Securing the Docker Daemon
Docker Service Configurations
Docker operations can be managed with Systemctl commands:
systemctl start docker
systemctl status docker
systemctl stop docker
Docker can also be started as a foreground process using the command below. This can be used when the dockerd is not starting in the normal way and you need to troubleshoot it.
dockerd
To print more details, we can add the --debug flag.
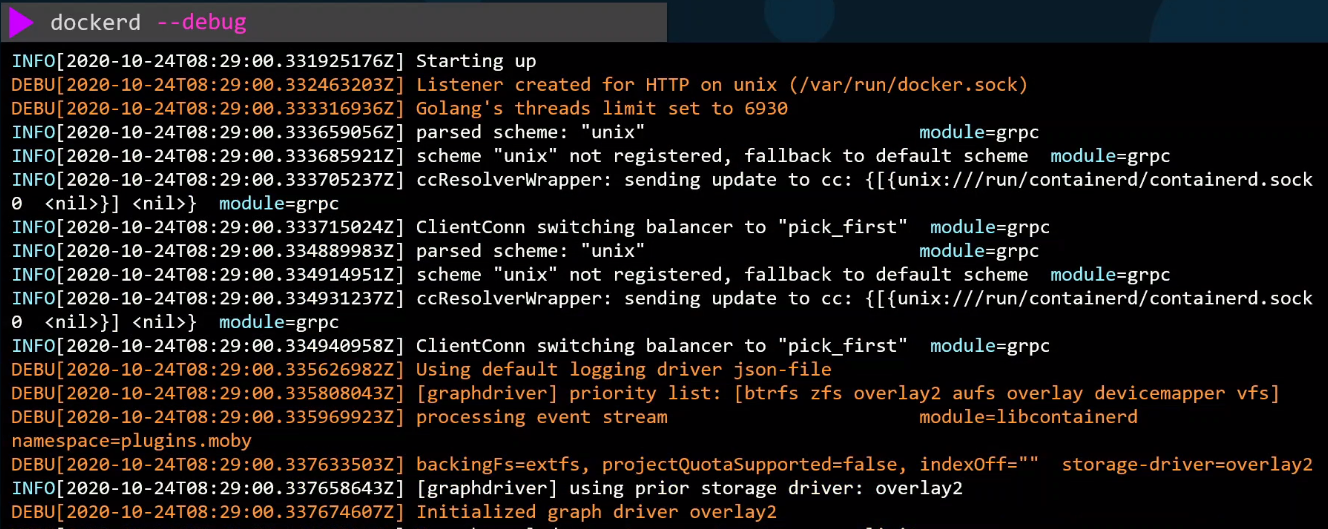
Unix Socket
The Docker daemon listens on an internal Unix socket at /var/run/docker.sock, allowing local access. The Docker CLI interacts with this socket.
TCP Socket
To allow external hosts to connect to the Docker daemon, use the --host flag and set the IP and port:
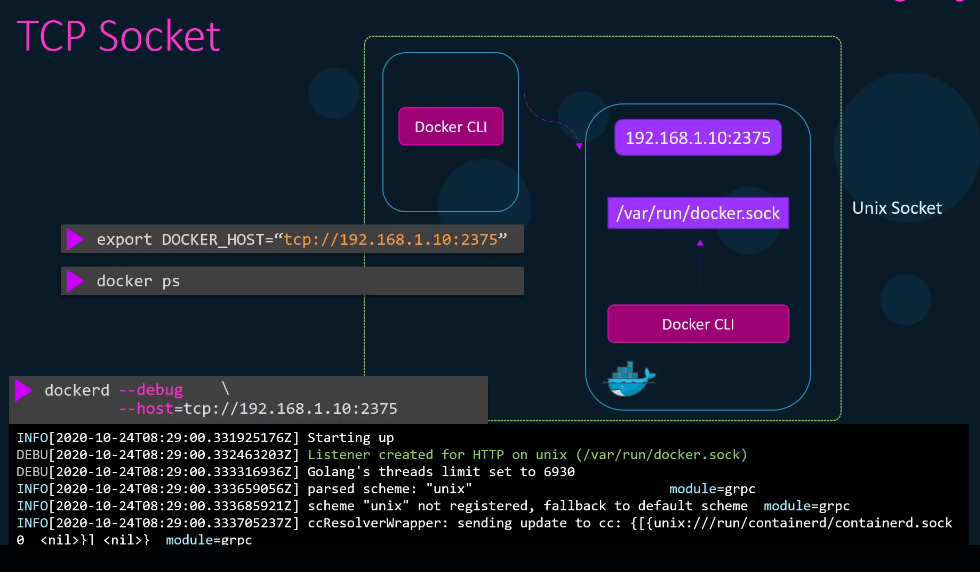
Before the other host can communicate to the Docker daemon in the first host, it must first set the variable for IP and port.
