Docker Cheatsheet
Docker commands
This section provides commands to create, manage, and interact with Docker containers.

Creating and Starting Containers
-
Create a container (but don't start it yet):
docker create <image-id> -
Start a container:
docker start <container-id> -
Run a container from an image:
docker run <image-id>
For example, to run an NGINX container, Docker checks the host for the image. If not found, it pulls the image from DockerHub:
sudo docker run nginx
Subsequent executions will reuse the same image. To see valid options for the run command:
docker run --help
Listing Containers
-
List running containers:
docker ps -
List all containers (running and stopped):
docker ps -a
Setting Container Names and Tags
-
Set a custom container name:
sudo docker run --name Thanos_of_2019 docker/whalesay cowsay I'm-Inevitable! -
Specify an image version (tag):
sudo docker run nginx:1.14-alpine -
Run multiple instances from the same image:
sudo docker run docker/whalesay cowsay Infinity-and-beyond!
sudo docker run docker/whalesay cowsay Hello-there!
sudo docker run docker/whalesay cowsay Cowabunga!
Pulling Images
To pull an image to your host (without running a container):
sudo docker pull <image-name>
sudo docker pull nginx
Managing Containers
-
Stop a running container:
docker stop <container-name>
docker stop <container-id> -
Remove a container:
docker rm <container-name> -
Forcefully remove a running container:
docker rm -f <container-name> -
Remove all containers:
docker rm -f $(docker container ls -aq) -
Remove all stopped containers without confirmation:
docker container prune -f -
Delete stopped containers, unused images, and build cache:
docker system prune
Removing Images
-
Remove an image (ensure no containers are using it):
docker rmi <image-name> -
Remove all images without associated containers:
docker image prune -a -f
Container Lifecycle
Containers are designed to run specific tasks or processes. When the task completes, the container exits. For example, running Ubuntu:
sudo docker run ubuntu
To run a process (like sleeping for 60 seconds):
sudo docker run ubuntu sleep 60
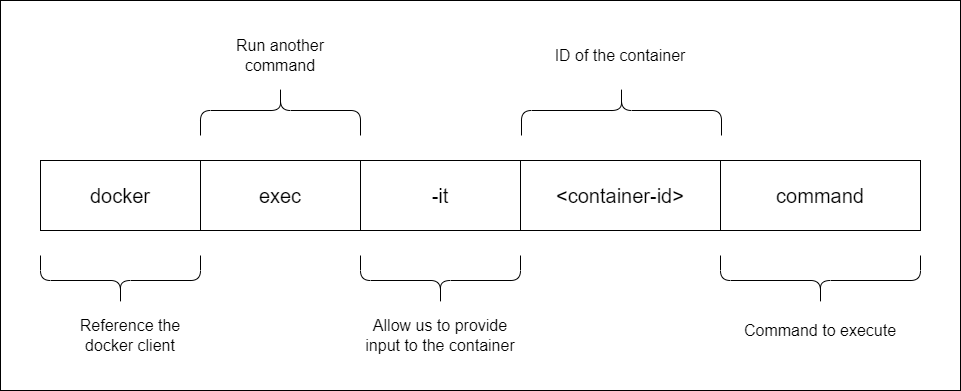
Executing Commands in Running Containers
To execute a command in a running container:
sudo docker exec <container-id> <command>
sudo docker exec <container-name> <command>
For example, to view the hosts file of a running container:
sudo docker exec <container-id> cat /etc/hosts
sudo docker exec <container-name> cat /etc/hosts