Kubelet Security
The Kubelet
The kubelet is a vital Kubernetes component responsible for managing and monitoring individual nodes in a cluster.
- Starts, stops, and maintains application containers.
- Runs readiness and liveness probes to check container health.
- Registers the node with the control plane.
- Handles volume mounting/unmounting for Pods.
- Reports node and pod statuses to the API server.
Viewing Kubelet Options
To inspect kubelet options, find its configuration file:
ps -aux | grep kubelet
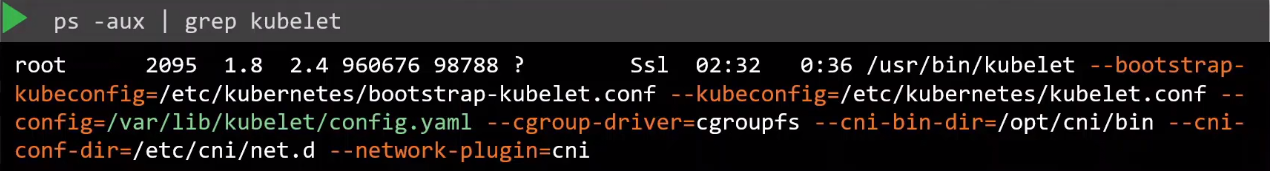
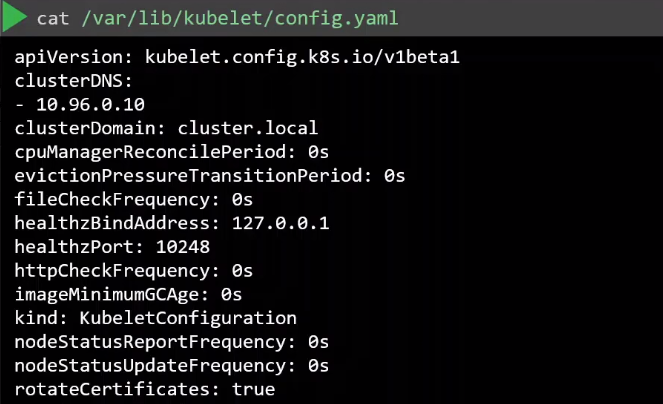
Once located, review the options in the file.
Ports used by kubelet
The kubelet listens on two ports, which pose a security risk if exposed. Authentication and authorization mechanisms help secure access.

Disable Anonymous Authentication
Anonymous access allows unauthenticated users to list pod details. Disable it by setting --anonymous-auth=false in the kubelet configuration:
## kubelet.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kubelet
Documentation=https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/#kubelet
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kubelet \
--config=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf \
--container-runtime=docker \
--kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.kubeconfig \
--fail-swap-on=false \
--cgroup-driver=cgroupfs \
--network-plugin=cni \
--pod-manifest-path=/etc/kubernetes/manifests \
--allow-privileged=true \
--anonymous-auth=false
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
This parameter can also be set in the kubelet config file.
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
Authentication Mechanisms
Certificate (x509)
Configure the kubelet to use TLS certificates for secure communication with the API server. Specify the CA file in the kubelet service file and ensure certificates are valid and up-to-date.
## kubelet.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kubelet
Documentation=https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/#kubelet
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kubelet \
. . .
--anonymous-auth=false \
--client-ca-file=/path/to/ca.crt
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Similary, it can be specified in the kubelet config file.
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
x509:
clientCAFile: /path/to/ca.crt
Once you have the certificates, we can pass this to the curl command:
curl -sk https://localhost:10250/pods/ \
--key kubelet-key.pem \
--cert kubelet-cert.pem
When the kube-apiserver tries to communicate to kubelet, the kube-apiserver also has to authenticate to the kubelet. This means that the kube-apiserver needs to have kubelet client cert and key.
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes API Server
Documentation=https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/command-line-tools-reference/kube-apiserver/
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kube-apiserver \
. . .
--kubelet-client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.crt \
--kubelet-client-key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.key \
--kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname \
API Bearer Tokens
Bearer tokens authenticate kubelets to the API server via the "Authorization" header in HTTP requests.
- Tokens are sent in this format:
Authorization: Bearer <token>. - The API server verifies the token.
- Valid tokens allow the operation; invalid ones are denied.
Below is a simplified example of how a Bearer Token might be used in a kubelet configuration:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Config
clusters:
- name: my-cluster
cluster:
server: https://api-server-address
users:
- name: kubelet-user
user:
token: <bearer-token-here>
contexts:
- name: my-context
context:
cluster: my-cluster
user: kubelet-user
current-context: my-context
Authorization Mechanisms
Once the user gains access to the system, authorization defines what resources the user can interact with.
AlwaysAllow
This is the default authorization mode and will always allow all requests to the API.
## kubelet.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kubelet
Documentation=https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/#kubelet
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kubelet \
. . .
--anonymous-auth=false \
--client-ca-file=/path/to/ca.crt
--authorization-mode=AlwaysAllow
kubelet config file:
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
x509:
clientCAFile: /path/to/ca.crt
mode: AlwaysAllow
Webhook
When set to Webhook, the kubelet first makes a call to the API server to determine is the request should be granted or not.
## kubelet.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kubelet
Documentation=https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/#kubelet
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kubelet \
. . .
--anonymous-auth=false \
--client-ca-file=/path/to/ca.crt
--authorization-mode=Webhook
kubelet config file:
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
x509:
clientCAFile: /path/to/ca.crt
mode: Webhook
Read-only Metrics API
The metrics API allows read-only access which doesn't need any authentication or authorization.
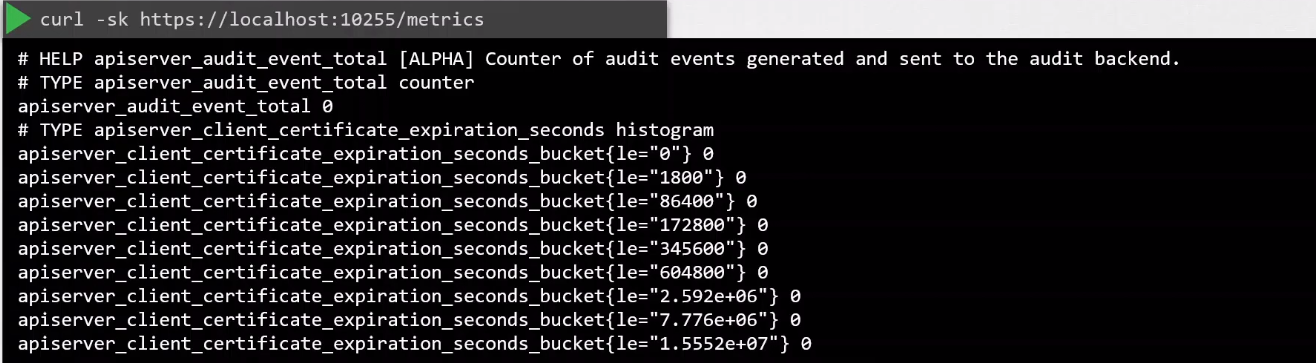
This is enabled when the read-only-port flag is set to non-zero number in the kubelet service file.
## kubelet.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kubelet
Documentation=https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/#kubelet
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kubelet \
. . .
--anonymous-auth=false \
--client-ca-file=/path/to/ca.crt
--authorization-mode=Webhook
--read-only-port=10255 ## If set to zero, metrics is disabled