Security Primitives
Updated Mar 11, 2022 ·
Secure Hosts
Hosts or nodes in the cluster are the first line of defense and need to be secured by:
- Disabling root access
- Disabling password-based authentication
- Enabling SSH key-based authentication
API Server
The API server controls all operations in Kubernetes. To secure access, two questions need to be addressed:

Who can access?
This is managed by authentication mechanisms, including:
- Basic authentication
- Bearer tokens
- x509 certificates
- Service accounts
- External providers (e.g., LDAP, OpenID Connect)
What can they do?
Authorization mechanisms define what actions users can take, such as:
- RBAC
- ABAC
- Node Authorization
- Webhook Mode
For more information, please see Authentication and Authorization
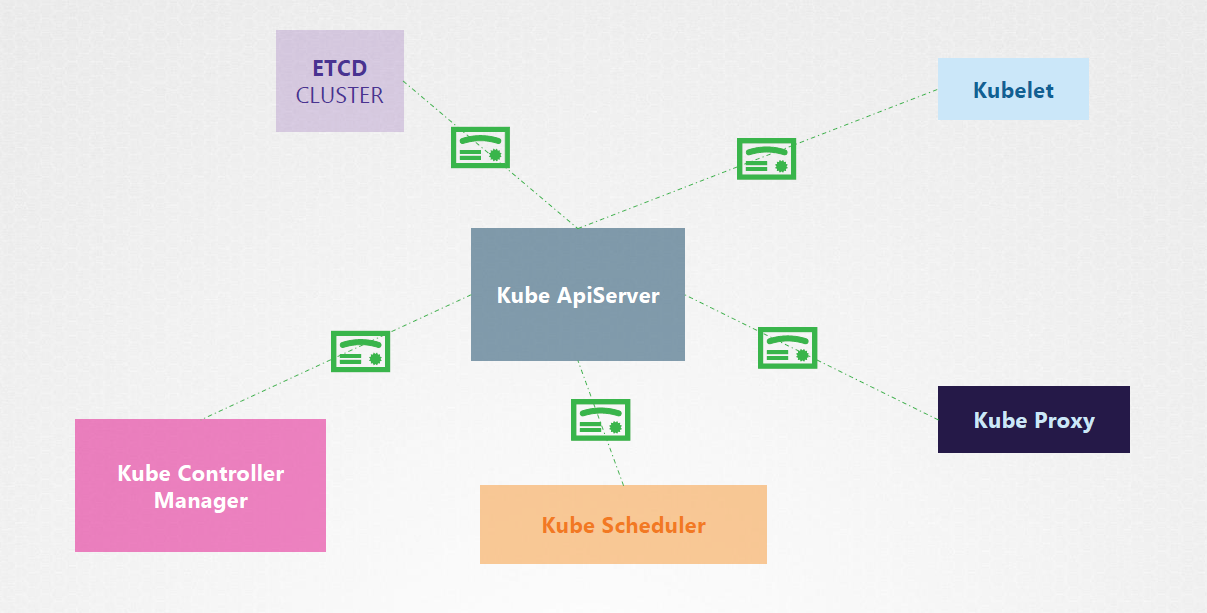
TLS Certificates
Cluster communication is secured with TLS encryption, protecting:
- etcd
- Kubecontroller Manager
- Scheduler
- API Server
For more information, please see TLS Certificates.
Network Policies
By default, applications can communicate within the cluster, but network policies can be used to restrict this access.