Networking Fundamentals
Network
A network refers to the connection of two or more computers for the purpose of sharing data, information, or resources.
-
Local Area Network (LAN)
- Typically spans a single floor or building.
- Limited geographical area.
-
Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Encompasses long-distance connections between geographically remote networks.
Ethernet
Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) is a standard that defines wired connections of networked devices. This standard defines the way data is formatted over the wire to ensure disparate devices can communicate over the same cables.
Device Address
Media Access Control (MAC) Address
- Assigned to every network device.
- Example: 00-13-02-1F-58-F5.
- First 3 bytes (24 bits) denote the vendor or manufacturer of the physical network interface.
- No two devices can have the same MAC address in the same local network.
Internet Protocol (IP) Address
- Logical address associated with a unique network interface.
- MAC addresses are assigned in the firmware, while IP addresses are logical.
- Helps maintain communications when physical devices are swapped.
- Examples: 192.168.1.1 and 2001:db8::ffff:0:1.
Wifi
Widely adopted for its easy deployment and cost-effectiveness, wireless networking provides versatility, enabling devices to roam freely within signal range.
-
Wi-Fi Evolution
- Evolving over time with faster updated versions, Wi-Fi continues to improve its performance.
-
Security Considerations
- Despite its benefits, wireless networks introduce additional vulnerabilities. Unlike wired networks, intrusions can occur remotely, without physical access to the network.
For more information, please see Wireless Networking.
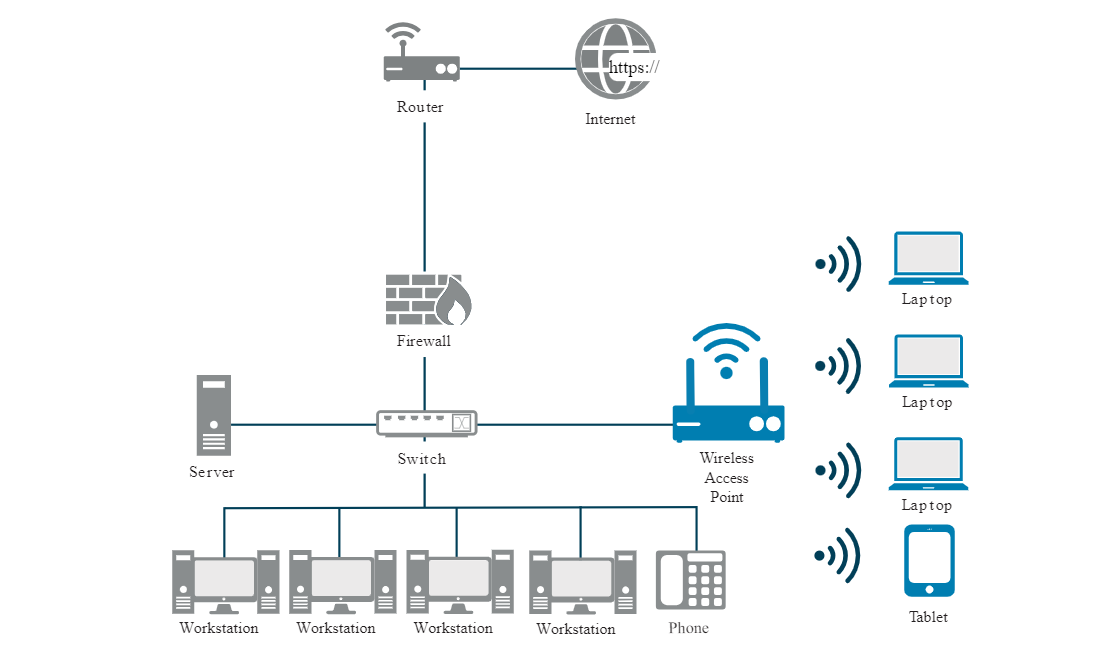
Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to the technology that allows the network to prioritize certain types of traffic over others.
- Prioritizes critical traffic like VoIP or video conferencing.
- Uses classes of service (CoS), packet classification, and traffic shaping.
Traffic shaping refers to controlling network traffic to allow for the optimization or the guarantee of certain performance levels
Networking Tools
-
Ping Sweep
- Common method to map live hosts in a network.
- Involves sending ping messages (ICMP Echo Requests) to a range of IP addresses.
- Online hosts respond, allowing mapping of live hosts on the network.
- Reference: ISC2 Study Guide, Chapter 4, Module 3.
-
Geolocation
- Determines a device or user's physical location based on IP or MAC address.
-
Traceroute
- Maps network topology and diagnoses connectivity/routing issues by tracing packet hops to an IP address.
-
Wireshark
- Network protocol analyzer tool for viewing and analyzing packet contents, including IP addresses and host names.