export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://192.168.1.10:2375" ## Set IP and port here
TLS Authentication
For encrypted connections, use the following command:
dockerd \
--debug \
--tls=true \
--tlscacert=/path/to/ca.pem \
--tlscert=/path/to/server-cert.pem \
--tlskey=/path/to/server-key.pem \
--host=tcp://192.168.1.10:2376
Ports:
- 2375 - Unencrypted
- 2376 - Encrypted
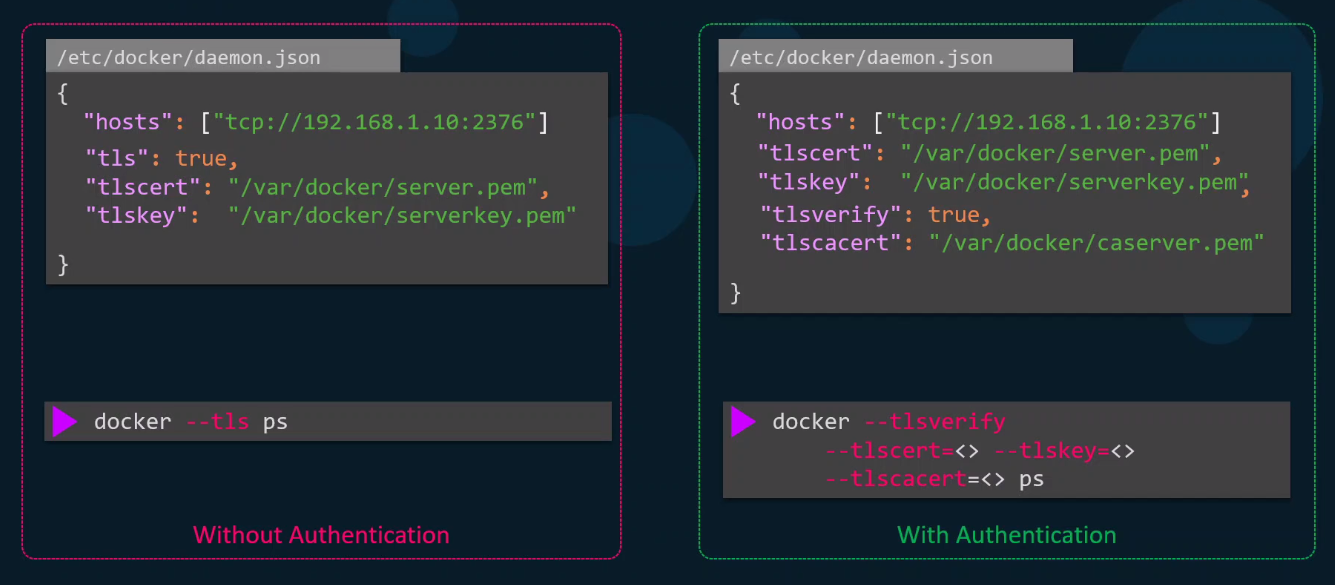
These settings can also be configured in /etc/docker/daemon.json:
{
"tlsverify": true,
"tlscacert": "/path/to/ca.pem",
"tlscert": "/path/to/server-cert.pem",
"tlskey": "/path/to/server-key.pem",
"hosts": ["tcp://0.0.0.0:2376"]
}
On the client hosts that need to access the Docker daemon in the central host, specify the variables:
export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://192.168.1.10:2376"
export DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY=true
Ensure that the keys and certificates are also in the client hosts.
tls versus tlsverify
The tls flag enables encryption, while tlsverify adds authentication.
Secure Docker Server
To secure the Docker Daemon:
- Disable password-based authentication
- Enable SSH key-based authentication
- Define user access
Encrypt Docker Daemon Data at Rest
To secure data on disk:
-
Use Docker’s encrypted volumes (e.g.,
overlay2). -
Encrypt underlying file system using OS-level tools (e.g.,
dm-crypt).