Natural Language Processing
Overview
Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows computers to understand human language, making it possible for them to identify and categorize entities in text.
-
NLP enables computers to locate and classify named entities
-
Sorted into categories such as names of persons and locations

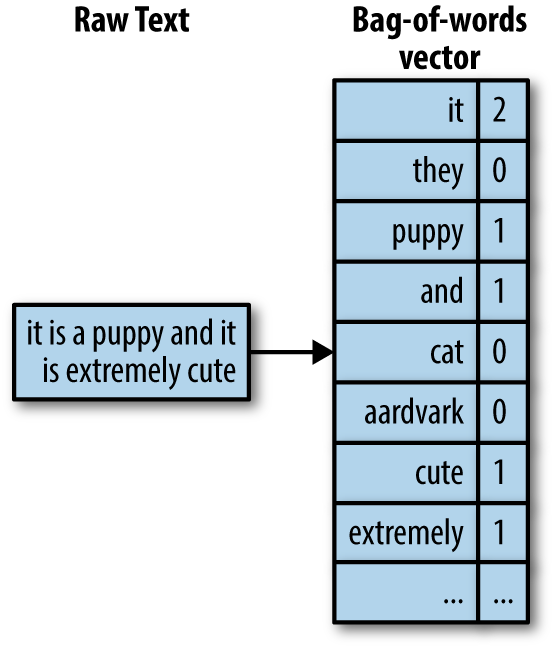
Bag of Words
When dealing with text data, we use different techniques to extract features for machine learning models.
- Text data can be represented by counting the frequency of important words
- This technique is known as the bag of words
To understand bag of words, consider analyzing sentences for word counts.
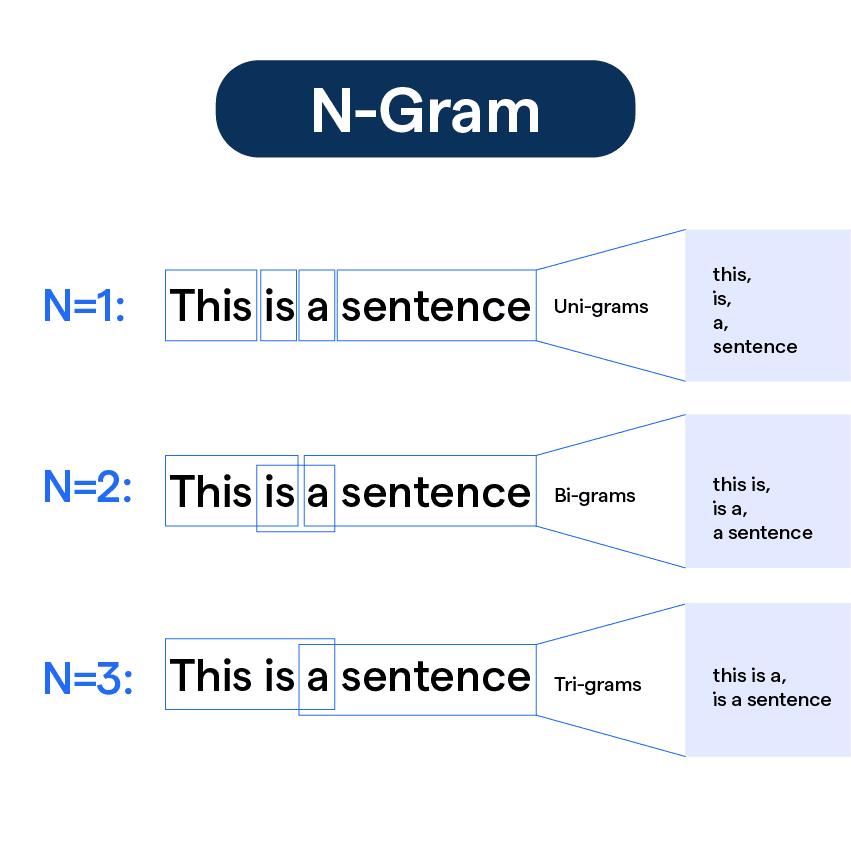
N-grams
N-grams improve the bag of words technique by considering sequences of words.
- Counting sequences of words helps capture more contextual information
- Example: Counting "This is" together instead of just "This"
Diagram:
Limitations
There are limitations to the bag of words approach, such as handling synonyms.
-
Word counts alone do not account for synonyms
-
Different words for "blue" like "navy-blue", "cobalt", "vivid cerulean" should ideally be grouped

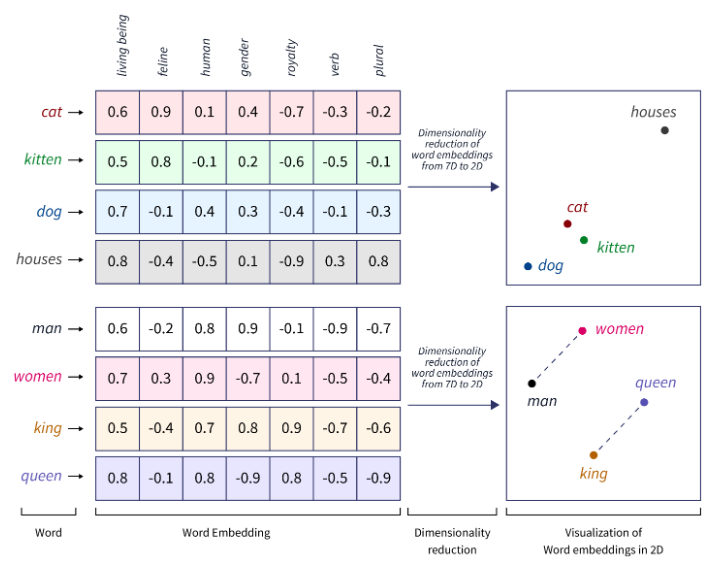
Word Embeddings
Word embeddings address some limitations of the bag of words by grouping similar words.
- Word embeddings create similar features for similar words
- Mathematical representations of words that follow intuitive rules
- Example: "King" - "man" + "woman" ≈ "Queen"
A more advanced example is using word embeddings together with dimensionality reduction.
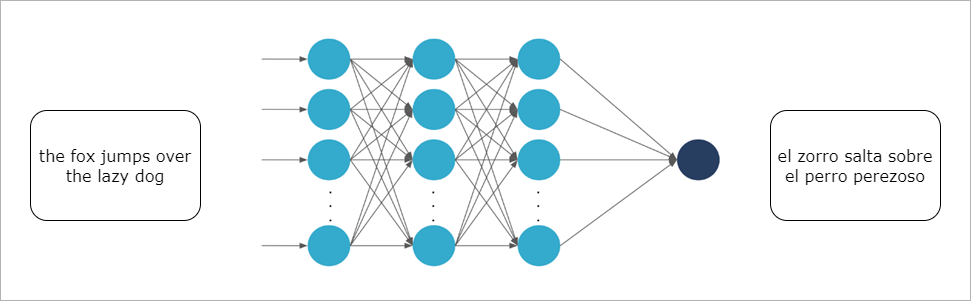
Language Translation
Mapping words or sentences to numbers allows neural networks to perform tasks like language translation.
-
Techniques like bag of words and word embeddings are used
-
Example: Translating from Spanish to English
Applications
NLP powers many common applications, making our interaction with technology more intuitive.
- Language translation apps (e.g., Google Translate)
- Chatbots for customer service
- Personal assistant apps (e.g., Siri, Alexa)
- Sentiment analysis to gauge emotions in text