Data Pipelines
Updated Sep 26, 2019 ·
Data as the New Oil
The phrase "Data is the new oil," coined by The Economist, helps us understand how data flows within an organization.
-
Extracting Data
- Like extracting crude oil, data is collected from various sources.
-
Processing and Using Data
- Crude oil is processed and separated into useful products.
- Similarly, data moves through pipelines, gets processed, and is organized for different uses.
Using streaming platform companies as examples again, a data engineer manages data in a process similar to oil processing.
-
Data Sources
- Data is collected from the mobile app, desktop app, website, and internal systems like HR.
-
Ingesting Data
- Data moves from these sources to thr data lake, forming the first set of pipelines.
-
Organizing Data
- Data is organized into databases for artists, albums, tracks, playlists, customers, and employees, creating additional pipelines.
-
Processing Data
- Tracks are checked for readability, correct size, and proper association with artists.
- Clean data is stored in a new database for data scientists to use.
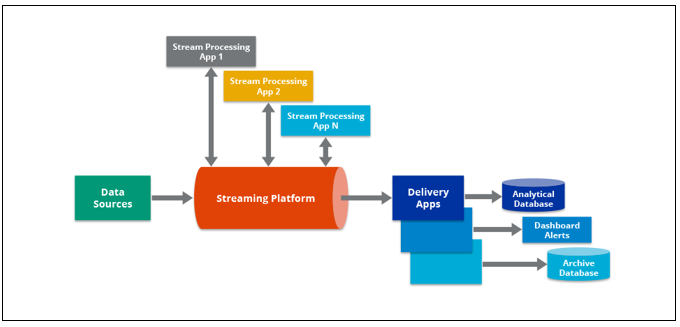
Data Pipelines
The data engineering pipeline involves extracting data from various sources, processing it with a cluster computing framework, and loading it into an analytical database.
- Scheduling frameworks like Airflow ensure tasks run in a specific order.
- External APIs or other file formats can also serve as data sources.
- Automate processes to minimize errors and speed up availability.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) frameworks automate data movement and processing.
- Data is extracted, transformed, and loaded into new databases.
- Data is sometimes routed directly to applications without transformation.