User Management and Security
Build Accounts
The default user that Jenkins uses is a non-interactive user. This can be seen when you grep for Jenkins in the /etc/passwd file.
cat /etc/passwd | grep jenkins
Output:
jenkins:x:994:990:Jenkins Automation Server:/var/lib/jenkins:/bin/false
We can modify this so that we can login using Jenkins username on the terminal when we need to do some troubleshooting.
sudo sed -i "s/jenkins:\/bin\/false/jenkins:\/bin\/bash/" /etc/passwd
cat /etc/passwd | grep jenkins
Output:
jenkins:x:994:990:Jenkins Automation Server:/var/lib/jenkins:/bin/bash
Next, setup the password for the jenkins user.
sudo passwd jenkins
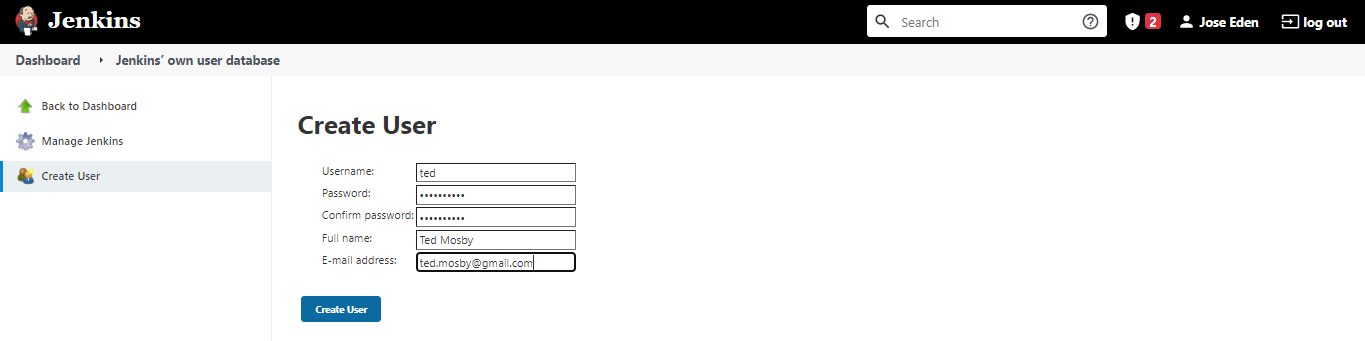
To create users, see Managing Users.
Security Configuration
To see the security configuration, follow the steps below:
Manage Jenkins --> Configure Global Security
Under the Authorization section, the default option is Logged-in users can do anything.

Matrix Security
We can limit the scope of what a user can do by selecting the Matrix-based security. Here we can the actions that can be done by an anonymous user versus an authenticated user.
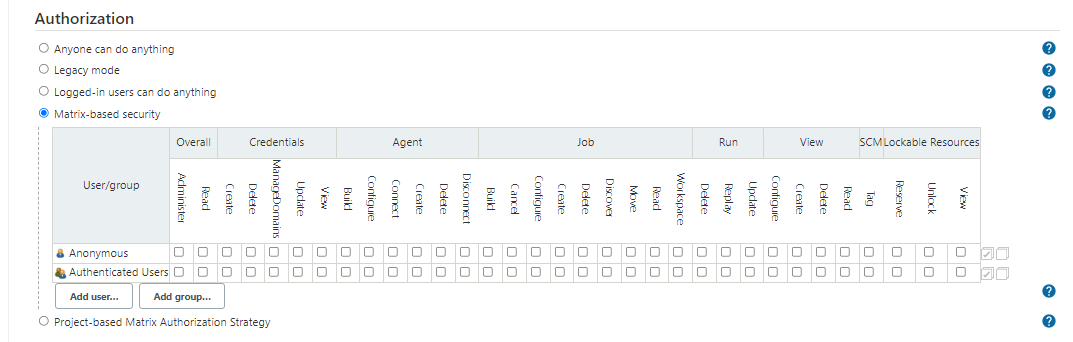
This can be Global or Project based:
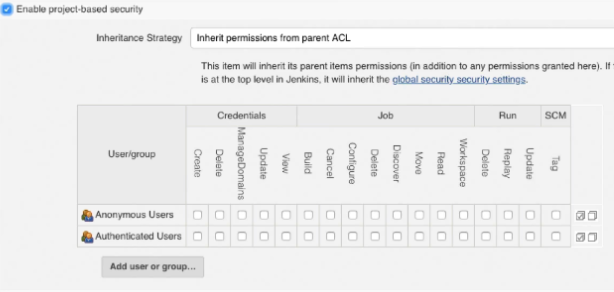
Inheritance is selectable from the dropdown bar in the Project:
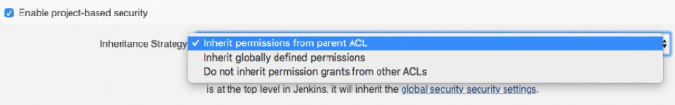
Inherit permissions from Parent ACL - This is for projects that are in a folder, or are the child of another object. Note that the description of this type is important, as this indicates where permissions can be added in the chain.
Inherit globally defined permissions - This is for projects that are in a folder, or are the child of another project, but do not want the permissions from the folder or parent, only global permissions.
Do not inherit permission grants from other ACLs - This options prevents the job inheriting any permissions from either the global settings or parent items.
Auditing
Auditing is the process of verifying that the access permissions are working as intended.
- Ensures that least privilege is maintained
- Jenkins is an explicit allow-model, which means ther is no deny
- If something is not explicitly allowed, then it is denied
Also, Jenkins permission are additive and it follows the order described below. If something is allowed at the above level and inheritance is enabled, then it is allowed in the levels below.
global --> parent --> job
Credentials
A credential is any value that provides access to a restricted resource. Also known as a secret, credentials are used by Jenkins to access restricted resources.
- Exampels are username and password
- SSH username and private key
- Secret files, secret tokens, and certificates
A credential provider is a location that has been configured for Jenkins to retrieve credentials
Managing Users
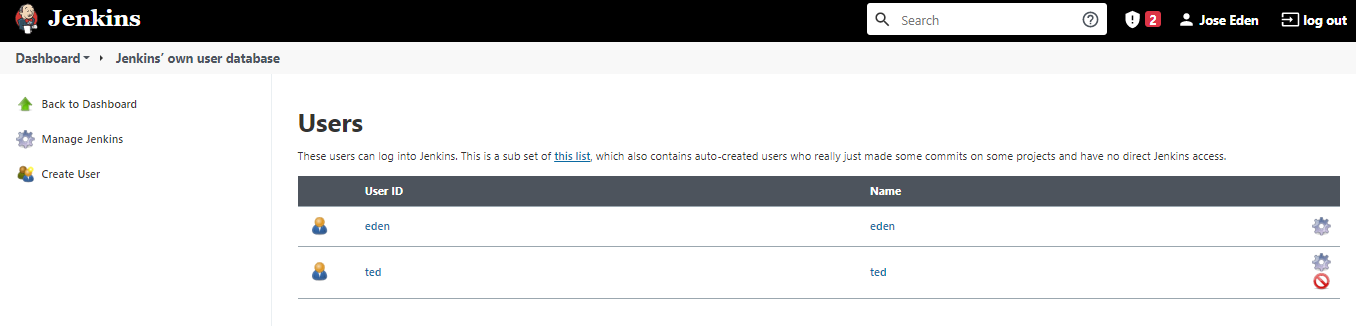
To manage users:
Manage Jenkins --> Manage Users
To create a user:
Manage Jenkins --> Manage Users --> Create User