Elasticsearch SQL
Overview
Elasticsearch SQL lets you query data in Elasticsearch using SQL syntax. You can run queries from the Elastic Cloud console or directly via the terminal.
If you're using Elastic Cloud, go to Management > DevTools, enter your SQL commands in the Console Editor, and click the Play button to see results.
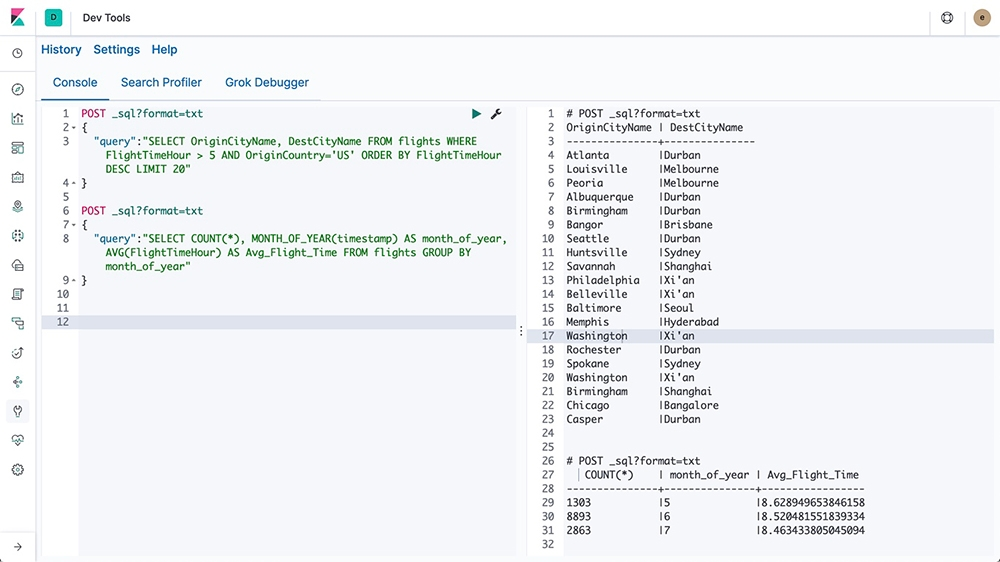
If you are using a self-managed Elasticsearch cluster, you can run SQL queries from the terminal using curl:
curl -XPOST https://add-your-endpoint-here/_xpack/sql?format=txt -d '
{
"query": "DESCRIBE index-name-here"
}'
How it Works
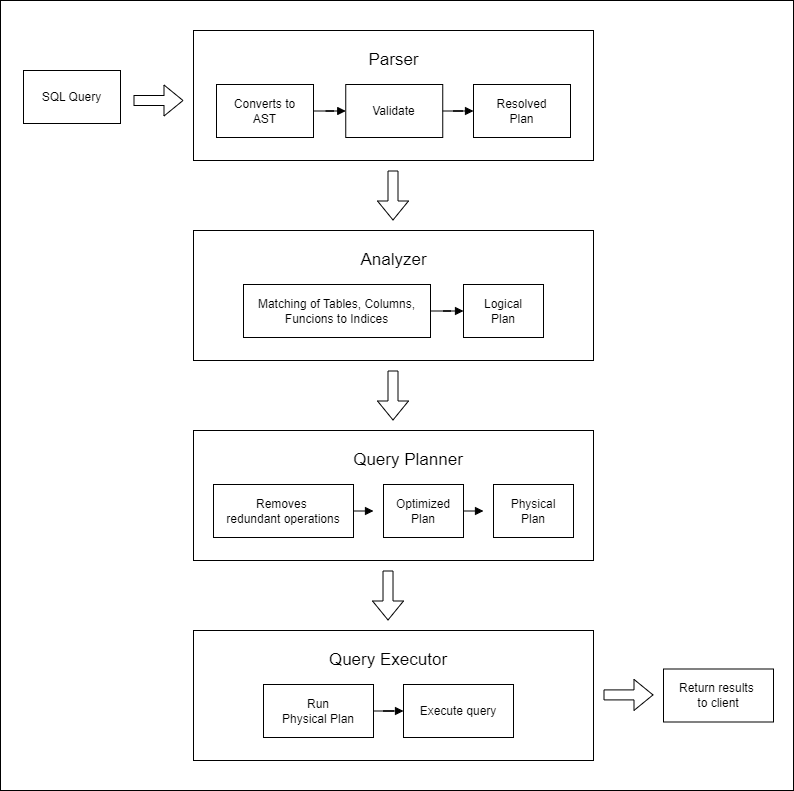
Elasticsearch SQL processes queries in several steps:
- Parser: Converts the SQL query into an internal abstract syntax tree (AST) and validates it.
