Symmetric Encryption
Overview
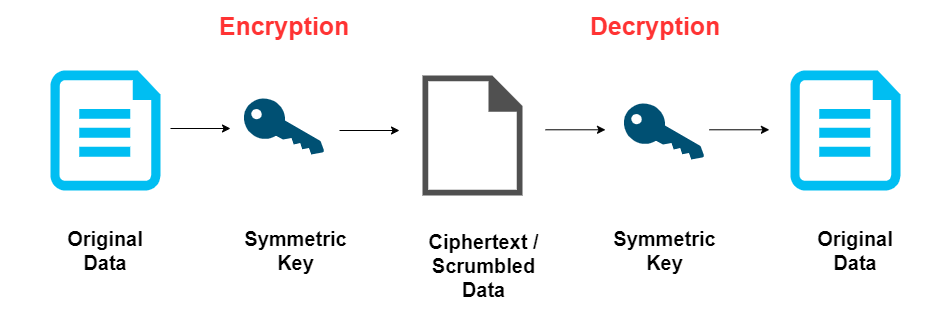
Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. The sender and receiver must share this key, keeping it secret from others.
- Session key - single key is used to encrypt and decrypt data.
- Both parties must have this key.
Symmetric encryption is generally faster and less computationally intensive compared to asymmetric cryptography. It is also effective for encrypting large volumes of data.
Symmetric key cryptography can also be called secret key cryptography and private key cryptography.
In some cases, symmetric cryptography may be used with temporary keys that exist only for a single session. In those case, the secret key is called an ephemeral key.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Secure communication within closed networks
- Encrypting files or databases
- Securing backups
Disadvantages:
- Key distribution and management can be challenging
- If the key is compromised, the entire system is at risk.
Key Exchanges
Key exchange is a process in which two communicating parties establish a shared secret key, typically used for symmetric encryption.This key is established in a manner so that eavesdroppers, even if they intercept the key exchange messages, cannot determine the shared key.
Sending the key:
-
In-band
- Sending the key along with the encrypted data
- Risky, vulnerable to sniffing
-
Out-of-band
- Providing the key separately from the encrypted data
- Can be provided beforehand or via phone/SMS
Out-of-Band Key Exchange
Out-of-Band (OOB) key exchange is a method for securely sharing cryptographic keys outside the regular communication channel used for encrypted data transfer. This approach enhances security by reducing the risk of key interception through the primary channel.
- Face-to-face meeting, if both parties know each other by sight
- Physically mail the drive containing the key
- Telephone call, if both parties know each other's voices
In-Band Key Exchange
Out-of-Band methods can be time-consuming. For instance, if Alice and Bob are far apart, a physical meeting might not be practical. Sending a physical letter with the key takes days, and reading a long encryption key over the phone is difficult.
As a solution, we can use In-Band Key Exchange for key exchange over the same network used for communication, even if secure methods of communication are unavailable. This method simplifies the process but requires careful implementation to maintain security.
Block Ciphers
Block ciphers encrypt data in fixed-size chunks instead of one bit at a time. They apply mathematical transformations repeatedly to hide the original data.
- Operates on fixed-size data blocks
- Encrypts data in blocks, such as 64 or 128 bits
- Each block of plaintext becomes one block of ciphertext
- The larger the block size, the faster the encryption.
- More rounds of encryption means stronger protection
Common features:
- Easier to implement and generally more secure than stream ciphers
- Often used in software-based encryption systems
- Common in protocols and file encryption where data comes in chunks
- Requires padding if data doesn't perfectly fit into blocks
- Can run in different modes to provide flexibility and added protection
Substitution boxes, or S-boxes, are used within block ciphers. S-boxes contain lookup tables to determine how a block of data is encrypted or decrypted. The key is used to decide which S-box to utilize with each block.
