DLQ Plugin
Overview
A Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) is used to store events that fail to process due to errors or misconfigurations. It helps in troubleshooting by capturing problematic events for later analysis and debugging. Once the events are in the dead letter queue, we can process these events using another Logstash configuration and make the necessary changes before indexing them back to Elasticsearch.
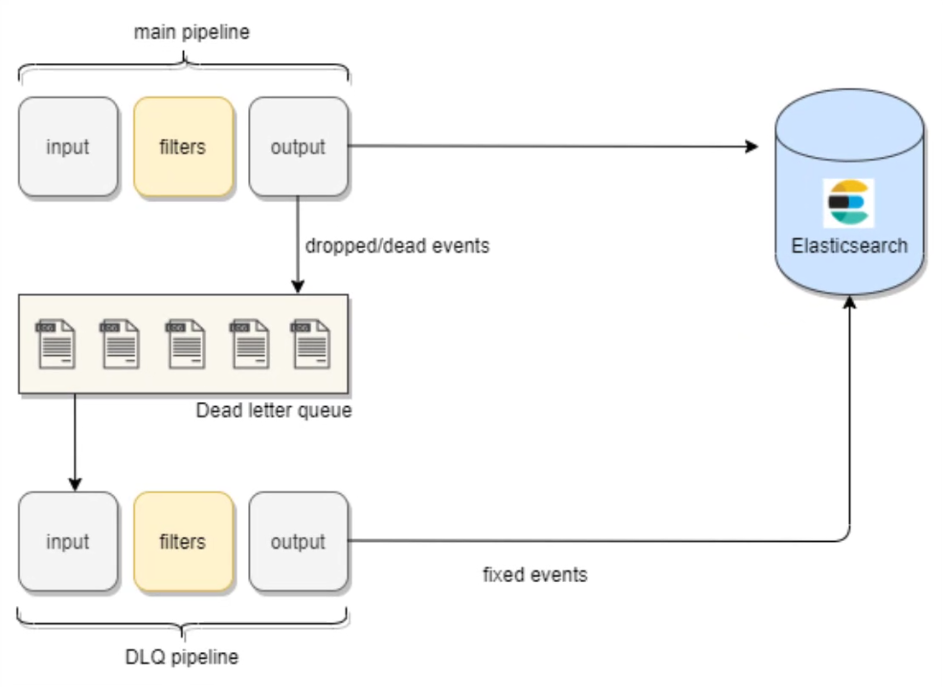
This lab focuses on testing input plugins in Logstash and integrating them with Elasticsearch for log processing and data visualization.
Lab Environment
| Node | Hostname | IP Address |
|---|---|---|
| Node 1 | elasticsearch | 192.168.56.101 |
| Node 2 | logstash | 192.168.56.102 |
Setup details:
-
The nodes are created in VirtualBox using Vagrant.
-
An SSH key is generated on the Elasticsearch node
-
The Logstash node can reach Elasticsearch node via port 9200
Pre-requisites
- Create the nodes in VirtualBox
- Install Elasticsearch on node 1
- Install Logstash on node 2
- Configure SSL on Elasticsearch
- Share Elasticsearch CA cert to Logstash
- Install jq on Elasticsearch node
Download the Sample Data
The sample dataset can be downloaded here: sample-data-dlq.json
{"age":39,"full_name":"Shelley Bangs","gender":"Female"}
{"age":32,"full_name":"Sally Penylton","gender":"Female"}
{"age":39,"full_name":"Janot Maxfield","gender":"Female"}
{"age":28,"full_name":"Isaak Taynton","gender":"Male"}
{"age":36,"full_name":"Pavel Braund","gender":"Male"}
{"age":43,"full_name":"Eleanore Seaton","gender":"Female"}
{"age":46,"full_name":"Ely Fullilove","gender":"Male"}
{"age":23,"full_name":"Deeann Moon","gender":"Female"}
{"age":27,"full_name":"Niels Milam","gender":"Male"}
{"age":23,"full_name":"Lorne Cuxson","gender":"Female"}
{"age":false,"full_name":"Robbyn Narrie","gender":"Female"}
{"age":true,"full_name":"Clyde Marney","gender":"Male"}
{"age":false,"full_name":"Frankie Semble","gender":"Male"}
{"age":true,"full_name":"Aggy Reditt","gender":"Female"}
{"age":true,"full_name":"Fionna Dozdill","gender":"Female"}
{"age":true,"full_name":"Erroll Hallut","gender":"Male"}
{"age":true,"full_name":"Gayle Terrell","gender":"Female"}
{"age":true,"full_name":"Lucita Garthside","gender":"Female"}
The age field is correctly set as an integer for the first 10 documents. However, from the 11th record onwards, the age field contains boolean values. Logstash will assign the long integer type to the age field and accept it for the first 10 documents, but since a field can only contain one data type, it will reject any documents where the age is a boolean after it has already been set to integer type. Therefore, Logstash will accept the first 10 documents but reject the ones that follow.
