Network Appliances
Network Appliance
A network appliance is a dedicated hardware device with pre-installed software that is designed to provide specific networking services.
SD-WAN
Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) is a virtualized network architecture that allows enterprises to leverage any combination of transport services, including MPLS, LTE, and broadband internet services, to securely connect users to applications.
- Cuts reliance on expensive MPLS circuits.
- Optimizes traffic for better user experience.
- Simplifies WAN management with a single interface.
- Includes encryption, firewalls, and secure tunneling.
SASE
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is a network architecture that combines WAN capabilities with comprehensive security functions, such as SWG, CASB, FWaaS, and ZTNA, into a single, cloud-delivered service model.
- Uses the cloud for scalability and performance.
- Provides consistent security policies everywhere.
- Eliminates the need for multiple security solutions.
Network Tools
Network Protocol Analyzers
Network Protocol Analyzers capture data packets transmitted over the network, decode them, and present the information in a human-readable format. These tools to diagnose issues, ensure optimal network performance, and detect malicious activities by providing detailed insights into network traffic.
- Physical, wireless, or software installed on desktop or obile phones.
- Network placement is crucial, recommended to put them your internal network and router.
- Packet captures can be saved for a later analysis.
- View packet headers (addressing) and packet payload (data).
- Features like TCP stream and filter to view and display the entire packet.
Below are some available network analyzers:
- tcpdump
- NetFlow
- SFlow
- IPFIX
Note that the packet captures can be forged, with tools like hping3. This tools can spoof headers and payload just like in a legitimate traffic.
SPAN Mode
Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN) mode is a feature on network switches that allows the monitoring of network traffic by mirroring the traffic from one or more source ports or VLANs to a designated destination port.
- Laptop can be plugged into a switch configured in SPAN Mode.
- All traffic going through the switch can be copied over to the device running the analyzer.
- Useful for analyzing the mirrored traffic without disrupting the network’s normal operation. - Particularly useful for troubleshooting network issues and monitoring network performance.
tcpdump
tcpdump is a powerful command-line packet analyzer tool used for capturing and analyzing network traffic on Unix-like operating systems.
Sample Commands:
-
Capture packets on a specific interface:
tcpdump -i eth0 -
Capture only TCP traffic:
tcpdump tcp -
Save captured packets to a file:
tcpdump -w capture.pcap -
Read packets from a file:
tcpdump -r capture.pcap -
Capture packets from a specific host:
tcpdump host 192.168.1.1 -
Capture packets on a specific port:
tcpdump port 80 -
Capture packets on a specific port, from a specific source:
tcpdump src 10.10.10.10 and port 514 and udp -
Capture packets going to a specific destination, and save to a file:
tcpdump -X dst www.cnn.com -w cnn-traffic -
Run packet capture in the background:
tcpdump -X dst www.cnn.com -w cnn-traffic & -
See packet captures running in the background:
jobs -
To bring the background job to foreground, use 'fg' then specify the number.
fg 1 -
Read a packet capture file:
tcpdump -r cnn-traffic.log
nmap
nmap (Network Mapper) is a widely-used open-source tool for network discovery and security auditing. It can quickly scan large networks to determine which hosts are up, what services they are offering, and what operating systems and versions they are running.
Sample Commands:
-
Scan a single IP address:
nmap 192.168.1.1 -
Scan a single IP address in verbose mode:
nmap -v 192.168.1.1 -
Scan a range of IP addresses:
nmap 192.168.1.1-254 -
Perform a ping scan to check which hosts are up:
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24 -
Detect service versions on open ports:
nmap -sV 192.168.1.1 -
Perform a stealth scan:
nmap -sS 192.168.1.1 -
Scan for open ports and OS detection:
nmap -A 192.168.1.1 -
Save scan results to a file:
nmap -oN output.txt 192.168.1.1 -
OS fingerprinting, getting details about the OS.
nmap -O 192.168.1.1
Wireshark
Wireshark provides a comprehensive suite of tools for capturing and interactively analyzing network traffic.
Capture traffic on a specific interface (using the GUI):
- Open Wireshark.
- Select the network interface you want to capture from.
- Click the "Start" button to begin capturing packets.
