Encryption Tools
Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
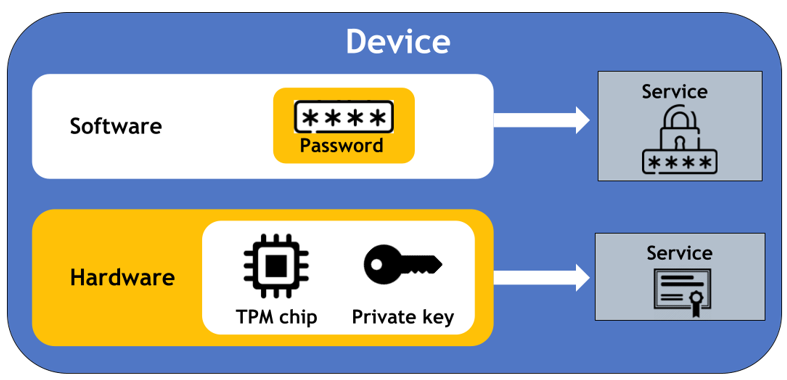
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a hardware-based microcontroller designed to securely generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys and other sensitive information.
- Securely stores encryption keys, certificates, and passwords.
- hardware-based encryption and attestation (system integrity).
- Supports secure boot and platform integrity checks.
Applications:
- Laptops and desktops, secure boot processes and protect encryption keys.
- Enterprise environments for secure device authentication and attestation.
Checks boot integrity of the host using:
- UEFI secure boot
- Measured boot
- Boot attestation
TPM is likened to a personal vault, while HSM is to a high-security bank vault.
Secure Boot
Secure Boot, also called UEFI Secure Boot, is a security feature that helps ensure a device only boots using trusted software signed by authorized keys.
- Prevents unauthorized or malicious code from running during startup.
- Uses cryptographic signatures to verify bootloader and OS integrity.
- Helps protect against rootkits and boot-level malware.
Measured Boot
Measured Boot records cryptographic hashes of boot components as the system starts, creating a log of what was loaded.
- Hashes each component during boot to track system state.
- Stores measurements in a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) for verification.
Boot Attestation
Boot Attestation verifies the integrity of the measured boot logs, often remotely, to confirm the system started securely.
- Compares boot measurements against known good values.
- Halt or alert if unauthorized changes are detected during startup.
Internal Memory
A TPM has two types of internal memory used for specific purposes:
-
Persistent Memory
- Static in nature
- Stores certificates, and configuration permanently
- Retains data even when the device is powered off
- Used for long-term security functions like device identity
- Contains the following:
- Endorsement key
- Storage root key
-
Volatile Memory
- Temporary storage for session keys and runtime data
- Cleared when the device is powered off
- Supports active cryptographic operations and computations
- Contains the following:
- Attestation identity key
- Platform configuration register hashes
- Storage key
Persistent memory ensures long-term secure storage, while volatile memory supports temporary operations and fast processing.
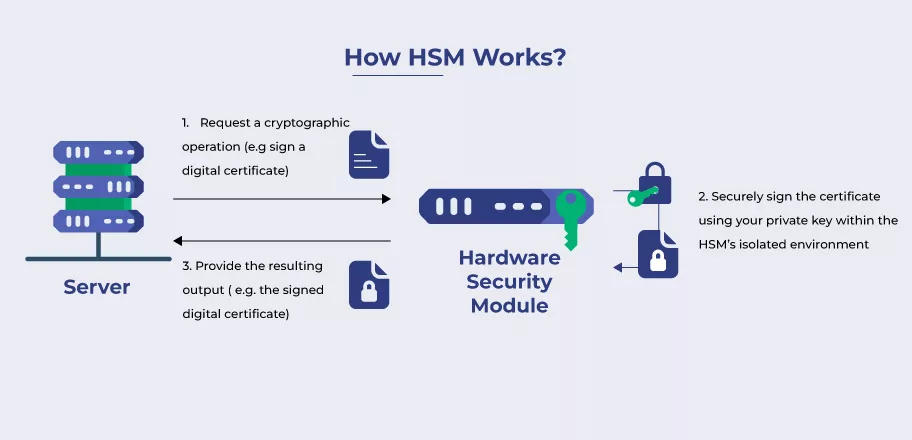
Hardware Security Module (HSM)
A Hardware Security Module (HSM) is a dedicated hardware device that safeguards cryptographic keys and perform cryptographic operations in a tamper-proof environment.
- Securely stores and manages cryptographic keys.
- Performs encryption, decryption, and digital signature operations.
- Supports high-availability configurations for mission-critical apps.
Applications:
- Used in banking and financial institutions
- Data centers; key management and securing sensitive data.
