Docker Objects
Overview
Docker objects are the essential components that make up a Docker environment, facilitating application deployment and management.
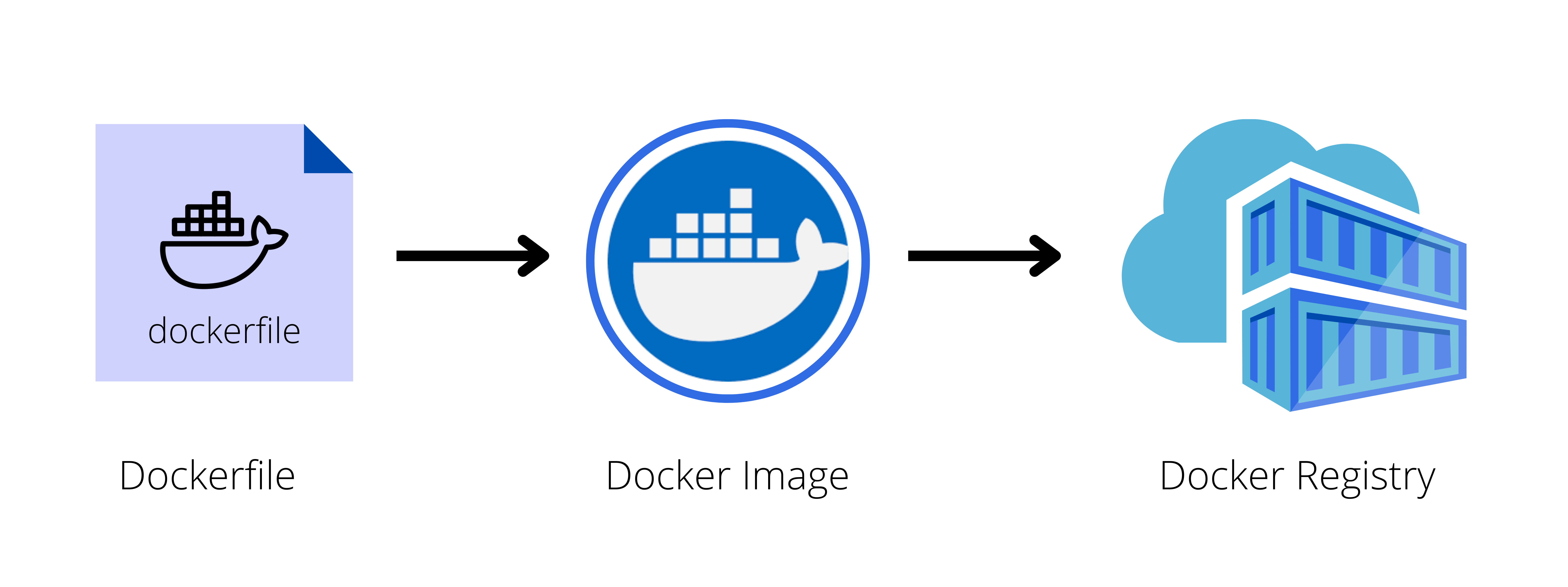
Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a series of instructions for creating a Docker image:
- Packages code and dependencies.
- Each command creates a layer that is cached.
- Only modified layers are rebuilt when changes occur.
For a complete list of instructions, refer to the official Docker documentation. Common instructions include:
FROM- Specifies the base image.RUN- Executes a command during image build.COPYand ADD - Transfer files from the host to the container.CMD- Default command to run when the container starts.EXPOSE- Opens a port for communication.
Here’s an example Dockerfile for a Python hello-world application:
# Set the base image
FROM python:3.8
# Set the maintainer label
LABEL maintainer="Eden Jose"
# Copy files to the container
COPY . /app
# Set the working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Install dependencies
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
# Command to run on container start
CMD [ "python", "app.py" ]
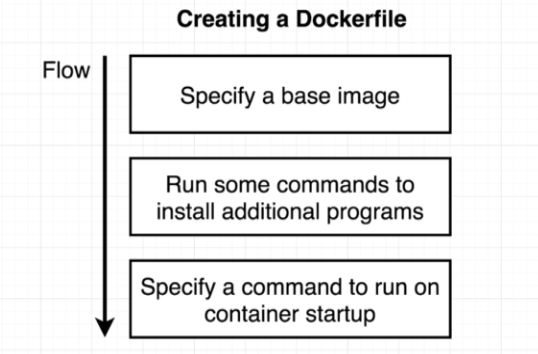
Creating the Dockerfile
Before creating the image, outline the steps to deploy the application. For example, deploying a web application might involve:
- Start with OS - CentOS
- Update repo
- Install dependencies
- Install Python packages
- Copy source code to /opt
- Run the web server
With these steps, you can begin containerizing your application:
- Create a Dockerfile.
- Build your image using the Dockerfile.
- Push it to a Docker registry.
Here's a basic flow for creating a Dockerfile:
Docker Image
After creating the Dockerfile, you can build a Docker image, which is:
- A read-only template.
- Composed of an overlay filesystem.
- Used to run container instances.
Overlay Filesystem
A Docker image consists of multiple layers, starting with a base image and adding installed packages on top. The last layer is writable; data written here will be lost once the container stops unless specific storage options are set.
Building the Docker Image
To build a Docker image from a Dockerfile, use the docker build command:
docker build [OPTIONS] PATH
To see all valid options for the build command, use:
docker build --help
For example, to build a Python "Hello-world" application from the current directory:
docker build -t python-helloworld .
To build from a different directory, use:
docker build -t python-helloworld /another/directory/python-app
To list all available images:
docker images