Block ciphers typically have 64-bit block size, but in reality its only 56 bits because 8 bits is reserved for overhead/parity to ensure that the other 56 bits are accurate.
| Algorithm | Block Size | Number of Rounds | Key Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES (Data Encryption Standard) | 64-bit | 16 rounds | 56-bit | Older method, no longer secure for modern use. |
| 3DES (Triple DES) | 64-bit | 48 rounds (3×16) | 168-bit | Repeats DES three times to strengthen encryption. |
| IDEA (International Data Encryption Algorithm) | 64-bit | 8 rounds | 128-bit | More secure than DES but less commonly used. |
| AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) | 128-bit | 10/12/14 rounds | 128/192/256-bit | Current global encrypti on standard. |
| Blowfish | 64-bit | 16 rounds | 32–448-bit (variable) | Open-source replacement for DES. |
| Twofish | 128-bit | 16 rounds | 128/192/256-bit | AES finalist, still secure and efficient. |
A few notes about each algorithm:
-
3DES
- Encrypts data three times for better protection
- Can use one, two, or three keys for flexibility
- Secure for limited use but slow for large data
- Harder to crack but also increases processing time.
-
AES
-
Uses substitution and transposition to mix data thoroughly
-
Same key is used to encrypt and decrypt data
-
Widely supported across devices and systems
infoAES remains the strongest and most trusted standard for encryption today.
-
-
Blowfish
-
Free to use without any license restrictions
-
Once popular but no longer recommended for new systems
-
Creator suggests using Twofish instead
-
Blowfish and twofish were both released as open source
infoAlthough fast, Blowfish’s small block size makes it outdated for modern security needs.
-
-
Twofish
- Publicly available and still considered secure
- Supports 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit key sizes
- Performs efficiently on both hardware and software
- Reliable encryption choice, especially for open systems.
Streaming Ciphers
Also known as Rivest Cipher (RC) Suites, the streaming ciphers comprises a range of ciphers, from block to stream, with varying levels of flexibility and security.
- Encrypts data in a continuous stream instead of fixed blocks
- Uses a key stream generator to create random-looking bits
- The key stream is XORed with the plaintext to get the ciphertext
Common features:
- Same key is used for both encryption and decryption
- Often implemented in hardware for faster performance
- Works well for real-time data like voice or video streams
- Becomes weak if the same key stream is reused or not random enough
Unlike block ciphers, streaming ciphers encrypt one bit a time. It is wideless used in encrypting wireless networks.
| Algorithm | Cipher Type | Block Size | Number of Rounds | Key Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC2 | Block Cipher | 64-bit | Variable rounds | 8-128 bit (variable) | Early block cipher; adjustable key size, mostly used in legacy applications. |
| RC4 | Stream Cipher | N/A | Variable | 40-2048 bit (variable) | Used in SSL and WEP; now considered insecure due to vulnerabilities in key scheduling. |
| RC5 | Block Cipher | 32/64/128-bit | Variable rounds | 0-2040 bit (variable) | Highly flexible block cipher with variable block size, key size, and rounds. |
| RC6 | Block Cipher | 128-bit | 20 rounds | 128/192/256-bit | Extended version of RC5; designed for high security and was a finalist in the AES competition. |
A few notes:
- RC1 was never published.
- RC2 was considered weak and was skipped over.
- RC3 was cracked before it was even released to the public.
- RC4, RC5, and RC6 are commonly used in networks today.
- Some are now considered insecure (like RC4)
- Had broader applications in history (like RC5 and RC6).
Stream ciphers are useful for real-time communication, where speed and efficiency are key, but they must use unique and random key streams to stay secure.
CAST Algorithms
CAST algorithms are symmetric key block ciphers designed by Carlisle Adams and Stafford Tavares. They use a Feistel network structure, similar to DES, to provide strong encryption and flexibility. There are two main versions of CAST: CAST-128 and CAST-256.
- Built using Feistel network design
- Supports variable key sizes for different security levels
- Designed for speed and resistance to known attacks
- Commonly used in encryption applications and security protocols
In simple terms, CAST algorithms balance speed and strength, making them useful for both software and hardware encryption.
| Algorithm | Block Size | Number of Rounds | Key Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAST-128 (CAST5) | 64-bit | 12 or 16 rounds | 40–128-bit | Used in tools like PGP; efficient and secure for smaller data blocks. |
| CAST-256 | 128-bit | 48 rounds | 128/160/192/224/256-bit | Improved version with larger blocks and higher security; designed for AES competition. |
Symmetric Block Modes
Symmetric block ciphers can operate in various modes that define how blocks of plaintext are transformed into ciphertext. Different modes address specific requirements and security concerns.