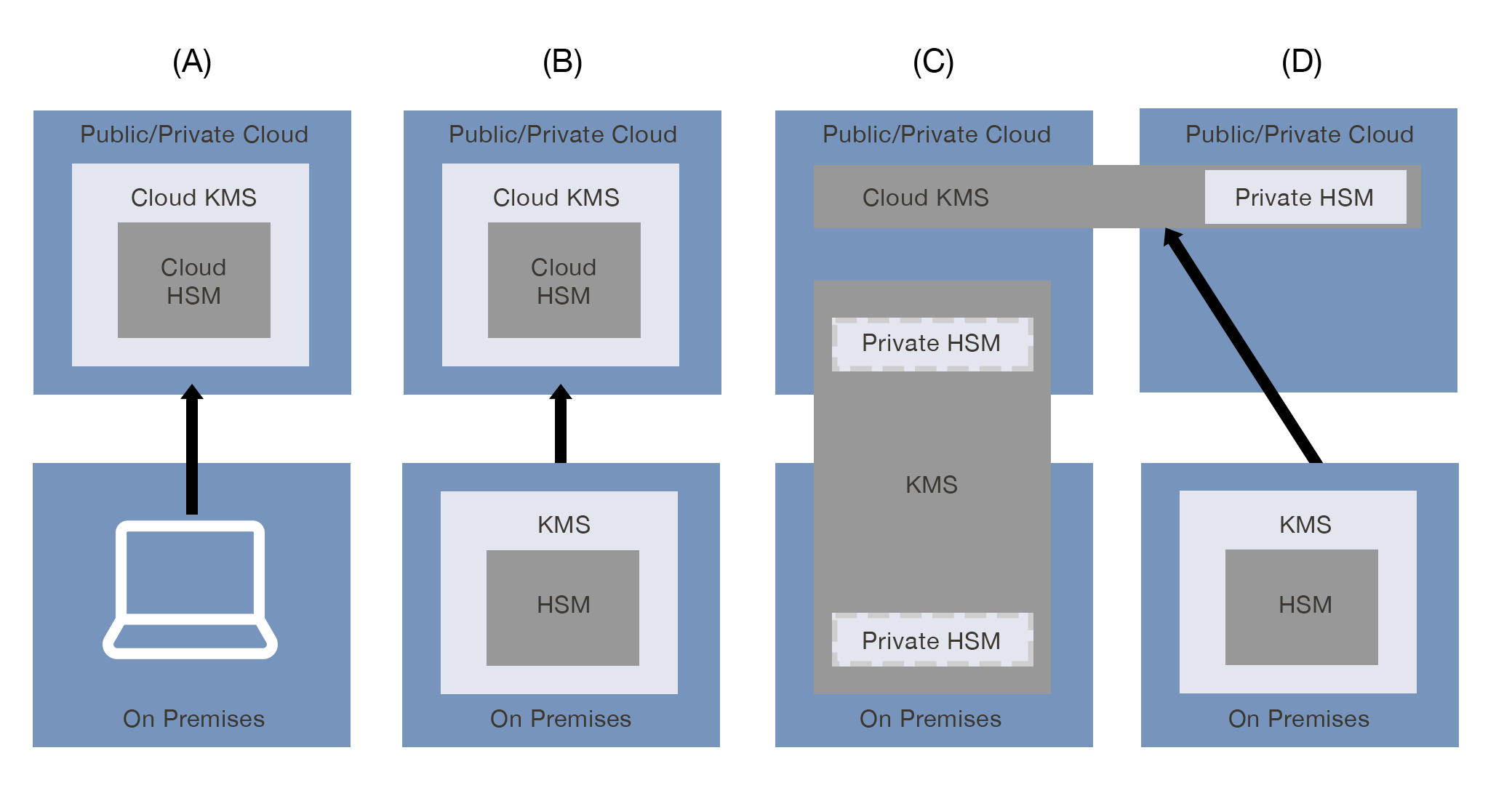
Hardware Security Module as a Service (HSMaas)
HSMaaS is a cloud-based solution that provides secure, scalable, and centralized encryption key management using hardware security modules.
- Centralized key control across clouds
- Secure key storage, reduces risk and complexity
- Supports importing existing org-owned keys
- Low latency for fast cryptographic operations
- Works across clouds (e.g., AWS CloudHSM, Azure HSM)
Key Management Service (KMS)
A Key Management Service (KMS) is a cloud-based or on-premises service designed to manage cryptographic keys, providing centralized control and automated key lifecycle management.
- Generates, rotates, and revokes cryptographic keys.
- Supports role-based access controls for key management.
- Integrates with various services for encryption and decryption.
Applications
- Used in cloud environments to manage encryption keys for storage and data protection.
- Enterprise systems;automate key lifecycle management and ensure compliance with security policies.
Secure Enclave
A Secure Enclave is a hardware-based co-processor or device designed to perform sensitive operations and store sensitive data in a secure manner.
- Encrypts and stores sensitive data, like biometric information or encryption keys.
- Performs secure computations that are isolated from the main OS.
- Provides a trusted environment for sensitive tasks, like authentication and digital signing.
- Even if data gets compromised, secure enclaved remains untouched.
Applications
- Mobile devices (e.g., Apple's Secure Enclave); protect biometric data and manage encryption keys.