Public Key Infrastructure
Trust Models
Trust models define how trust is established and managed in a system or network. They provide a framework for determining the authenticity and integrity of entities, such as users, devices, or services.
Centralized Trust Model
In a centralized trust model, trust is placed in a central authority, such as a Certificate Authority (CA) in a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
- Trust is placed in a central authority
- CA issues digital certificates linking public keys to identities
- Entities rely on the CA to validate authenticity
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Uses a centralized trust model to manage secure communications
- Trusted CAs issue certificates to confirm identities
- Ensures authenticity and integrity of certificates during exchanges
- Structured hierarchically: Root CA at the top, subordinate CAs below
- Commonly used in securing networks, including HTTPS connections
The centralized model simplifies trust management by relying on a single authority, but the security of the system depends entirely on that authority’s reliability.
Decentralized Trust Model
A decentralized trust model spreads trust across multiple participants instead of relying on a central authority.
- Common in peer-to-peer networks and blockchain systems
- Trust is built using consensus mechanisms or cryptographic proofs
- Example: blockchain and distributed ledger technologies
Web of Trust
- Uses decentralized trust where users validate each other’s keys
- Used in PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) and similar encryption tools
- Users sign each other’s public keys, creating a network of trust
- Trust is transitive: if A trusts B and B trusts C, A can also trust C
This model removes dependence on a single authority, making trust more distributed and resilient.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public Key Infrastructure or PKI is a combination of software, encryption technologies, processes, and services that enables an organization to secure its communications and business transactions.
- Uses asymmetric encryption with public and private key pairs
- Generates and manages keys for encryption and decryption
- Ensures confidentiality, integrity, authentication, access control, and non-repudiation
As a recap:
| Requirement | Description | PKI Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality | The secure transmission of information over networks ensuring that it is not accessed by unauthorised individuals | Data encryption |
| Integrity | To validate that all the outputs are equivalent to the inputs. Any alter of the data can be immediately detected and prevented. | Digital signatures |
| Authenticity | Both the sender and recipient should be able to validate each other's identities. | Hash algorithms, message digests, digital signatures |
| Non-repudiation | To ensure that the sender or receiver of a message cannot deny either sending or receiving such a message in future. | Digital signatures, audit logs |
| Availability | Information should be consistently and readily accessible for authorized parties. Involves properly maintaining hardware and technical infrastructure and systems that hold and display the information. | Redundancy |
Components of PKI:
- Certificate Authority (CA)
- Registration Authority (RA)
- Key Escrow
- Key Recovery Agent
- Digital Certificates
- Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs)
- Certificate Templates
- Certificate Revocation Standards
Certificate Authority (CA)
Primary component of a PKI. The CA server is used for issuing certificates for users, applications, and other CAs as well. In the CA server, the following are configured:
- Policies
- Rules
- Conditions fo the certificates
- Subordinate CA is also known as Issuing CA
- Hierarchy of the CAs: Root CA, Subordinate CA
Hierarchical Structure:
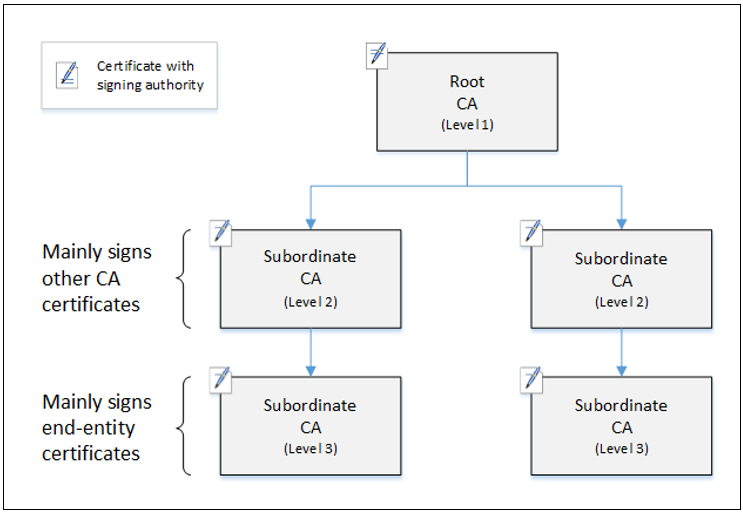
How it works
How it works:
- Root CA is precious, usually taken offline.
- Intermediate CAs do all the hardwork.