- Analyzer: Matches tables, columns, and functions to the underlying indices and creates a logical execution plan.
- Query Planner: Optimizes the logical plan by removing redundant operations and generates a physical plan.
- Query Executor: Runs the physical plan to execute the query. Returns the query results to the client.
Here’s a diagram illustrating the Elasticsearch SQL query execution process:
Lab Environment
| Node | Hostname | IP Address |
|---|---|---|
| Node 1 | elasticsearch | 192.168.56.101 |
Setup details:
- The node is created in VirtualBox using Vagrant.
- An SSH key is generated on the Elasticsearch node
- The Logstash node can reach Elasticsearch node via port 9200
- The Logstash node needs to have internet access for this lab.
Pre-requisites
You can run a virtual machine in VirtualBox or use cloud-based compute instances.
- Create the nodes in VirtualBox
- Install Elasticsearch on node 1
- Configure SSL on Elasticsearch
- Install jq
Verify Connection
First, define your Elasticsearch endpoint and credentials:
ELASTIC_ENDPOINT="https://your-elasticsearch-endpoint:9200"
ELASTIC_USER="your-username"
ELASTIC_PW="your-password"
If running these commands on an Elasticsearch node, set the endpoint to https://127.0.0.1.
Run the following command to check connectivity:
curl -s -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW \
-XGET $ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200
Expected output:
{
"name" : "node1",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "UYlLyPlmRkGGSHGZQxUIhw",
"version" : {
"number" : "8.17.0",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "2b6a7fed44faa321997703718f07ee0420804b41",
