Deployment-Driven
Overview
To avoid deploying a model that can't be used, we need to consider deployment early in development. This is called Deployment-driven Development.
Infrastructure Compatibility
Before developing a model, ensure it will work on the target platform.
- Check resource requirements (e.g., memory, cores).
- Verify it can run on the target device (e.g., mobile, cloud).
It’s easy to create a model that requires a lot of resources, only to realize later it can't run on the intended device. Understand the target platform as early as possible.
Transparency and Reproducibility
Track every detail about how the model was created for future reference.
- Keep records of who trained the model, when, and with which data.
- Use versioned datasets to maintain consistency.
- Document the model training pipeline for transparency.
The model’s origin should have clear record to make it easy to recreate or understand how it was built in the future.
- Transparency means there should be no doubt about how the model was built
- Reproducibility means it should be easy to recreate the exact model.
Additionally, logging experiments from the exploration phase is important to prevent future maintainers from reinventing the wheel. This can be done using the metadata store.
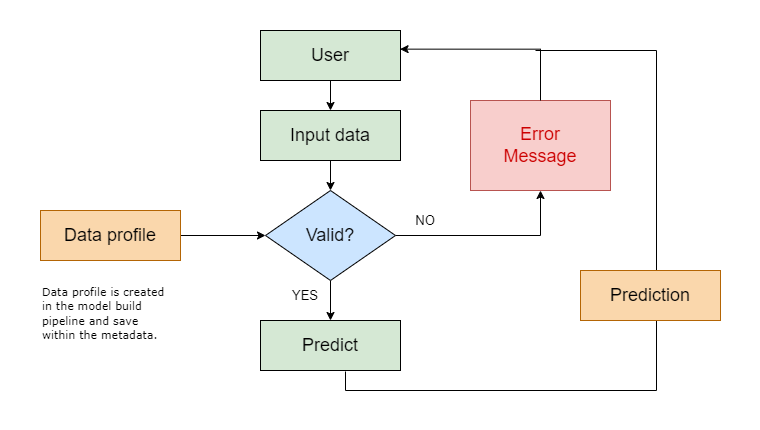
Data Validation
Make sure the data used by the model is correct and fits the expected format.
- Set rules for valid input data (e.g., positive values only).
- Validate data before it is fed into the model.
Data issues, like incorrect values, can cause errors. Validate the data before using it in the model.
Monitoring
Track how well the model performs over time to identify issues early.
- Log the inputs and predictions made by the model.
- Monitor for performance drops or changes in behavior.
Ongoing monitoring ensures you can spot issues early and take action if the model's performance decreases.
Debugging
Prepare for errors by setting up a detailed logging system.
- Implement logging for all model activities.
- Use logging tools designed for debugging.
Without proper logging, debugging becomes difficult. Set up a reliable logging system early to quickly track down issues when they occur.
Testing
Write and continuously run tests to catch bugs and ensure smooth updates to your model and app.
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- Load tests
- Stress tests
- Deployment tests
Testing is crucial to prevent introducing new bugs. Make sure to have tests ready for any fixes or updates you make.
For more information, please see Testing.