Common filters:
-
Apply a display filter to show only HTTP traffic:
http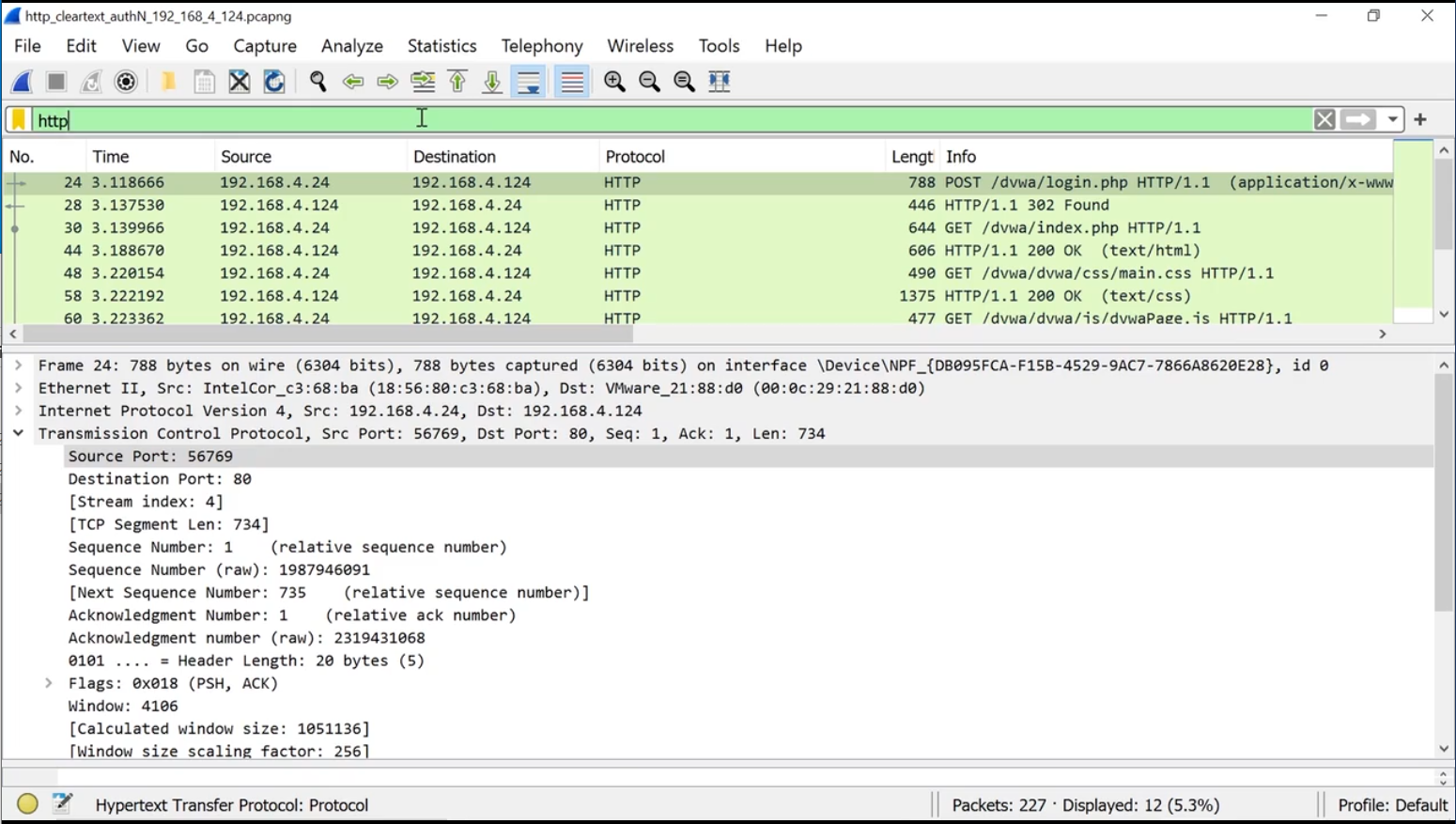
-
Capture traffic from a specific IP address:
ip.addr == 192.168.1.1 -
Filter traffic to a specific port, such as port 80 (HTTP):
