Installing Logstash
Overview
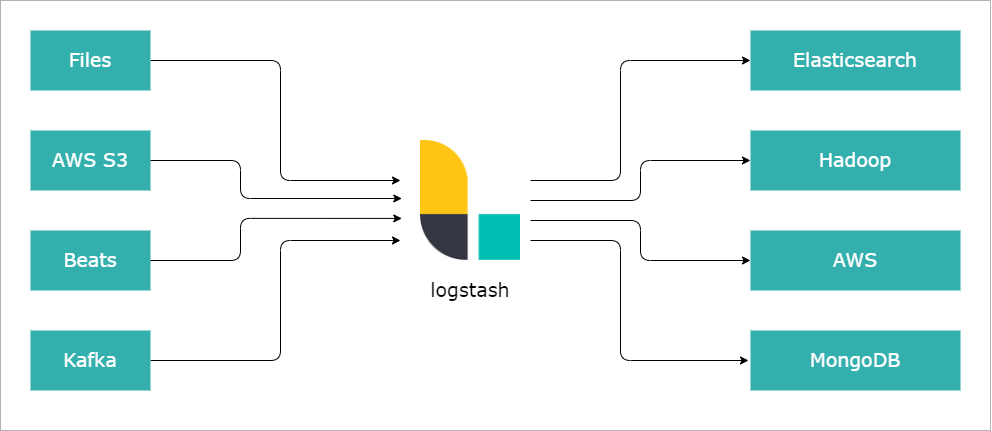
Logstash is an open-source tool for processing logs and events. It can import, transform, and send data to various destinations like Elasticsearch, S3, Beats, or Kafka.
- Logstash handles input from multiple sources, including files and systems.
- It processes and filters data in real time.
It’s more than just plumbing:
- Parses, transforms, and filters data.
- Derives structure from unstructured data.
- Anonymizes or excludes personal data.
- Performs geo-location lookups.
- Scales across multiple nodes.
- Guarantees at-least-once delivery.
- Handles load spikes efficiently.
Sources and Destinations
Sources:
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| elastic | beats | cloudwatch | couchdb | drupal |
| elasticsearch | windows event log | shell output | local files | ganglia |
| gelf | gemfire | random generator | github | google pubsub |
| graphite | heartbeats | heroku | http | imap |
| irc | jdbc | jmx | kafka | lumberjack |
| meetup | command pipes | puppet | rabbitmq | rackspacecloud queue |
| redis | relp | rss | s3 | salesforce |
| snmp | sqlite | sqs | stdin | stomp |
| syslog | tcp | udp | unixsockets | |
| varnish log | websocket | wmi | xmpp | zenoss |
| zeromq |
"Stash" Destinations:
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| boundary | circonus | cloudwatch | csv | datadoghq |
| elasticsearch | exec | local file | ganglia | |
| gelf | bigquery | google cloud storage | graphite | graphtastic |
| hipchat | http | influxdb | irc | jira |
| juggernaut | kafka | librato | loggly | lumberjack |
| metriccatcher | mongodb | nagios | new relic insights | opentsdb |
| pagerduty | pipe to stdin | rabbitmq | rackspacecloud queue | redis |
| redmine | riak | riemann | s3 | sns |
| solr | sqs | statsd | stdout | stomp |
| syslog | tcp | udp | webhdfs | websocket |
| xmpp | zabbix | zeromq |
Use Cases
-
Real-time Data Processing
- Ingestsreal-time data from sources like IoT devices and websites.
- Enriches data during the processing stage.
-
Analytics and Monitoring
- Aggregates data from multiple sources for real-time insights.
- Monitors system performance and activity.
-
Log Management and Security
- Parses and structures log data for easier analysis.
- Supports security analysis and compliance reporting.
-
Data Integration
- Integrates data from different systems and applications.
- Centralizes data for analysis and automation.
Installing Logstash
In my current lab setup, I use Vagrant to provision virtual machines in VirtualBox.
For further details, refer to Using Vagrant to Setup Elastic Stack..
-
Login to your Logstash node and install the Java.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install -y openjdk-8-jre-headless -
Add the Elastic repository to your system.
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/apt stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-8.x.list' -
After adding the repository, update the package list:
sudo apt update -
Install Logstash.
sudo apt install -y logstash -
Add the
/usr/share/logstash/binto your~/.bashrcfile.cat >> ~/.bashrcEnter the following:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/share/logstash/binReload the shell:
source ~/.bashrc -
Verify the installation by checking the Logstash version.
logstash --versionOutput:
Using bundled JDK: /usr/share/logstash/jdk
logstash 8.17.0 -
Enable and start the Logstash service.
sudo systemctl enable --now logstash
sudo systemctl status logstash
Configuration Files
The logstash.yml and logstash.conf files are both configuration files used by Logstash, but they serve different purposes and control different aspects of Logstash's behavior.
Locations:
/etc/logstash/logstash.yml/etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash.conf
logstash.yml
This is the main configuration file which contains general settings.
- Pipeline Settings: Define pipeline workers, batch size, and other pipeline-related options.
- Memory Settings: Configuration for heap size and JVM settings.
- Logging Configuration: Specifies the log level and log location.
- Security: SSL, user authentication, and certificate settings.
Example:
# Path to where logstash should store logs
path.logs: /var/log/logstash
# The number of pipeline workers
pipeline.workers: 4
# Logging level
log.level: info
logstash.conf
This is the pipeline configuration file. It specifies how data flows through Logstash, including where to fetch data from (input), how to process it (filter), and where to send it (output).
- Input: Specifies where Logstash should gather data (e.g., from files, Kafka, Beats).
- Filter: Defines how data should be transformed or processed (e.g., grok, mutate, date).
- Output: Defines where to send the data (e.g., Elasticsearch, files, stdout).
Example:
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/*.log"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}" }
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"]
index => "logs"
}
}