Enable the DLQ
First, create the directory which will store all the failed messages stored by the dead letter queue.
mkdir /tmp/dead_letter_queue
Change the ownership to the Logstash user.
sudo chown -R logstash:logstash /tmp/dead_letter_queue
Next, enable the setting in the Logstash configuration file.
sudo vi /etc/logstash/logstash.yml
Set to true, then set the path of the DLQ directory:
dead_letter_queue.enable: true
path.dead_letter_queue: /tmp/dead_letter_queue
Using the Plugin
Consider the sample plugin-dlq.conf below. This configuration uses the Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) plugin to process failed events stored in the specified directory and sends them to Elasticsearch.
Make sure to change the path to the path of the sample dataset.
input {
file {
start_position => "beginning"
path => "/mnt/fileshare/datasets/sample-data-dlq.json"
sincedb_path => "/dev/null"
}
}
filter {
json {
source => "message"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200"] ## address of elasticsearch node
index => "dlq-1"
user => "elastic"
password => "enter-password-here"
ssl => true
ssl_certificate_authorities => "/usr/share/ca-certificates/elastic-ca.crt" ## Shared Elasticsearch CA certificate path
}
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
Run the configuration using Logstash. We need to add the path.settings parameter to instruct Logstash to use the logstash.yml stored in the specified directory.
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash \
--path.settings /etc/logstash \
-f /etc/logstash/conf.d/plugin-dlq.conf
Store the Elasticsearch endpoint and credentials in variables:
ELASTIC_ENDPOINT="https://your-elasticsearch-endpoint"
ELASTIC_USER="your-username"
ELASTIC_PW="your-password"
To verify the indexed data in Elasticsearch:
curl -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW --insecure \
-X GET "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_cat/indices?v"
Output:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size dataset.size
yellow open generator QrAsivG1R9STC0Sz4rl_HQ 1 1 89126 0 5mb 5mb 5mb
yellow open dlq-1 nMAzva42Ti6FjaZqzswoHA 1 1 10 0 14.8kb 14.8kb 14.8kb
Next, let's inspect the indexed documents. The dataset contains 18 documents in total. However, some documents contain an incorrect age value, which causes Logstash to reject them. As a result, only 10 valid documents are successfully indexed into Elasticsearch.
curl -s -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-XGET $ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/dlq-1/_search?pretty=true -d'
{
"track_total_hits": "true",
"size": "0"
}' | jq
The rejected documents will be logged into the DLQ:
$ ls -la /tmp/dead_letter_queue/main/
total 36
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 4 12:05 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 logstash logstash 4096 Jan 4 11:51 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 24141 Jan 4 11:58 1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1 Jan 4 11:58 2.log.tmp
Reading the Queue
Logstash can also be configured to read from the dead letter queue (DLQ) by specifying the DLQ directory in the configuration file. Consider the plugin-dlq-read.conf example. Note that the DLQ data is imported into a separate index.
input {
dead_letter_queue {
path => "/tmp/dead_letter_queue"
# We can also add "commit_offsets => true" here if we want Logstash to continue
# where it left off, instead of re-processing all events in DLQ at subsequent runs
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200"] ## address of elasticsearch node
index => "dlq-2"
user => "elastic"
password => "enter-password-here"
ssl => true
ssl_certificate_authorities => "/usr/share/ca-certificates/elastic-ca.crt" ## Shared Elasticsearch CA certificate path
}
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
Run the configuration using Logstash.
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash \
--path.settings /etc/logstash \
-f /etc/logstash/conf.d/plugin-dlq-read.conf
As always, verify the indexed data in Elasticsearch:
curl -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW --insecure \
-X GET "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_cat/indices?v"
Output:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size dataset.size
yellow open generator QrAsivG1R9STC0Sz4rl_HQ 1 1 89126 0 5mb 5mb 5mb
yellow open dlq-2 HWiWQUtLQD-GDPM7-CeK8A 1 1 8 0 23.9kb 23.9kb 23.9kb
yellow open dlq-1 nMAzva42Ti6FjaZqzswoHA 1 1 10 0 14.9kb 14.9kb 14.9kb
Check the indexed data:
curl -s -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-XGET $ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/dlq-2/_search?pretty=true -d'
{
"size": 1
}' | jq
Output:
{
"took": 3,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 8,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "dlq-2",
"_id": "xyQ6MZQBoqYOKoM-_X02",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"@version": "1",
"age": false,
"@timestamp": "2025-01-04T11:58:36.900014493Z",
"log": {
"file": {
"path": "/mnt/fileshare/datasets/sample-data-dlq.json"
}
},
"event": {
"original": "{\"age\":false,\"full_name\":\"Robbyn Narrie\",\"gender\":\"Female\"}"
},
"host": {
"name": "node2"
},
"full_name": "Robbyn Narrie",
"message": "{\"age\":false,\"full_name\":\"Robbyn Narrie\",\"gender\":\"Female\"}",
"gender": "Female"
}
}
]
}
When Logstash reads the dead letter queue, it does not clear the contents of the queue by default. To prevent documents that have already been read from being indexed again, you can specify the commit_offsets => true in the configuration file.
input {
dead_letter_queue {
path => "/tmp/dead_letter_queue"
commit_offsets => true
}
}
Cleanup
Use the command below to delete the indices after the lab. Make sure to replace enter-name with the index name.
curl -s -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-XDELETE "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/enter-name" | jq