DOM
Overview
JavaScript makes web pages interactive by allowing changes to HTML and CSS while the page is open.
- HTML and CSS define the structure and style
- JavaScript enables actions and changes
- It can modify, add, or remove elements
With JavaScript, web pages no longer need to reload for updates.
Document Object Model (DOM)
When a web page loads, the browser creates the Document Object Model (DOM).
- DOM represents the page as a structured tree
- It lets JavaScript access and modify HTML elements
- The
documentobject is how JavaScript interacts with the DOM
Using the DOM, JavaScript can change elements dynamically.
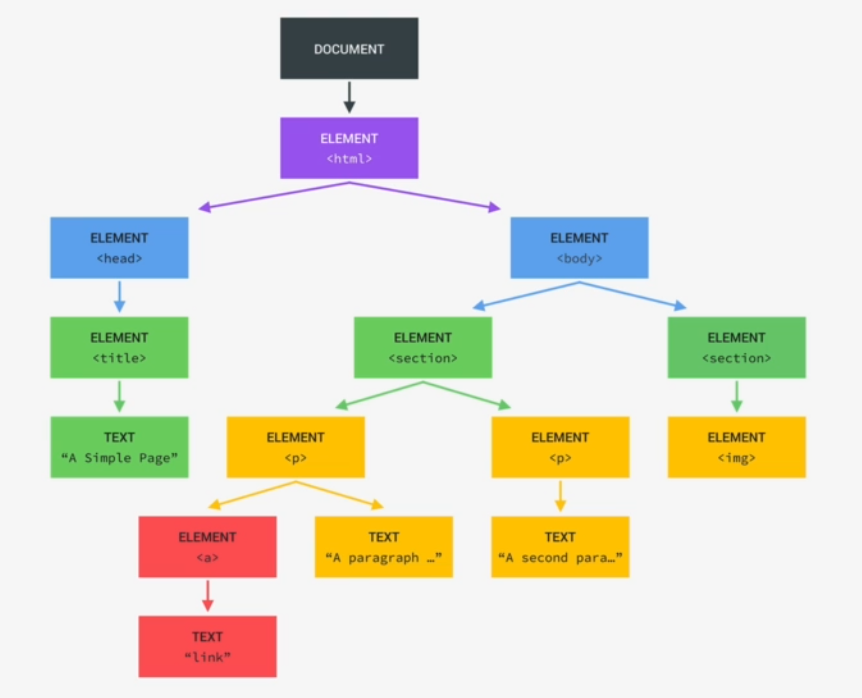
DOM Tree Structure
The DOM is stored in a tree structure, where each element is an object. The document at the top serves as the entry point, and you can use document.querySelector to select elements.
