What is Docker
From VMs to Containers
Traditionally, applications were deployed using virtual machines (VMs). Each VM runs its own operating system, utilizing the OS file system and resources. VMs efficiently maximize infrastructure by allowing multiple applications to run on a single physical machine via a hypervisor.
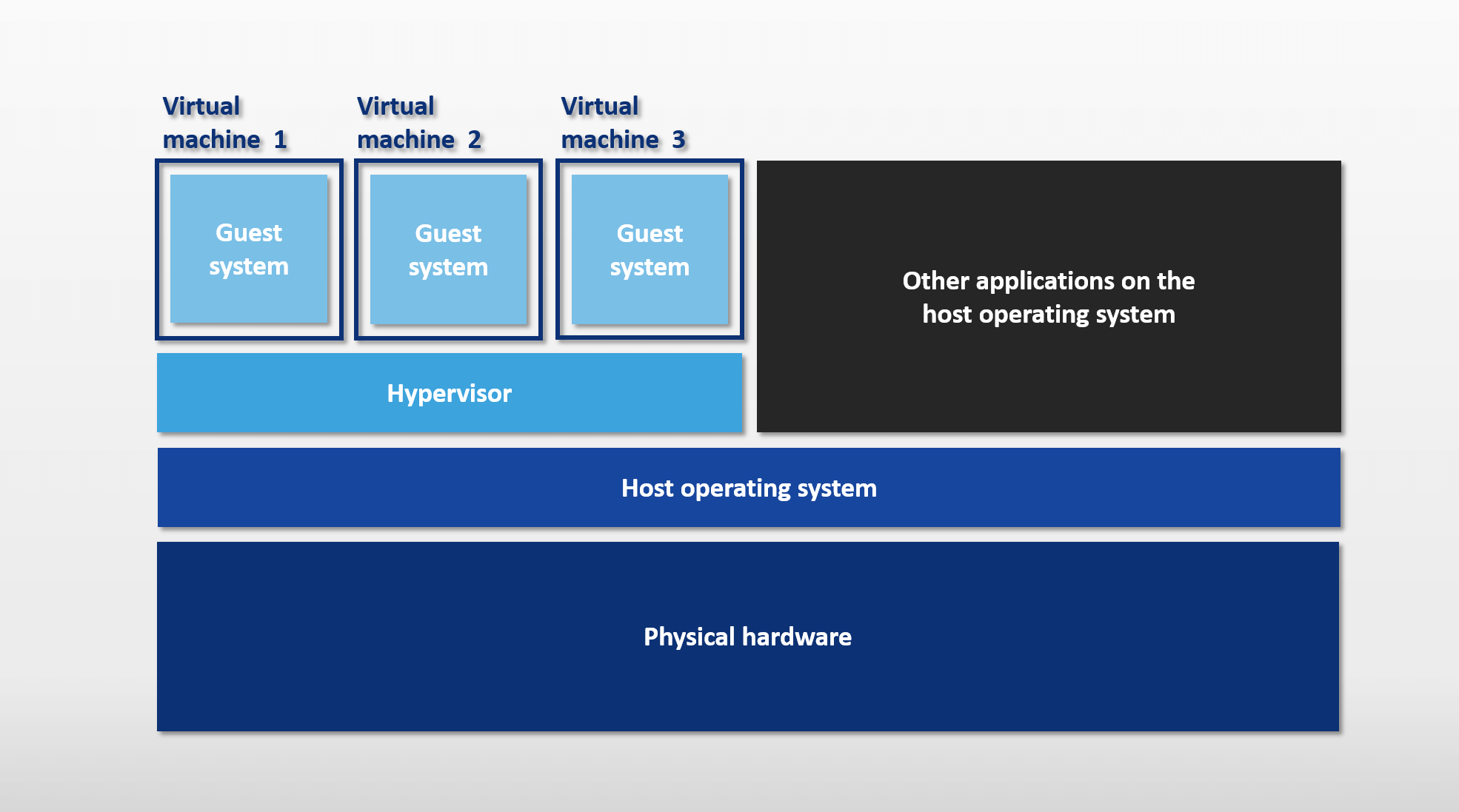
However, VMs come with drawbacks:
- Each VM requires its own operating system.
- Multiple VMs mean multiple OS installations, consuming more resources.
- Each VM's OS and libraries take up significant space on the host machine.
Enter containers. Containers allow for operating system virtualization, meaning we can run multiple containers without replicating the OS. All containers share the same underlying operating system of the physical machine.
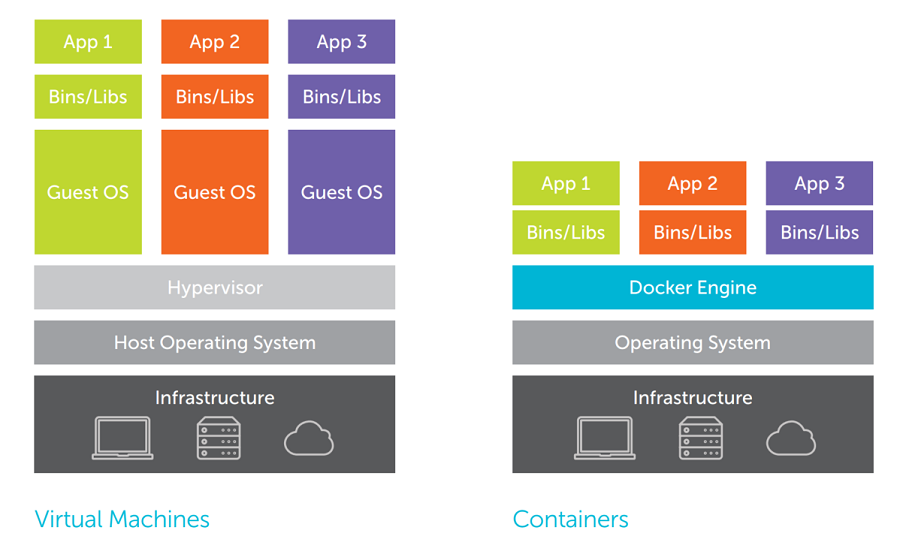
To create and manage containers, we can use a container engine tool like Docker.
The benefits of containers include:
- Lightweight and efficient
- Better resource utilization
- Consistent application performance across platforms
- Easy management and scalability
Understanding Docker
Docker is a container platform that enables you to:
- Isolate applications from the infrastructure
- Package code and dependencies into a single unit
- Run this unit on any supported system

Benefits for Developers
Docker offers several advantages for developers:
- Speeds up onboarding
- Prevents application conflicts
- Ensures consistent environments
- Accelerates software delivery
This consistency and efficiency allow developers to focus on coding, leading to faster, more reliable releases.
Next Steps
After implementing the software, the next step is to release it. Key actions include:
- Packaging source code, config files, and dependencies into a container
- Deploying it using a container management tool