- Electronic Codebook Mode (ECB)
- Cipher Block Chaining (CBC)
- Cipher Feedback (CFB)
- Counter (CTR)
- Galois/Counter Mode (GCM)
GCM and CCM modes both include data authenticity in addition to confidentiality, which is why they are also known as Authenticated modes of encryption.. On the other hand, ECB, CBC, CFB, and CTR only provide confidentiality, and are knows as Unauthenticated modes.
Electronic Codebook Mode (ECB)
Electronic Codebook mode can show identical blocks for identical plaintext inputs, compromising security.
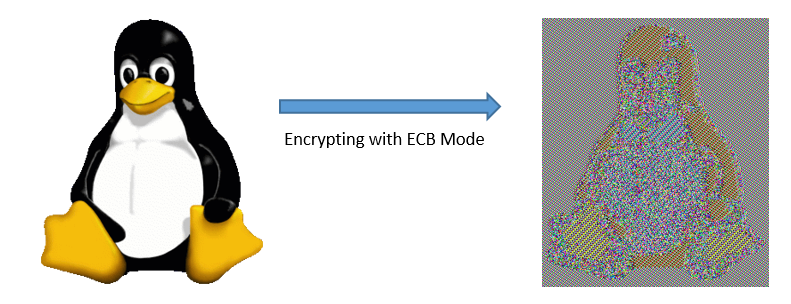
As an example, if we encrypt the image above, we'll get a scrambled image that still shows some patterns. Although it is encrypted, the image is still recognizable.
Advantages:
- Simple and fast
- Allows random access to blocks.
Disadvantages:
- Patterns in plaintext are retained in ciphertext
- Identical plaintext blocks result in identical ciphertext blocks
- This makes it vulnerable to analysis
Cipher Block Chaining (CBC)
Each block of plaintext is XORed with the previous ciphertext block before encryption. The first block uses an initialization vector (IV).
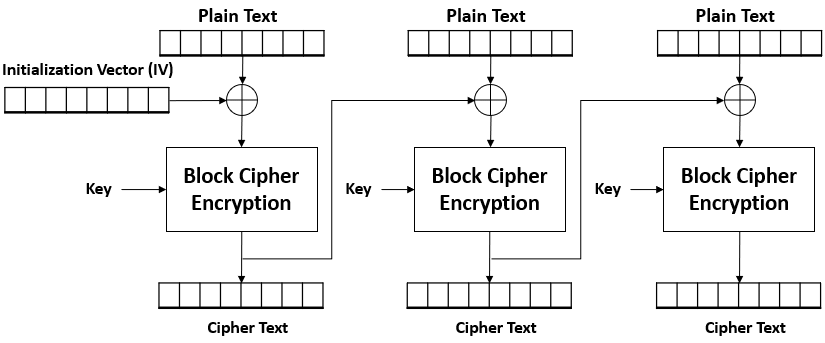
Initialization vector
- Same size as the other blocks.
- The first block is applied with XOR using the IV.
- The output will then be used as the IV for the next block, repeating the cycle.
Advantages:
- Adds randomness to encryption
- Even identical plaintext blocks yield different ciphertext due to chaining.
Disadvantages:
- Requires sequential processing
- Small changes in plaintext can affect the whole chain
- Complicates decryption if data is corrupted
One important consideration when using the CBC mode algorithm is that error propagate.
If one block corrupted during transmission, it becomes impossible to decrypt the block and the next block as well.
Cipher Feedback (CFB)
CFB is the streaming version of CBC. It turns block ciphers into self-synchronizing stream ciphers. The previous ciphertext block (or IV) is encrypted and then XORed with the plaintext to produce ciphertext.
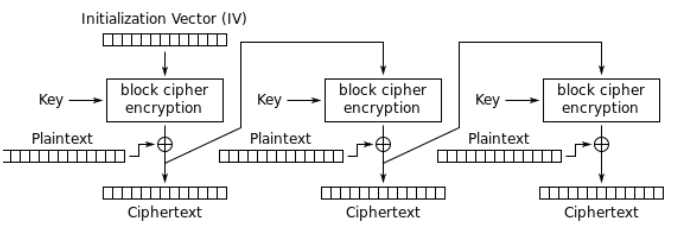
Instead of breaking messages into blocks, CFB uses memory buffers of the same block size. As the buffer becomes full, it is encrypted and then sent to the recipients, The system then waits for the next buffer to be filled as new data is generated before it is in turn encrypted and then transmitted.
