Docker Architecture
Client and Server Architecture
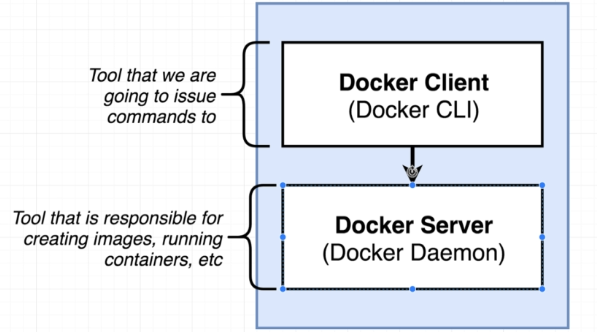
Docker operates on a client-server architecture:
- Docker Daemon: Acts as the server, managing container operations.
- Docker Client: The command-line interface (CLI) that users interact with to issue commands.
This architecture allows for a clear separation between the user interface and the backend processes.
Docker also utilizes a container runtime, which serves as the engine for container solutions. This runtime acts as an intermediary layer between the host system and the containers.
Docker Daemon
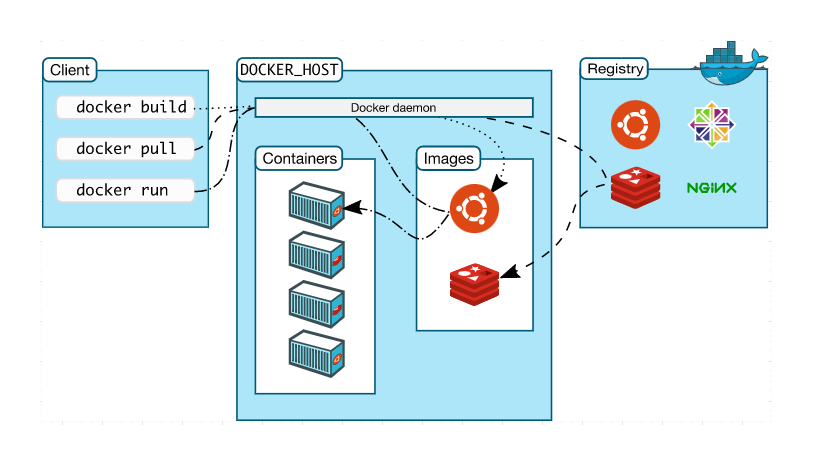
The Docker daemon manages Docker objects, including images, containers, and networking components. It exposes a REST API that the client interacts with via a Unix socket or network interface. Key functions include:
- Managing images
- Running APIs
- Handling networking
- Ensuring authentication and security
- Orchestrating containers
Docker Client
The Docker client consists of commands that allow users to interact with the Docker daemon. When you enter Docker commands, you are using this client, which is the primary interface for controlling Docker.
- Executes commands to manage containers
- Sends requests to the Docker daemon
- Provides feedback and status updates to users
Container Engine
The container engine is responsible for transforming a container image into a running container. It typically includes a runtime, a command-line interface, and occasionally a daemon.
The process flow is as follows:
- User types commands into the client.
- Commands are converted into REST API calls.
- The daemon receives the API calls.
- The daemon invokes
containerdwith the API parameters. containerdforwards the image to an instance ofrunc, which starts the containers.
Container Runtime
The container runtime is a specific component within the container engine that directly manages the lifecycle of containers.
- Facilitates the creation and management of container instances
- Interfaces with the Docker daemon and underlying OS resources
runc
runc is the default implementation defined by OCI runtime specifications. It is responsible for:
- Creating and managing container instances
- Providing a wrapper for libcontainer to manage container lifecycle
containerd
containerd originated from the Docker daemon but has been separated as a standalone component. Its responsibilities include:
- Managing container operations such as start, stop, pause, and remove
- Work with
runcand the Docker daemon to execute container management tasks