Roles and their Tools
Overview
Data engineering is all about designing, developing, and maintaining systems to collect, store, and process data. It's essential for building the infrastructure and architecture needed for effective data management.
- Ensures efficient data collection
- Supports data storage solutions
- Facilitates seamless data processing
Roles
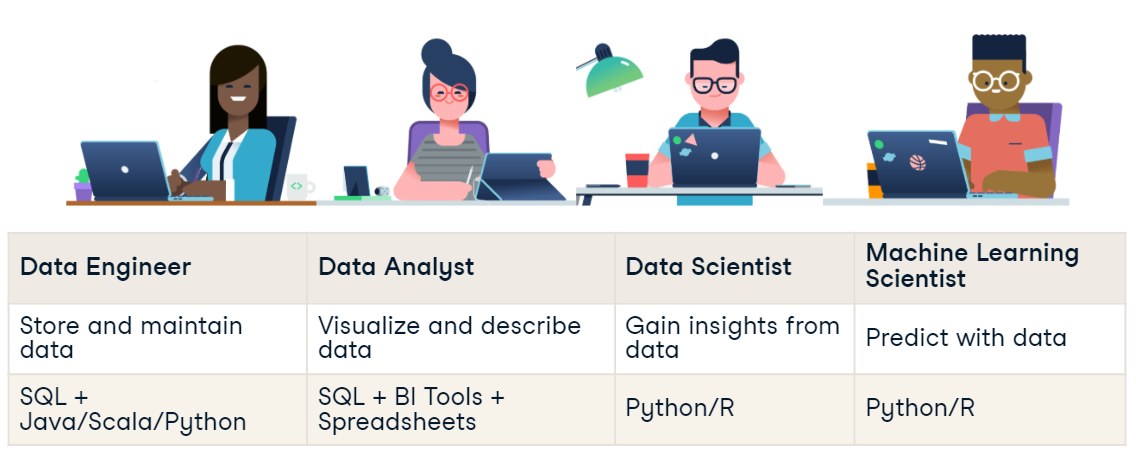
Data Engineer
Data engineers are responsible for building, testing, and maintaining the architecture (such as databases and large-scale processing systems) that allows for the efficient handling of data. They play a key role in the first stage of the data science workflow: data collection and storage.
- Build and maintain data pipelines
- Design scalable infrastructure for data collection and storage
- Ensure data is easy to access and process
- Well-versed in cloud technology
- Clean corrupt data
Data engineers use a variety of tools and languages. They're proficient in SQL for organizing data, and they use programming languages like Java, Scala, or Python for processing data. They also use Shell for task automation and must be adept with cloud computing for managing large data volumes.
- SQL for data storage and organization
- Java, Scala, or Python for data processing
- Shell for automation
- Cloud computing for data ingestion and storage
Data Analyst
Data analysts focus on interpreting current data. They explore data, create visualizations and dashboards, and often clean data beforehand. With less emphasis on programming and statistics, they concentrate on data preparation, exploration, and visualization stages.
- Explore data and create visualizations
- Clean data before analysis
- Focus on data preparation and exploration
Data analysts use SQL for querying data and spreadsheets for simple analyses on small datasets. They employ Business Intelligence (BI) tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Looker to create dashboards and share their insights. Advanced analysts might also use Python or R for more complex tasks.
- SQL for querying data
- Spreadsheets for simple analyses
- BI tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Looker for dashboards
- Python or R for advanced data analysis
Data Scientist
Data scientists utilize their strong statistical backgrounds to uncover new insights from data. They apply machine learning for predictions and forecasts, focusing on later workflow stages like data preparation, exploration, visualization, and experimentation.
- Strong statistical background
- Use machine learning for prediction
- Data preparation and experimentation
- Monitor business processes
- Clean outliers in data
Proficiency in SQL and at least one programming language, typically Python or R, is essential for data scientists. They use data science libraries like pandas or tidyverse for common analytical tasks.
- SQL for data manipulation
- Python or R for data science tasks
- Libraries like pandas or tidyverse for data analysis
Machine Learning Scientist
Machine learning scientists specialize in using machine learning to analyze and predict data. They work with training data to classify and predict larger datasets, extending their efforts into deep learning for more complex predictions.
- Specialize in machine learning
- Use training data for classification and prediction
- Focus on deep learning for advanced predictions
Machine learning scientists use Python or R to create predictive models, leveraging popular libraries like TensorFlow for deep learning algorithms.
- Python or R for model creation
- TensorFlow for deep learning
Tools of the Data Engineer
Data engineers move data from various sources, process it, and load it into an analytical database. They use multiple tools for these tasks.
Databases
Data engineers are expert users of database systems. The data engineer's primary task revolves around databases.
- Hold and organizes large amounts of data
- SQL or NoSQL databases
- Retrieve/search data through DBMS
- Other databases are used for analysis
Processing
Data engineers use tools for processing data quickly, cleaning, aggregating, or joining it from different sources.
- Clean data
- Aggregate data
- Join data
Example:
Parallel processing frameworks like PySpark are used behind the scenes for operations that may resemble simple pandas operations.
Parallel processing with clusters of machines:
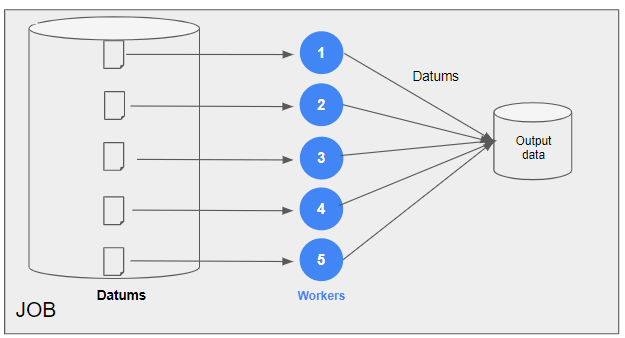
Scheduling
Scheduling tools ensure data moves correctly and timely.
- Manage jobs to run in the right order
- Resolve dependency requirements of jobs
Existing Tools
Databases:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
Processing:
- Apache Spark
- Apache Hive
Scheduling:
- Apache Airflow
- Oozie
Cloud Providers
Data engineers are heavy users of the cloud. As mentioned in the previous sections, data processing requires cluster of machines. This can be done on self-hosted machines in on-premise datacenters.
Considerations for datacenters:
- Electrical and maintenance costs
- Labor overhead for operators
- Optimizing peaks and quiet moments
As a solution, data engineers opt to use cloud providers.
- Cost: optimization and resource utilization
- Storage: Database reliability and disaster preparedness
Services:
-
Storage
- Used for uploading files to the cloud.
- Examples of storage services: AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage.
-
Computation
- Used for performing tasks on the cloud.
- Examples of computation services: AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
-
Databases
- Used for hosting databases.
- Examples of database services: AWS RDS, Azure SQL Database, Google Cloud SQL.