tcp.port == 80
To find packets containing specific keywords:
-
Edit > Find Packet
-
Enter the keyword that you want to search > Find
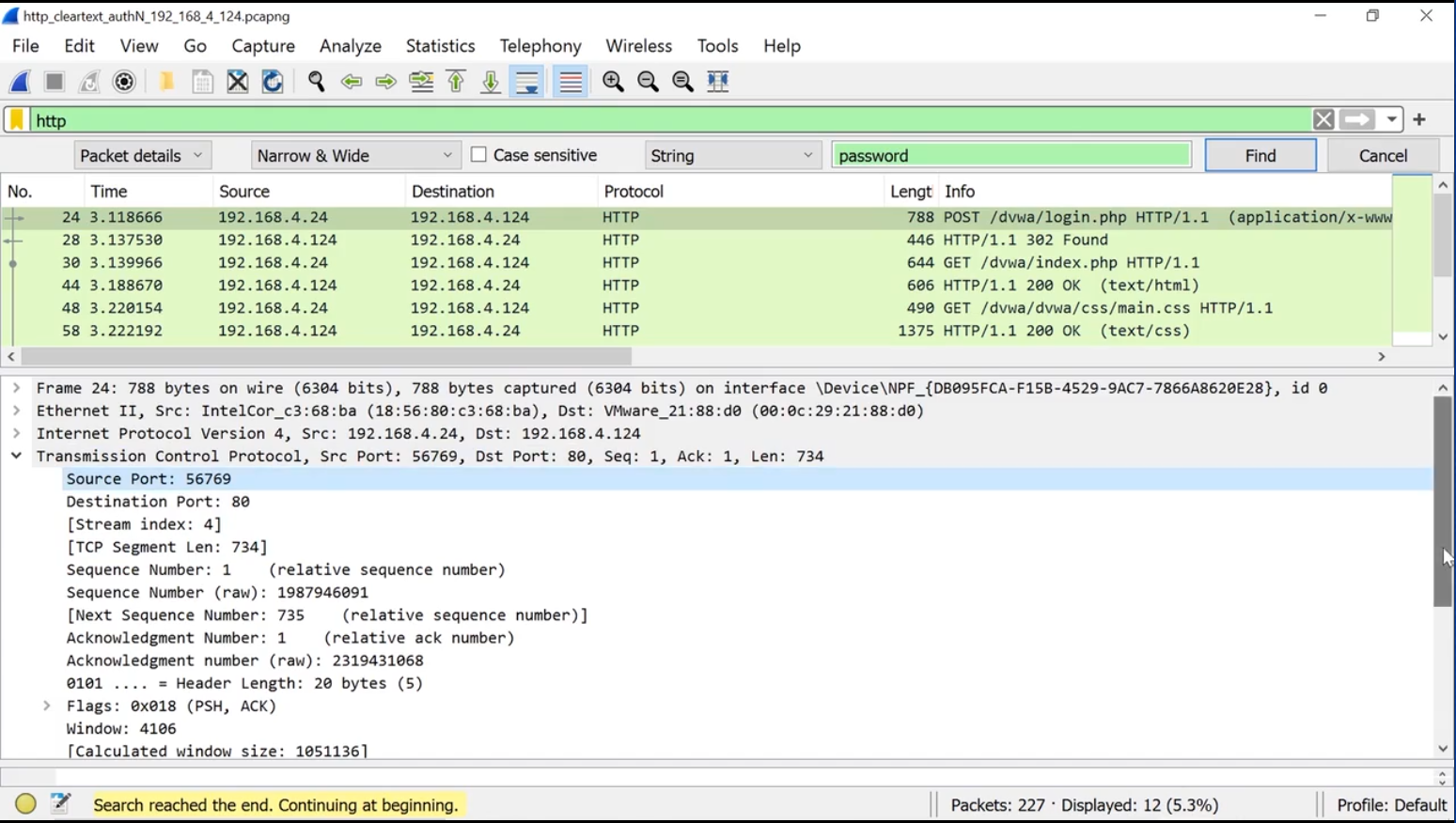
-
To see the entire stream, click Analyze > Follow.