"build_date" : "2024-12-11T12:08:05.663969764Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "9.12.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "7.17.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "7.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Import the Dataset
Download the dataset here: movies.json
Run the command below to create the movies index and import the dataset.
curl -s -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-XPUT $ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_bulk?pretty \
--data-binary @movies-2.json
Verify the index.
curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-XGET $ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_cat/indices?v
Using Self-Hosted Elasticsearch
To interact with Elasticsearch and run SQL-like queries, you can use the following cURL commands.
Example: Use this command to describe the movies index:
curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_sql" -d '
{
"query": "DESCRIBE movies"
}' | jq
Elasticsearch 7.0 and later replaced _xpack/sql with _sql:
Alternatively, you can try:
curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_sql" -d '
{
"query": "DESCRIBE movies"
}' | jq
Output:
{
"columns": [
{
"name": "column",
"type": "keyword"
},
{
"name": "type",
"type": "keyword"
},
{
"name": "mapping",
"type": "keyword"
}
],
"rows": [
[
"genre",
"VARCHAR",
"text"
],
[
"genre.keyword",
"VARCHAR",
"keyword"
],
[
"id",
"VARCHAR",
"text"
],
[
"id.keyword",
"VARCHAR",
"keyword"
],
[
"title",
"VARCHAR",
"text"
],
[
"title.keyword",
"VARCHAR",
"keyword"
],
[
"year",
"BIGINT",
"long"
]
]
}
You can also format the results for better readability:
curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_sql?format=txt" -d '
{
"query": "DESCRIBE movies"
}'
This will display the results in a table format, similar to SQL:
column | type | mapping