- User requests presents the digital certificates to the intermediate CAs.
- The intermediate CAs performs the confirmations themselves.
Known CAs
If you configure your browser to trust a CA, it will automatically trust all of the digital certificates issued by that CA. Browser developers preconfigure browsers to trust the major CAs to avoid placing this burden on users.
Some of the major CAs include:
- IdenTrust
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- GlobalSign
- ComodoCA
- Certum
- GoDaddy
- DigiCert
- SECOM Trust Systems
- Entrust
- Acalis
- Trustwave
Offline CA
CAs protect their own private keys by using an offline CA, which protects the root certificate which is the top-level certificate for their entire PKI.
- Offline CA is disconnected from networks
- Typicaly powered down until needed
- Root certificate is used to create subordinate intermediate CAs
- Intermediate CAs acts as online CAs to issue certificates routinely
Certificate Chaining
Certificate chains in PKI establish trust by linking a website’s certificate to a trusted root CA through one or more intermediate CAs.
- Browser verifies the identity of each intermediate CA
- Traces the chain of trust back to the known root CA
- A missing intermediate CA breaks the chain
- This prevents the browser from verifying the website's certificate.
Internal CA
Certificate Authorities (CAs) don’t always need to be third-party providers. Organizations often run internal CAs that issue self-signed certificates for use within private networks.
- Not trusted by external browsers or systems
- Internal systems can be configured to trust the internal CA
- Commonly used for testing, development, or internal services
- Reduce dependency on external CAs but require secure management
For more information, please see Self-Signed Certificates
Registration Authority (RA)
A Registration Authority (RA) authenticates and verifies the identity of individuals or organizations before digital certificates are issued by a Certificate Authority (CA).
- Verifies identity through interviews or background checks
- Collects and reviews identity documents from applicants
- Receives and validates certificate requests
- Forwards approved requests to the CA for issuance
- Keeps records of all requests and approvals for audits and tracking
Digital Certificates
Digital certificates are digitally signed electronic document that binds a public key with a user's identity.
- Purchased from a Certificate Authority (CA)
- Binds identity to a public key
- Provide authentication, encryption, integrity
- Commonly uses X.509 protocol standard.
- See Digital Certificate Types
For example, see the digital certificates for both Google and Apple’s websites below:
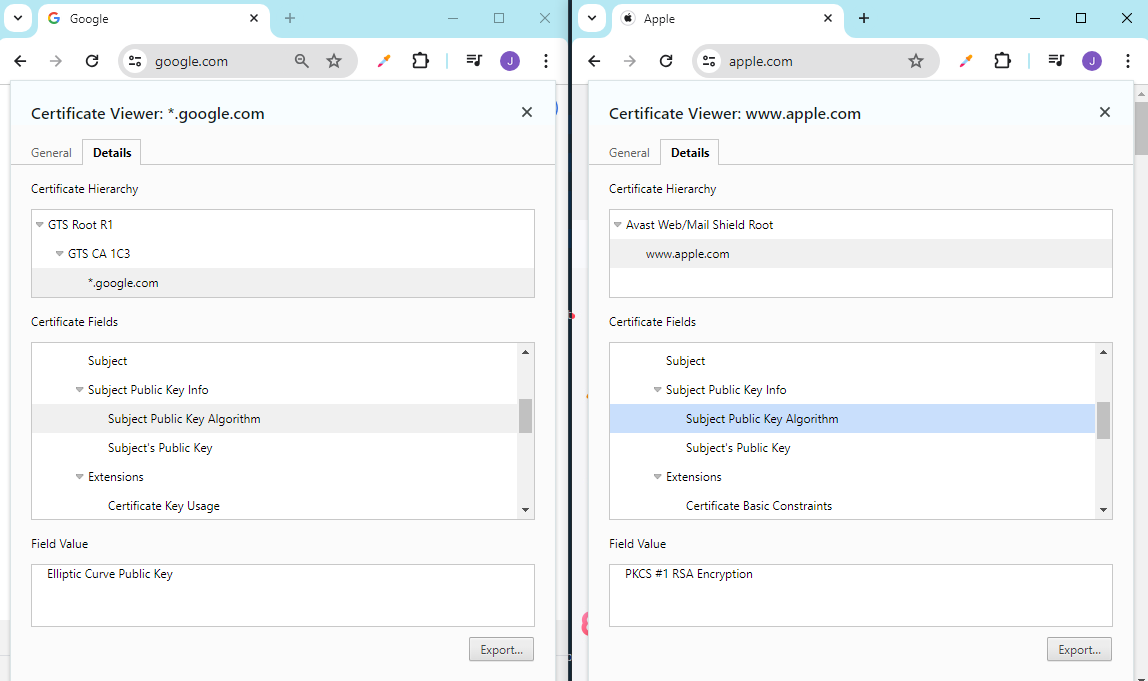
Google uses ECC certificates, while Apple uses RSA certificates.
