or large enterprise applications.
Popular platforms that have used/still uses Rails:
- Airbnb
- GitHub
- Basecamp
- Shopify
Gems and Packages
Gems are reusable code packages that add functionality to Rails apps. They can be found at Rubygems.org or GitHub.
MVC Structure in Rails
Rails follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern to organize web applications. MVC separates what users see from how the application works behind the scenes.
The principle divides the work of an application into 3 separate but closely cooperative subsystems.
-
Model
- Manages the data in the application.
- Typically, your database tables.
-
View
- Makes up the frontend of the application.
- Handles rendering responses in different formats.
- Comprise of HTML, JSON, XML, etc.
-
Controller
- User interactions and the logic for each request.
- Interacts with the model
Diagram:
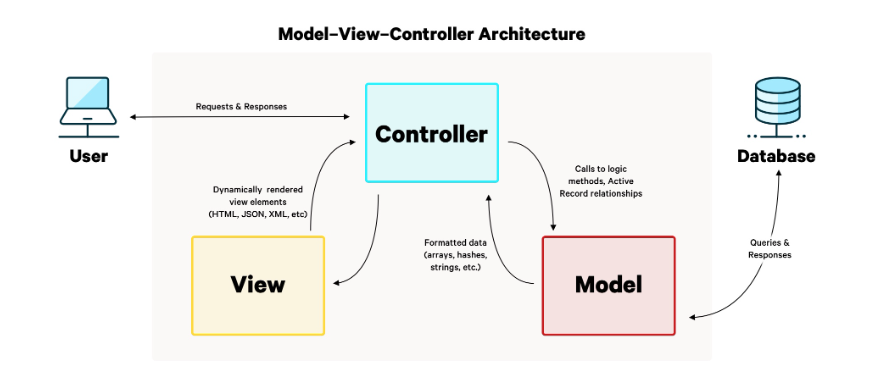
General flow of Rails application:
- A user makes a request (like visiting a URL)
- The router sends the request to the right controller action
- The controller talks to models to get or change data
- The controller picks a view to show the user
- The view renders HTML (or JSON/XML) and sends it back to the user
Models
Models represent the data and core resources of your application. They usually connect to a database.
- Models represent resources like users posts or products
- Each model usually maps to a database table
- Models handle data rules and database communication
For example, a user model works with a users table. This keeps data logic in one place and supports the MVC idea of separation.
Views
Views are the part of the application that users see and interact with.
- Views make up the front end
- They use HTML CSS and JavaScript
- Rails views use ERB templates
In Rails view, files usually end with .html.erb. This lets you mix HTML with Ruby code so pages can display dynamic data while still staying focused on presentation.
home.html.erbnew.html.erbfriends.html.erbportfolio.html.erb
Controllers
Controllers handle requests and connect models with views. They decide what happens when a user interacts with the app.
- Controllers process user requests
- They fetch or update data using models
- They choose which view to render
For example, a users controller manages actions related to users. Controllers act as the middle layer which keeps the MVC flow clear and predictable.
users_controllerposts_controllerarticles_controllerstocks_controller
MVC Folders in a Rails App
A standard Rails app shows MVC clearly through its folder structure.
- Controllers are in
app/controllers - Models are in
app/models - Views are in
app/views
Example structure:
app/
├── controllers/
├── models/
└── views/
We will also see files like application.html.erb which look like normal HTML but include embedded Ruby code. This layout ties views into the MVC structure.