Advantages:
- Provides flexibility in block size
- Allows for partial block updates
- Ideal for real-time encryption
Disadvantages:
- More complex error propagation
- If an error occurs, it affects multiple blocks
Output Feedback (OFB)
Similar to CFB, but the encrypted output (keystream) is generated independently of the plaintext and then XORed with the plaintext to produce ciphertext.
- IV is encrypted, then output is XORed to first block
- Same IV is used throughout the process.
Advantages:
- Errors in ciphertext do not propagate
- Ideal for secure data streaming
Disadvantages:
- If the same IV and key are reused, the entire encryption can be compromised
- Requires careful management of IVs
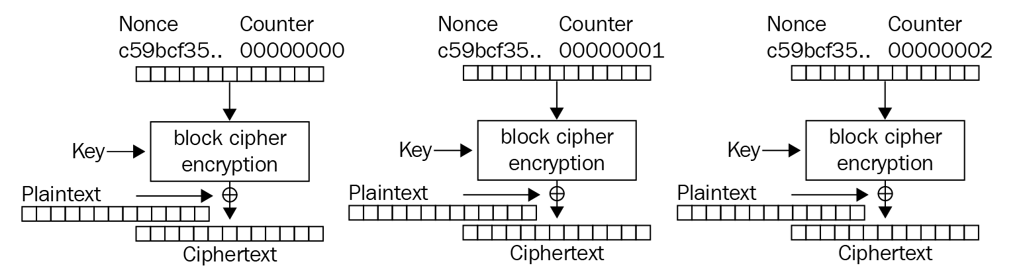
Counter (CTR)
Converts block ciphers into stream ciphers by using a counter that is encrypted to produce a keystream, which is then XORed with the plaintext.
- Uses a Nonce value + counter value
- Counter increments in binary
- Both are combined and then encrypted
- First block of plaintext ix XORed with the encrypted NONCE+Counter
- Output becomes the ciphertext
- Repeat steps for each block of plain text
Advantages:
- Allows for parallel processing
- Errors do not propagate
- Noo chaining issues
- Widely used in modern applications
Disadvantages:
- Counter and key must never repeat
- Can be vulnerable to attacks if not implemented carefully
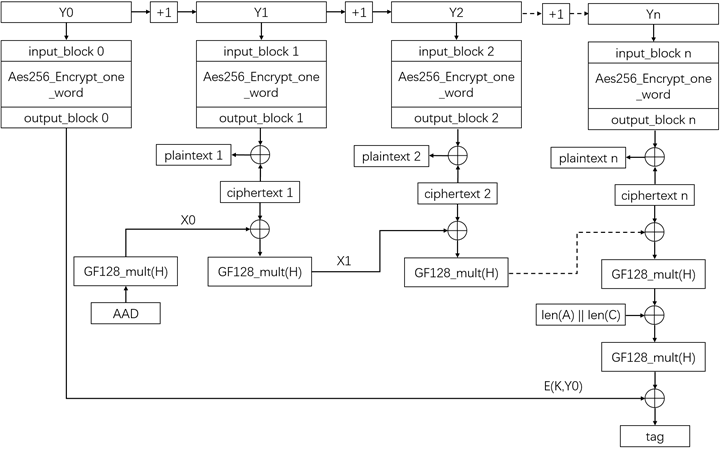
Galois/Counter Mode (GCM)
Combines CTR mode with a message authentication code (MAC) to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
Advantages:
- Provides authenticated encryption
- Ensures that ciphertext has not been tampered with
- Supports parallel processing
Disadvantages:
- More complex implementation
- Requires careful management of IVs and counters
Counter with CBC-MAC (CCM)
Counter with CBC-MAC (CCM) combines CTR mode for encryption with CBC-MAC for authentication, providing both confidentiality and integrity.
- CTR for confidentiality, CBC-MAC for data authenticity
- Currenly used with 128-bit block ciphers (like AES)
- Requires a "nonce" that must be changed for each transmission