Kubernetes Ingress
Ingress vs. Service
Ingress and Service are essential Kubernetes concepts, but they address different networking needs and operate at distinct layers.
Service
A Service exposes a set of pods as a network service for stable communication.
- Internal communication within the cluster.
- Provides a stable IP and DNS for service discovery.
Types:
- ClusterIP: Internal access within the cluster.
- NodePort: External access via a fixed port on each node.
- LoadBalancer: External access via a cloud load balancer.
- ExternalName: Maps to an external DNS name.
Sample Service Manifest:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: MyApp
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
Ingress
An Ingress in Kubernetes is used for external access to services within the cluster.
- For external access to services within the cluster.
- Routes external traffic to different services based on rules.
- Operates at Layer 7, supporting HTTP and HTTPS.
- Used for exposing applications to the external world.
Sample manifest:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: myapp.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /app
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: my-service
port:
number: 80
Ingress Controller
An Ingress Controller implements Ingress specifications to manage external access.
- Not included by default in Kubernetes.
- Traffic routing among pods or nodes.
- SSL/TLS termination.
- Examples: NGINX, Traefik, HAProxy.
Deploying NGINX Ingress Controller:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-ingress-controller
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-ingress-controller
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:latest
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
In addition to this, you will need to deploy the Service for the NGINX Ingress Controller:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
- name: https
port: 443
targetPort: 443
selector:
app: nginx-ingress-controller
If you've worked with NGINX before, you'll know that it also uses a set of configuration options. This can be deployed separately on a ConfigMap:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-configuration
namespace: ingress-nginx
data:
proxy-connect-timeout: "5"
proxy-send-timeout: "600"
proxy-read-timeout: "600"
use-proxy-protocol: "false"
Deploy:
kubectl apply -f ingress-controller.yaml
kubectl apply -f ingress-service.yaml
kubectl apply -f nginx-configmap.yaml
Ingress Resource
An Ingress resource in Kubernetes defines how external HTTP/HTTPS traffic is routed to services.
- Routes traffic based on hostnames, paths, or HTTP attributes.
- Specifies backend services for traffic.
- Supports TLS for SSL/TLS termination.
- Aannotations for additional Ingress Controller configurations.
Sample manifest:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: myapp.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /app
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: my-service
port:
number: 80
tls:
- hosts:
- myapp.example.com
secretName: my-tls-secret
Ingress Resource: The Imperative Way
Starting Kubernetes version 1.20, we can create an Ingress resource from the imperative way like this:
kubectl create ingress <ingress-name> --rule="host/path=service:port"
kubectl create ingress ingress-test --rule="wear.my-online-store.com/wear*=wear-service:80"
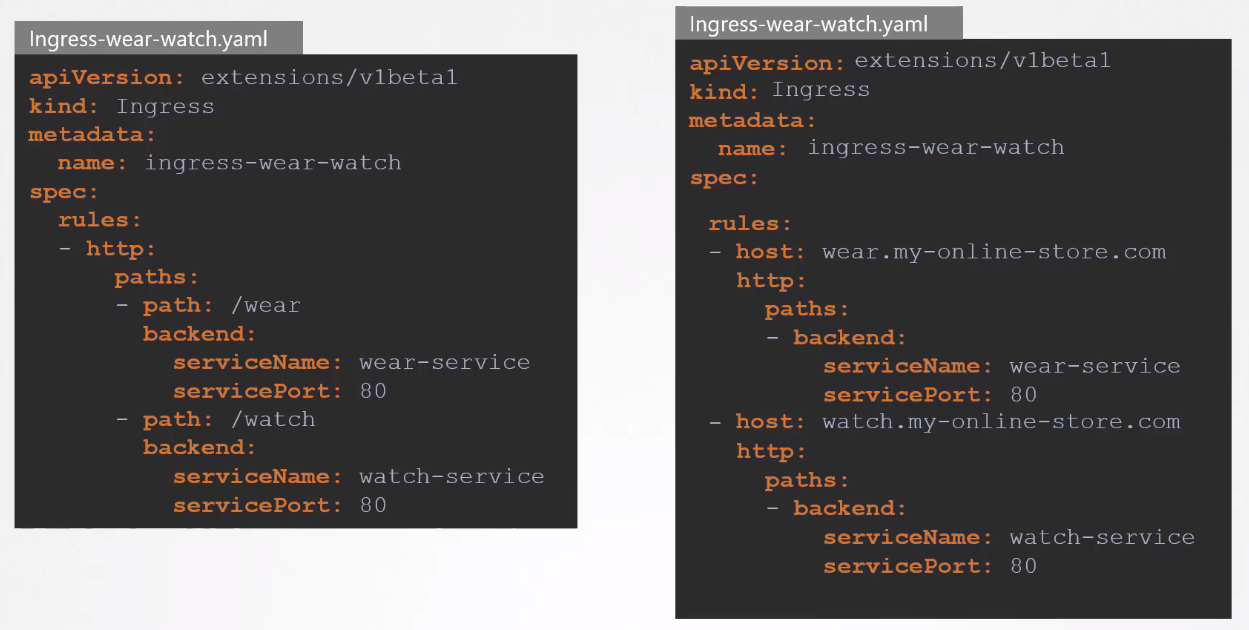
Splitting Traffic
Ingress can split traffic based on URLs or prefixes.
Annotations and rewrite-target
Annotations provide custom configurations. For example, NGINX annotations allow URL rewrites:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2
name: rewrite
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: rewrite.bar.com
http:
paths:
- path: /something(/|$)(.*)
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: http-svc
port:
number: 80
In this ingress definition, any characters captured by (.*) will be assigned to the placeholder $2, which is then used as a parameter in the rewrite-target annotation.
For example, the ingress definition above will result in the following rewrites:
- rewrite.bar.com/something rewrites to rewrite.bar.com/
- rewrite.bar.com/something/ rewrites to rewrite.bar.com/
- rewrite.bar.com/something/new rewrites to rewrite.bar.com/new
For more information, please see Rewrite.