Metadata Store
Updated May 15, 2023 ·
Metadata
Metadata stores information about machine learning (ML) experiments, models, and pipelines. It helps manage and monitor ML workflows efficiently.
- Tracks data from creation to consumption
- Shows transformations and usage.
- Logs experiment settings to ensure consistent results.
- Keeps records of pipeline execution, helps detect issues early.
Aspects of Metadata
Metadata helps track and manage ML experiments. Key aspects include:
-
Data lineage
- Tracks data from creation to consumption
- Shows transformations and usage
-
Reproducibility
- Logs experiment settings for consistent results
- Allows others to reproduce outcomes
- Increases trust in ML systems
- Includes hyperparameter settings
-
Monitoring
- Keeps records of pipeline execution
- Checks ML system status anytime
- Helps detect issues early
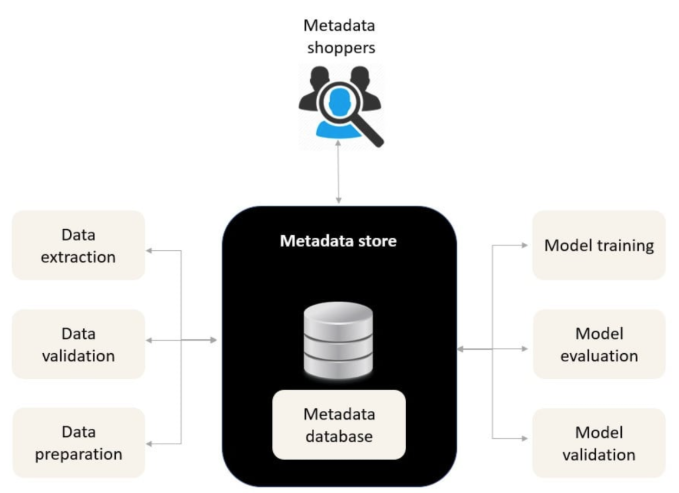
Metadata Store
A metadata store keeps track of ML experiments but does not store models or data. It logs artifacts, execution details, and system events.
- Works with all ML pipeline steps
- Reads and writes logs automatically
- Supports auto incident response
- Detects model drift
- Retrains models when performance drops
- Triggers automatic rollbacks if needed
With a metadata store, ML pipelines can track changes, automate monitoring, and maintain reliability in production.
Automated Model Retraining
A metadata store helps monitor models and trigger automatic updates to maintain performance. Here’s how it works:
- A fully automated MLOps system delivers predictions and is constantly monitored.
- Evaluation metrics are logged in the metadata store.
- If performance declines, the system detects model decay.
- The system triggers retraining and updates the model in the registry.
- The new model is deployed, updating the prediction service to handle drift.