TLS Basics
Overview
A TLS Certificate ensures trust between two parties by encrypting data during transmission. Data can be encrypted in two ways:
- Symmetric encryption - Same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the data
- Asymmetric encryption - Uses a private key and a public key
Encryption Keys
To generate SSH keys (asymmetric encryption) for SSH access:
ssh-keygen
For securing a website, generate a public and private keypair using the following commands:
openssl genrsa -out my-user.key 1024 # generates the private key
openssl rsa -in my-user.key -pubout > my-user.pem # generates the public key
Encryption Flow
- Generate both the public and private keys
- The server sends the public key to the client.
- The client's browser encrypts a symmetric key with the server's public key.
- The server uses its private key to decrypt the symmetric key.
- Both parties can now use the symmetric key for secure communication.
TLS Certificates
TLS certificates prevent attacks like MITM (Man-in-the-Middle). The certificate's legitimacy is confirmed by who signed it.
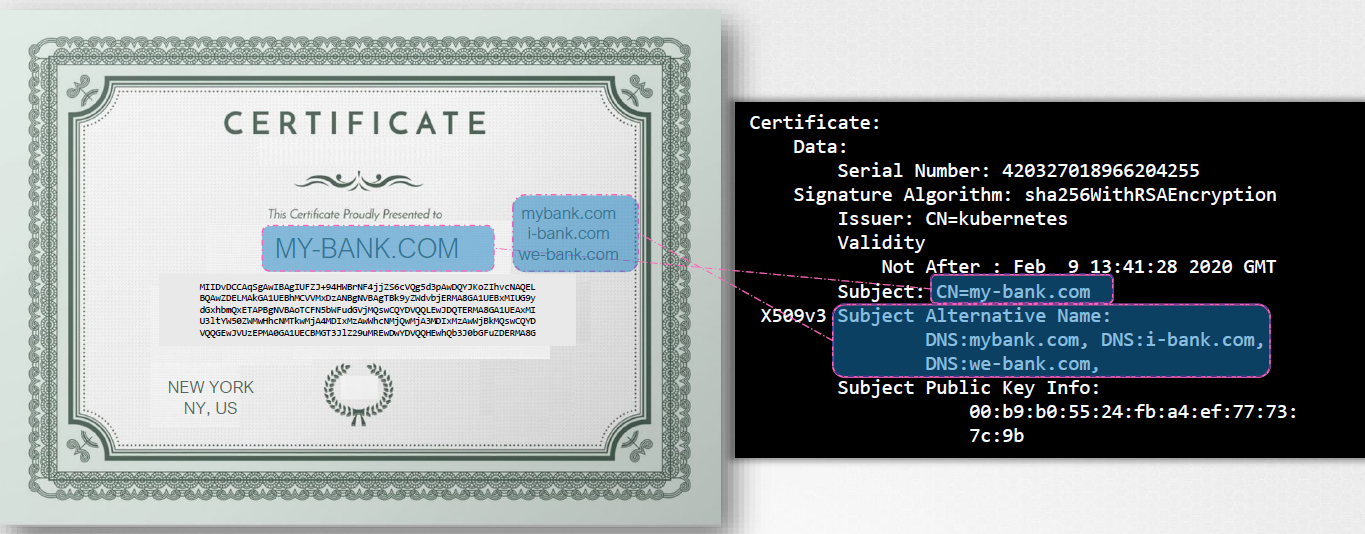
Creating a Signed Certificate
-
Generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) with your website details:
openssl req -new -key my-bank.key -out my-bank.csr -subj "/C=US/ST=CA/O=MyOrg,Inc./CN=my-bank.com" -
The Certificate Authority (CA) signs the certificate after verifying the details.
-
You now have a trusted certificate, signed by the CA, for secure communication.
Verifying CA Signatures
Public CAs use two keys: a private key to sign certificates and a public key to verify them. These public keys are included in browsers.
For internal use, private CAs like Symantec or open-source tools like EJBCA are available.
Client Certificates
While server trust is established, securing the client requires additional steps:
- The server requests a certificate from the client.
- The client generates a CSR, which the CA signs and returns.
- The client sends the signed certificate back to the server.
Note: Client certificates are rarely used manually by users and are often handled automatically by web servers.
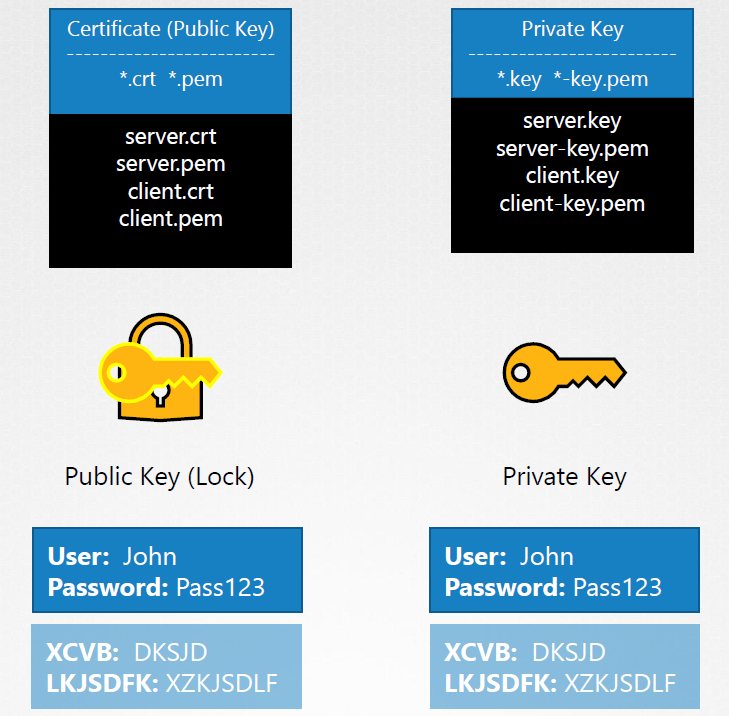
Key Naming Convention