Computer Vision
Overview
Computer vision aims to enable computers to see and interpret digital images, playing a crucial role in technologies like self-driving cars.
- Help computers understand digital images
- Essential for self-driving cars
- Used by manufacturers like Tesla, Volvo, Audi, and BMW
- Utilizes multiple cameras to detect objects, lane markings, and traffic signs
Image Data
Understanding how image data is structured is key to grasping how computer vision works. Below is an example of a grayscale and a colored image data and the pixels that makes up the each image.
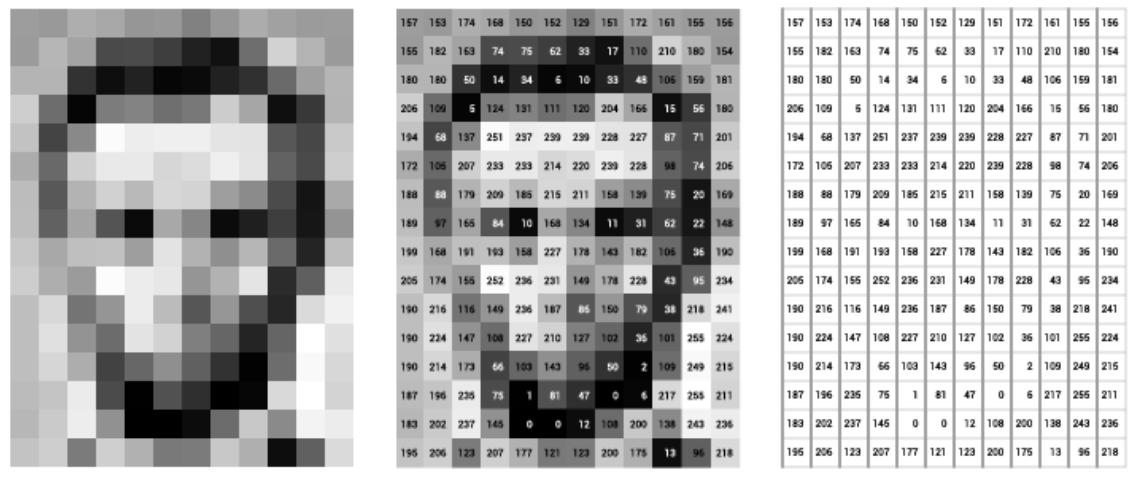
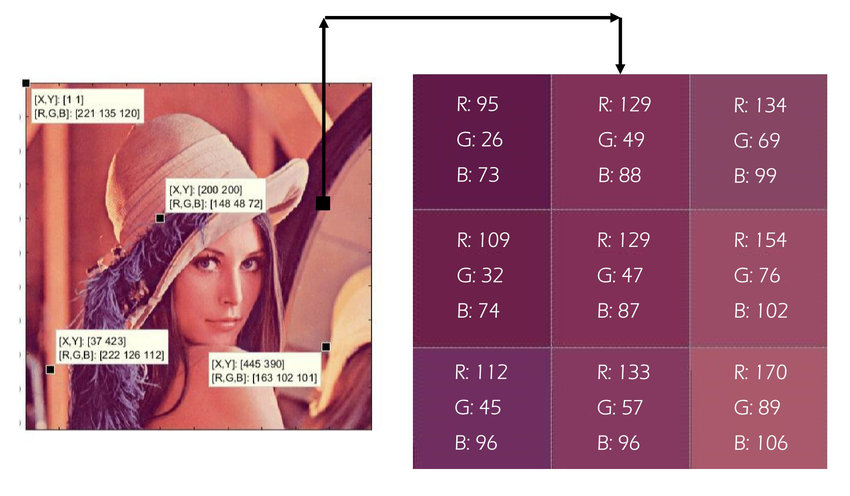
What an image data looks like:
- Images are made up of pixels containing color and intensity information
- Grayscale images have pixel intensities between 0 and 255
Similarly, we can have
- Colored images use the RGB system (Red, Green, Blue)
- Requires three rasters for each color channel
- Digital images can be represented as numerical data for machine learning models
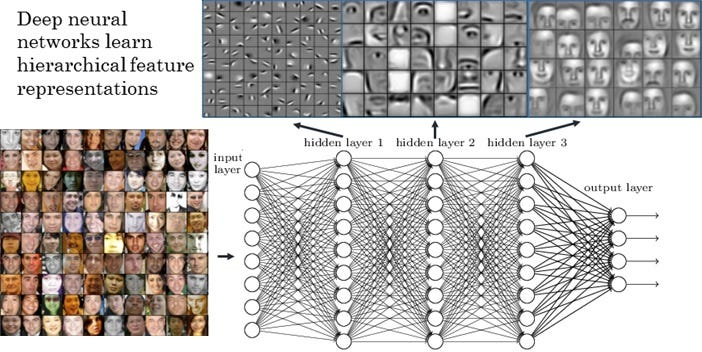
Face Recognition
Building a face recognition system involves processing images to identify individuals.
- Input: Pictures of people, such as instructors
- Neural network processes pixel intensities
- Early neurons detect edges
- Later neurons identify parts of objects (eyes, noses)
- Final neurons recognize face shapes
- Network outputs the identity of the person in the image
Diagram:
Another example is classifying image of vehicles as cars or trucks. The process will look like this:
- The car images are turned into numbers
- The pixel intensities are fed into the neural network
- Neurons will learn to detect edges
- Neurons will learn to distinguish more complex objects like wheels, doors, and windows
- Neurons will learn to detect shapes of vehicles
- Finally, the image will be classified as either a car or a truck
Training the Neural Network
Training involves feeding the network large amounts of labeled data to learn patterns.
- Provide images of faces (features) and corresponding identities (labels)
- Learning algorithm figures out neuron computations during training
- Middle layer neurons' functions are determined by the algorithm, reducing the need for manual intervention
Applications
Computer vision has a wide range of applications, from recognizing objects to generating realistic images.
- Facial Recognition: Identifies people from images
- Self-Driving Vehicles: Detects objects and navigates safely
- Medical Imaging: Automatically detects tumors in CT scans
- Image Generation: Creates realistic images, like deep fakes
- Deep fakes can generate new faces by understanding the structure of human faces