VLANs
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)
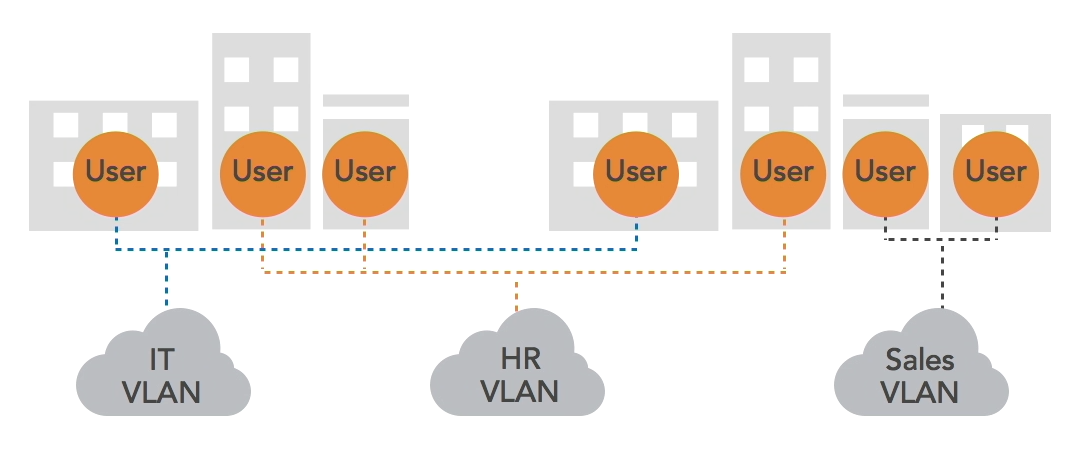
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) allow switches to segment a network logically without changing the physical setup.
- Improve network management and security.
- Enable traffic isolation between different groups.
- Simplify network design and reduce broadcast domains.
For example, VLANs can separate the network of one department from another, enhancing security and minimizing network congestion.
Configuring VLANs
Configuring VLANs involves setting up and managing VLANs on network switches to ensure proper traffic segmentation and network efficiency.
-
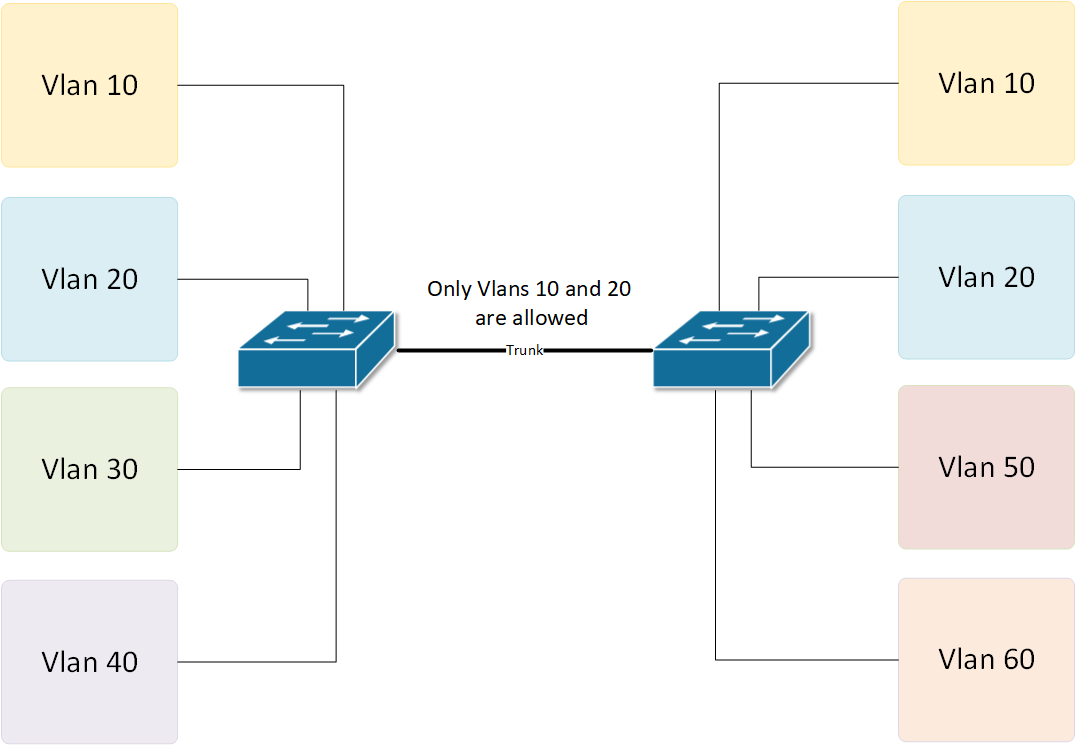
Enable VLAN Trunking
- Extends VLANs across multiple switches.