---------------+---------------+---------------
genre |VARCHAR |text
genre.keyword |VARCHAR |keyword
id |VARCHAR |text
id.keyword |VARCHAR |keyword
title |VARCHAR |text
title.keyword |VARCHAR |keyword
year |BIGINT |long
Other Example Queries
-
To get the first 10 movie titles from the
moviesindex.curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_sql?format=txt" -d '
{
"query": "SELECT title FROM movies LIMIT 10"
}'Output:
title
---------------------------
Toy Story
Jumanji
Grumpier Old Men
Waiting to Exhale
Father of the Bride Part II
Heat
Sabrina
Tom and Huck
Sudden Death
GoldenEye -
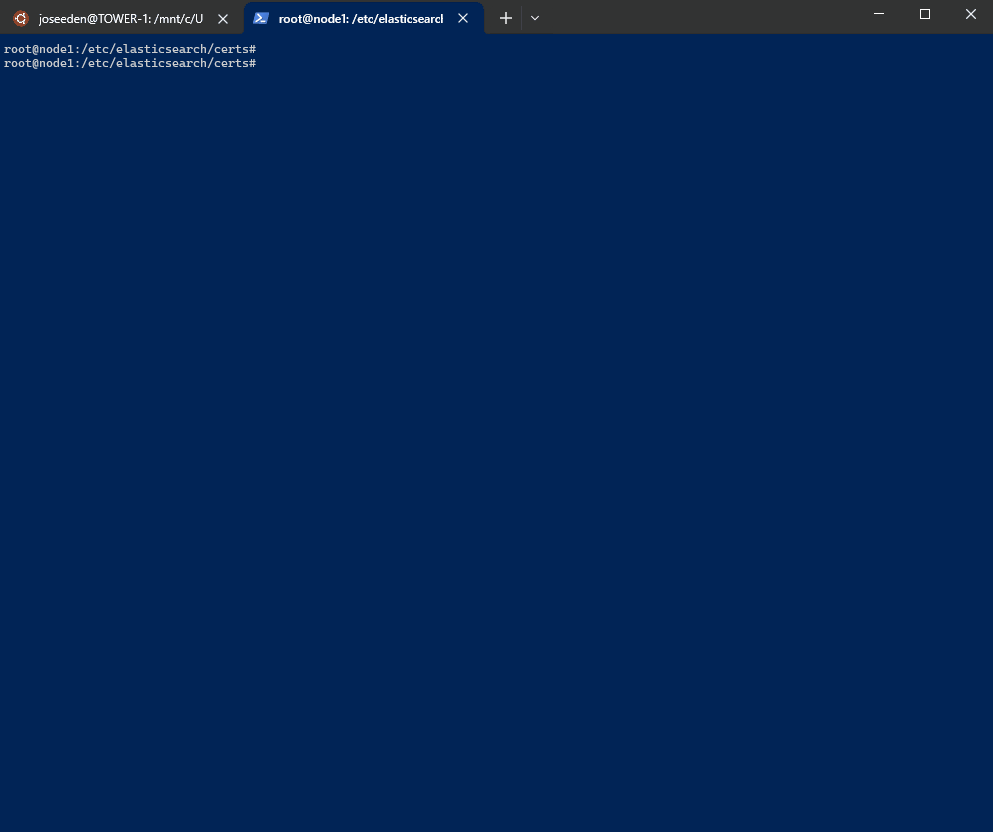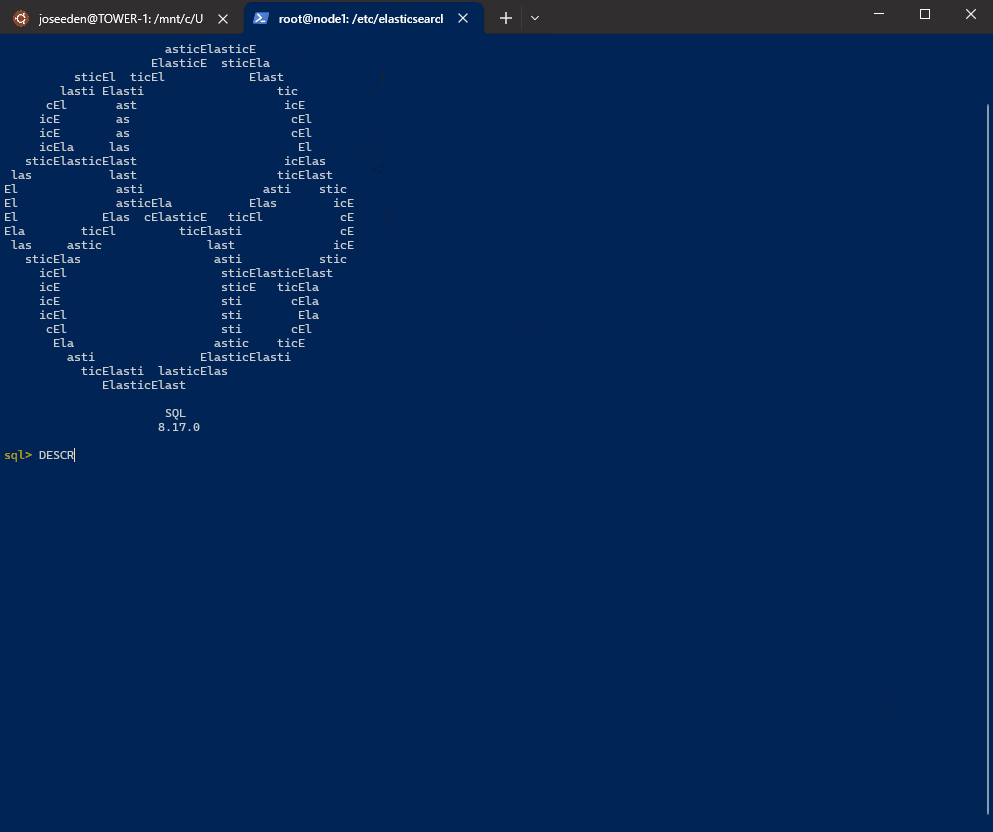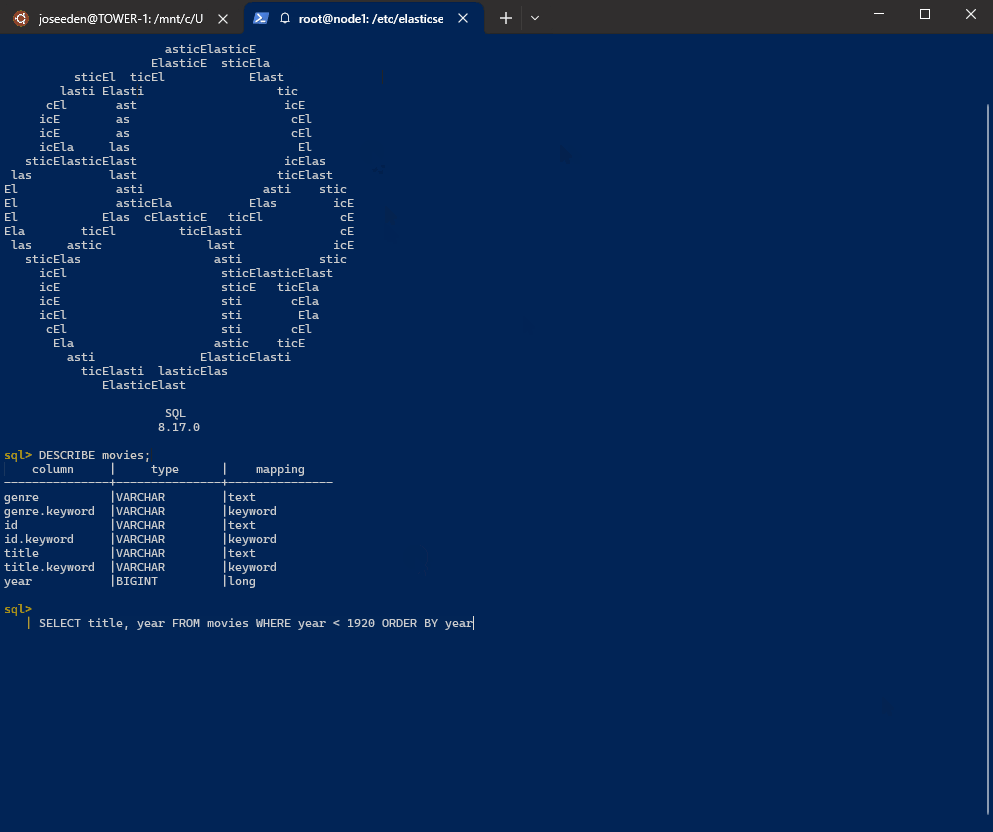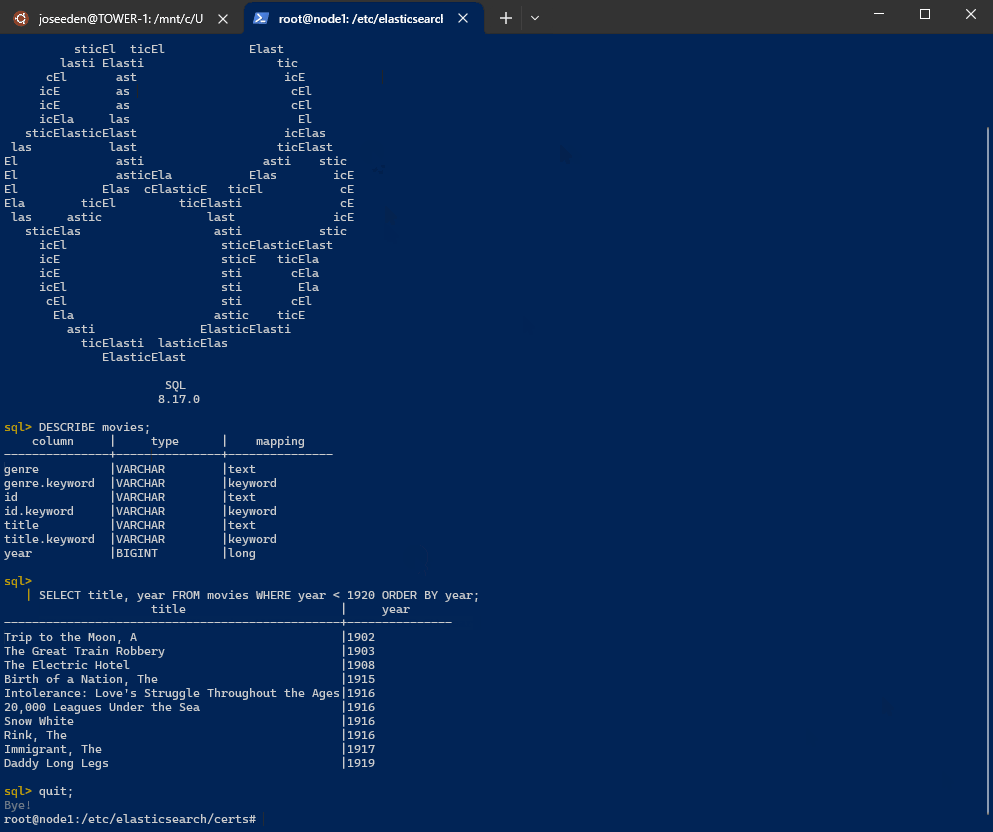
To retrieve the title and year for movies released before 1920, sorted by release year:
curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_sql?format=txt" -d '
{
"query": "SELECT title, year FROM movies WHERE year < 1920 ORDER BY year"
}'Output:
title | year
------------------------------------------------+---------------
Trip to the Moon, A |1902
The Great Train Robbery |1903
The Electric Hotel |1908
Birth of a Nation, The |1915
Intolerance: Love's Struggle Throughout the Ages|1916
20,000 Leagues Under the Sea |1916
Snow White |1916
Rink, The |1916
Immigrant, The |1917
Daddy Long Legs |1919
Using Elastic Cloud
You can also run SQL commands on indexes in Elastic Cloud. Same as before, set your variables first in a new terminal:
ELASTIC_ENDPOINT="https://your-elasticsearch-endpoint"
ELASTIC_USER="your-username"
ELASTIC_PW="your-password"
Next, ensure the movie dataset is imported:
curl -s -u $ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-XPUT $ELASTIC_ENDPOINT/_bulk?pretty \