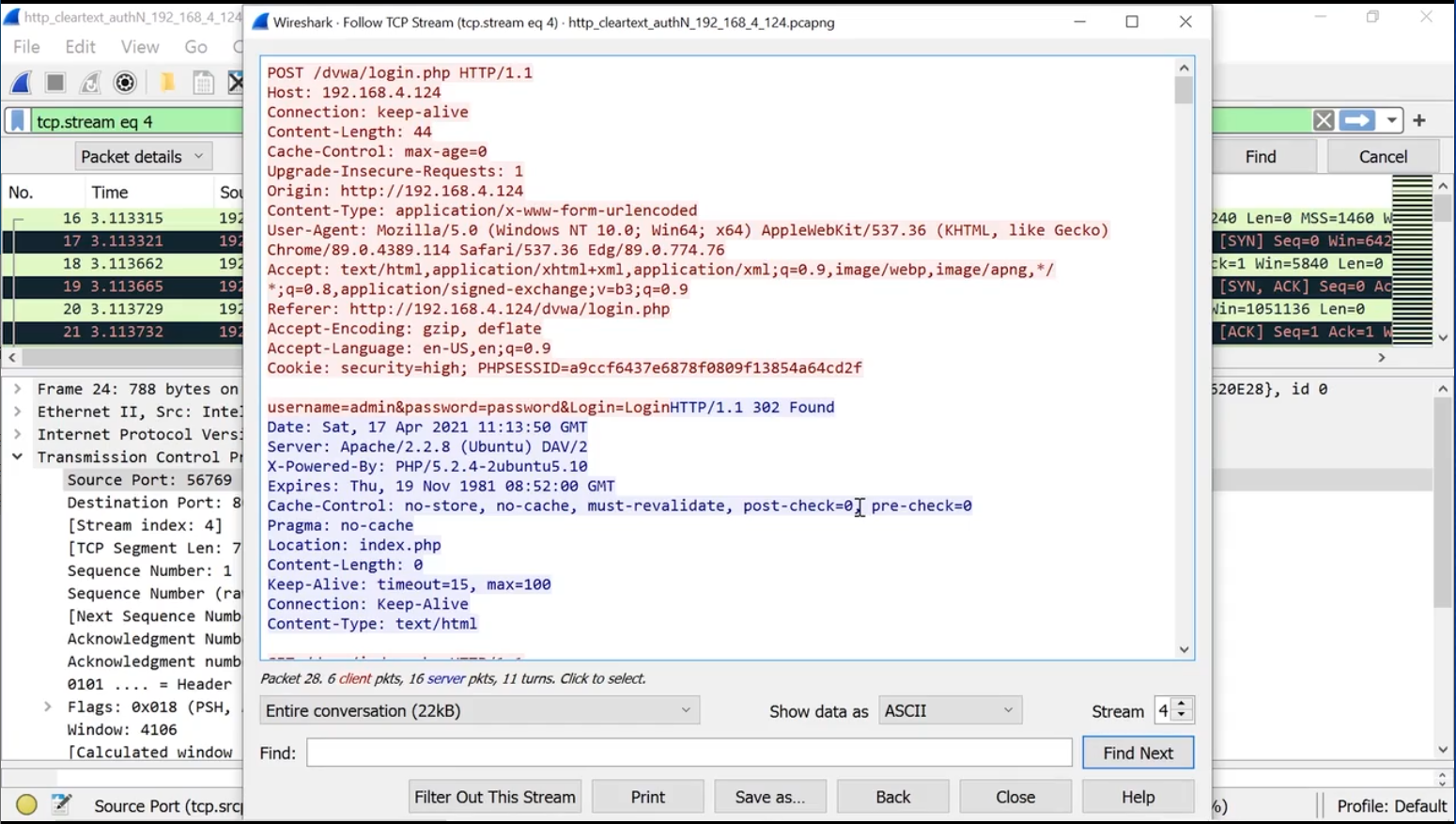
Save captured packets to a file (using the GUI):
- After capturing traffic, go to "File" > "Save As".
- Choose the desired file format and location.
- Click "Save".
Read packets from a file (using the GUI):
- Go to "File" > "Open".
- Select the capture file you want to analyze.
- Click "Open".