- The first child element is usually the
HTMLelement because it is the root of all HTML documents. HTMLtypically has two child elements:HeadandBody.- As you go deeper, more child elements are added, forming the complete DOM tree.
The Window Object
The window object is the top-level object in the browser.
window.documentrefers to the DOMwindow.alert()creates an alert box- Many built-in functions belong to
window
JavaScript interacts with the browser through the window and document objects.
- The browser loads HTML and CSS
- The JavaScript engine executes scripts
- JavaScript modifies the DOM dynamically
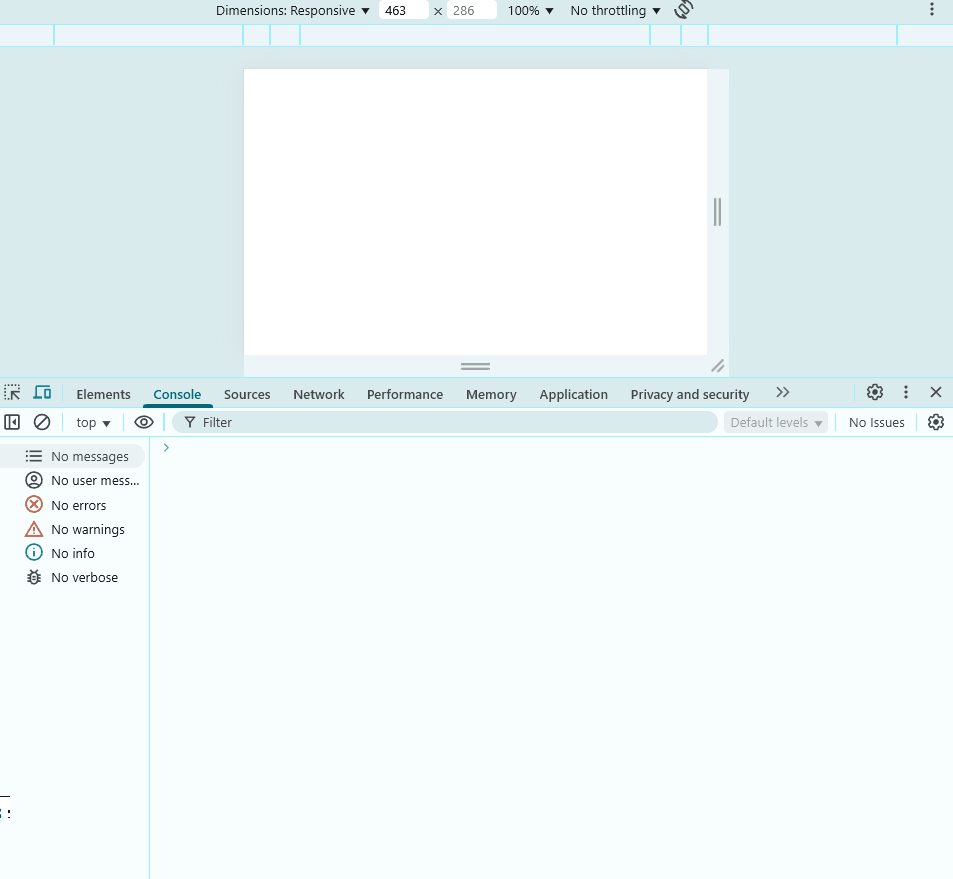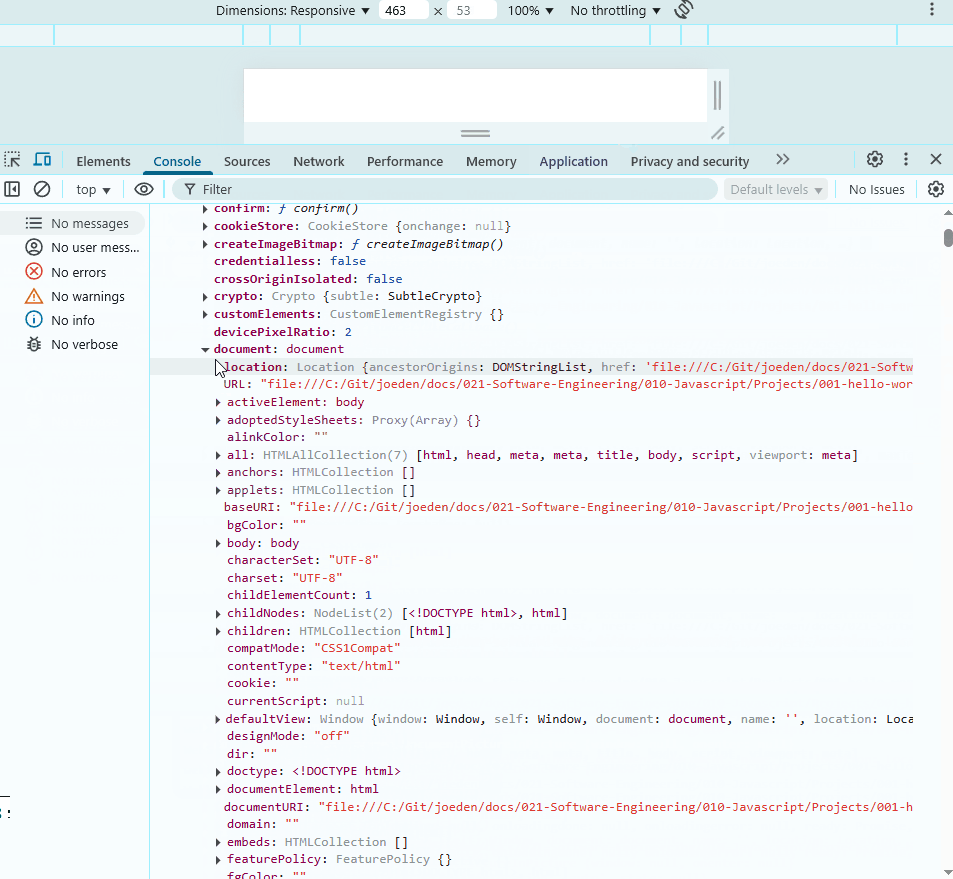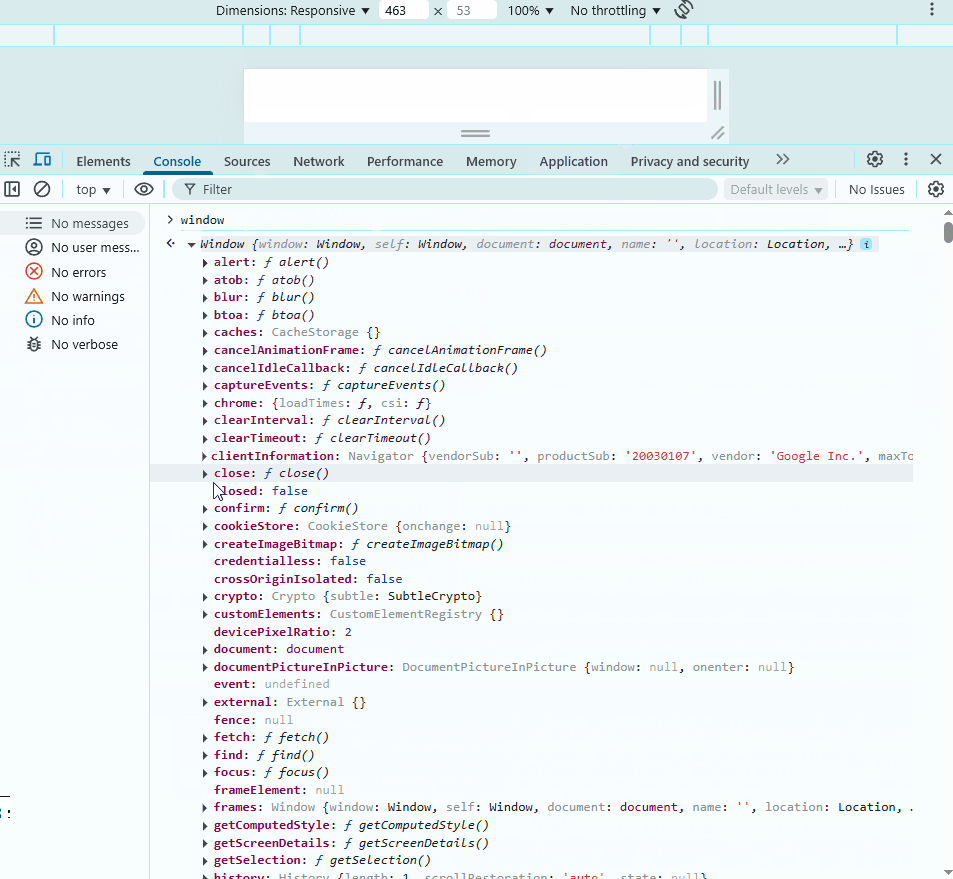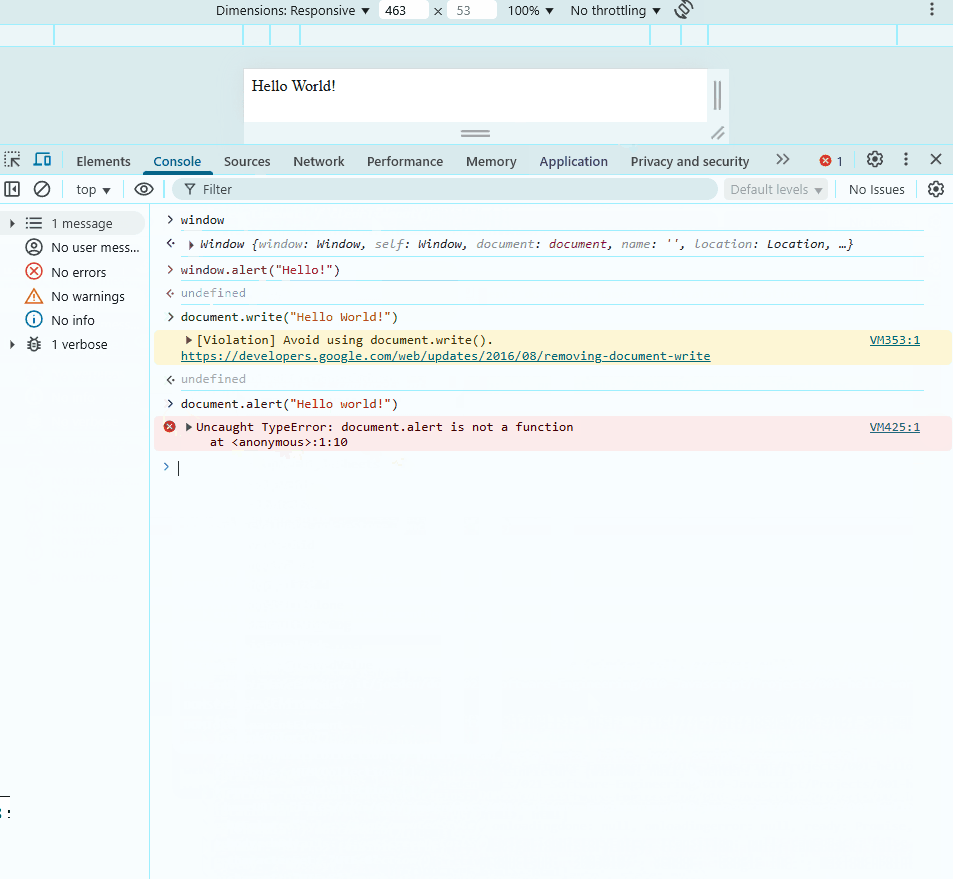
In the example below, we access window in the console. It is the main object that contains other objects like alert and document, which also have their own properties.
To access properties, use dot notation. Notice that the write method gives an error when used on window. This is because write belongs to document, not window.
DOM is not JavaScript
The DOM is part of the Web APIs, which are libraries browsers provide to interact with web pages.
- JavaScript uses the DOM API to manipulate web pages
- However the DOM itself is not part of JavaScript.
- Other Web APIs include timers, Fetch API, and many more.
Each browser has a JavaScript engine that reads and executes JavaScript.
- Chrome: V8
- Edge: ChakraCore
- Safari: Nitro
- Firefox: SpiderMonkey
Modifying the DOM
Modifying the DOM lets JavaScript change a webpage’s content and style instantly. This makes web pages interactive and dynamic.
For more information, please see DOM Manipulation.