--data-binary @movies-2.json
You can run the same SQL statements:
-
To describe the
moviesindex:curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT/_sql?format=txt" -d '
{
"query": "DESCRIBE movies"
}'Output:
column | type | mapping
---------------+---------------+---------------
genre |VARCHAR |text
genre.keyword |VARCHAR |keyword
id |VARCHAR |text
id.keyword |VARCHAR |keyword
title |VARCHAR |text
title.keyword |VARCHAR |keyword
year |BIGINT |long -
To get the first 10 movie titles in the
moviesindex:curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200/_sql?format=txt" -d '
{
"query": "SELECT title FROM movies LIMIT 10"
}'Output:
title
---------------------------
Toy Story
Jumanji
Grumpier Old Men
Waiting to Exhale
Father of the Bride Part II
Heat
Sabrina
Tom and Huck
Sudden Death
GoldenEye -
To get the title and year of movies released before 1920, sorted by release year:
curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT/_sql?format=txt" -d '
{
"query": "SELECT title, year FROM movies WHERE year < 1920 ORDER BY year"
}'Output:
title | year
------------------------------------------------+---------------
Trip to the Moon, A |1902
The Great Train Robbery |1903
The Electric Hotel |1908
Birth of a Nation, The |1915
Intolerance: Love's Struggle Throughout the Ages|1916
20,000 Leagues Under the Sea |1916
Snow White |1916
Rink, The |1916
Immigrant, The |1917
Daddy Long Legs |1919
Translate SQL to DSL
To view the DSL (the underlying JSON query), use this command. It works on both self-hosted Elasticsearch clusters and Elastic Cloud deployments. Just ensure you're using the correct endpoint URL.
curl -s -u "$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-XPOST "$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT/_sql/translate?pretty" -d '