- Google focuses on mobile devices
- Mobile devices have less processing power
- ECC uses smaller 256-bit keys, while RSA uses 2048-bit keys
- ECC is preferred for mobile and low-power devices
- RSA is preferred for desktops and high-capacity systems
Structure of an X.509 Certificate
Certificates that confirm to X.509 contain the following data:
- Version - X.509 version to which the certificate conforms
- Serial number - From the certificate creator
- Signature algorithm identifier - Method used by the CA to sign
- Issuer name - Information about the CA
- Validity period - Expiration date
- Subject Name - Common Name (CN) and Disntinguished Name (DN) of owner
- Subject's Public key - Actual public key by the owner
Wildcard
A certificate may include a wildcard (using “*”) to cover subdomains.
For example, a certificate issued to *.example.com is valid for:
example.orgwww.example.orgmail.example.orgsecure.example.org
Wildcard certificates apply only to one subdomain level, so the same wildcard will not work for:
www.mysite.example.com
Certificate Lifecycle
The certificate lifecycle defines the stages a digital certificate goes through.
-
Enrollment
- Before obtaining a certificate, requester must prove their identity to a CA
- Verification may require physical ID checks
- Other trusted methods include credit card data
- Once verified, the requester submits a CSR containing their public key
- The CA issues and signs an X.509 certificate with the verified information
- The user then receives and distributes the signed certificate
-
Verification
- Validate the CA’s digital signature using its public key
- Check that the certificate is within its validity period
- Ensure the certificate has not expired or been revoked
- Confirm its status using CRL or OCSP checks
-
Revocation
- Certificates are revoked if compromised (e.g., private key exposure)
- Also revoked if issued in error or if subject information changes
- Revoked when security roles or employment status changes
- Ensures compromised or invalid certificates can’t be trusted
- See Certificate Revocation
Certificate Pinning
Certificate pinning tells browsers to “pin” or associate a specific certificate or public key with a host for a set period.
- Domain or subdomain is binded to a known certificate or public key
- Alerts users if the certificate changes unexpectedly
- Prevents man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks using fake certificates
- See Public Key Pinning
Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs)
A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is a message sent from an applicant to a Certificate Authority (CA) to apply for a digital certificate. CSRs are typically generated by the entity requesting the digital certificate, such as a website owner or an organization's IT department.
- Public Key: Included in the digital certificate.
- Identity Information: Common name (CN), organization name, country.
- Key Information: Cryptographic algorithm and key size to be used.
- Signature: Signed by the private key corresponding to the public key.
Once the CSR is submitted to the CA:
- The CA verifies the information provided.
- The information is used to generate the digital certificate.
- The digital certificate is issued and returned to the entity.
- Issued certs can be installed on the entity's server for secure communications.
Certificate Templates
Certificate templates are predefined formats or structures that specify the key attributes and parameters for creating digital certificates.
- Streamline the certificate issuance process.
- Specify key usage, validity, attributes
- Allow customization to meet specific organizational needs
- Ensure consistency and compliance.
- Example is EFS - Encrypted File System
Certificate Revocation Mechanisms
Certificate revocation is the process of invalidating a previously issued digital certificate before its expiration date.
Key Escrow
Refers to the process where the user's private keys are stored in a secure, third-party location, which is effectively an "escrow".
- Key escrows can be set up using key escrow agents.
- In case of any investigation, keys can be retrieved from the escrow.
- Ensures encrypted data is always accessible.
- Access is strongly regulated.
- At least two administrators are required when taking out the key from the escrow.
Key Recovery Agent
A Key Recovery Agent (KRA) is specialized software or a designated role that enables the recovery of lost, damaged, or inaccessible encryption keys.
- Useful during major incidents or disasters when keys are lost
- Ensures data encrypted with lost keys can still be decrypted
- Works with the CA to securely retrieve or reissue encryption keys