- This allows VLANs to span different network locations.
- Uses trunk ports to carry traffic for multiple VLANs over a single link.
-
Assign switchport to VLANs
- Configure switchports to belong to specific VLANs.
- This ensures traffic is correctly segmented.
- Ports can be set as:
- an access port for one VLAN, or
- as a trunk port to carry multiple VLANs.
How it looks like:
Private VLANs
Private VLANs (PVLANs), also known as Port Isolation, enhance network security by isolating ports within the same VLAN.
- Isolate devices within the same VLAN
- Prevent direct communication between devices
- Reduce risk of internal attacks
Port isolation restricts traffic from a source port to a single destination port. This means that if a device is plugged into a particular isolated port (source port), it can only connect to the specified destination port and will not be able to connect to other devices.
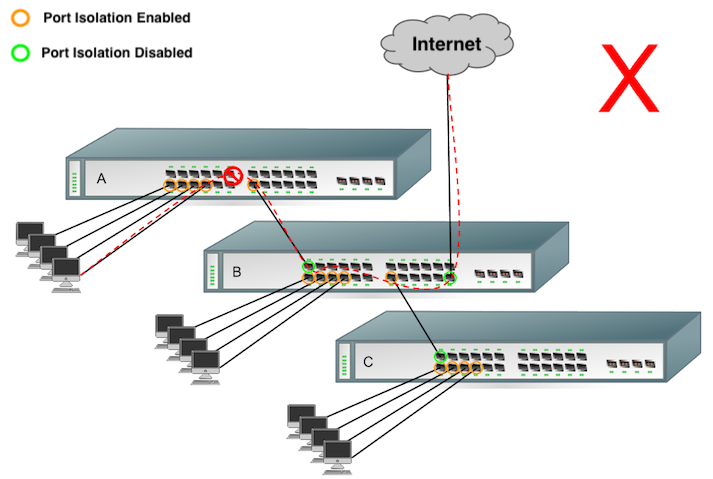
Port isolation is not recommended on a corporate network where devices often need to communicate with each other, share resources, or access multiple services. In contrast, it works very well on hotel guest room networks where guests should be isolated from each other to ensure privacy and prevent unauthorized access to other guests' devices.
VLAN Security
VLAN security protects network segments from unauthorized access and attacks.
-
VLAN Pruning
- Limits VLAN exposure to only necessary switches.
- Helps secure sensitive VLANs by restricting unnecessary trunking.
- Prevents VLAN traffic from spreading across the entire network.
- Reduces the risk of attackers accessing sensitive VLANs.
- Regularly review and update pruning configurations to maintain security.
-
VLAN Trunk Negotiation
- Attackers may use VLAN hopping to switch between VLANs.
- This attack tricks switches into trunking unauthorized VLANs.
- Disable automatic trunk negotiation to block VLAN hopping attempts.
- Manually configure trunks to only authorized VLANs.
- Use static VLAN assignments to further reduce risk.
-
Port Security
- Allows administrators to restrict which devices can connect to which port.
- Connection can be based on the network interface card's MAC address.
- Limits the MAC address that may be used on particular switchport.
- Trigger alerts or disable ports if unauthorized devices attempt to connect.
- For more information, please see Port Security.