{
"query": "SELECT title, year FROM movies WHERE year < 1920 ORDER BY year"
}'
Output:
{
"size" : 1000,
"query" : {
"range" : {
"year" : {
"lt" : 1920,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
},
"_source" : false,
"fields" : [
{
"field" : "title"
},
{
"field" : "year"
}
],
"sort" : [
{
"year" : {
"order" : "asc",
"missing" : "_last",
"unmapped_type" : "long"
}
}
],
"track_total_hits" : -1
}
Using the SQL Client
You can use the standalone SQL client for running SQL queries, which is similar to querying a database. However, note that this is only available on self-hosted Elasticsearch clusters, as you need access to the executable.
Same as before, set your variables first in a new terminal:
ELASTIC_ENDPOINT="https://your-elasticsearch-endpoint"
ELASTIC_USER="your-username"
ELASTIC_PW="your-password"
To run the SQL client:
sudo /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-sql-cli
If you're using HTTPS with a username and password, use this command. Provide the keystore password when prompted.
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-sql-cli \
https://$ELASTIC_USER:$ELASTIC_PW@$ELASTIC_ENDPOINT:9200 \
-k /etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.p12
Once the command runs, you’ll be in the SQL prompt:
asticElasticE
ElasticE sticEla
sticEl ticEl Elast
lasti Elasti tic
cEl ast icE
icE as cEl
icE as cEl
icEla las El
sticElasticElast icElas
las last ticElast
El asti asti stic
El asticEla Elas icE
El Elas cElasticE ticEl cE
Ela ticEl ticElasti cE
las astic last icE
sticElas asti stic
icEl sticElasticElast
icE sticE ticEla
icE sti cEla
icEl sti Ela
cEl sti cEl
Ela astic ticE
asti ElasticElasti
ticElasti lasticElas
ElasticElast
SQL
8.17.0
sql>
Running some sample queries: