Deep Learning
Overview
Deep learning uses neural networks inspired by the human brain. These networks learn patterns from data and solve complex problems.
- Neurons (nodes) process information and pass it forward
- Handles unstructured inputs like images, text, and audio
- Requires large amounts of data for training
Deep learning builds on classical machine learning to solve more advanced tasks, learning from data like a brain does.
Capabilities
Modern deep learning can do tasks that were once very difficult.
- Recognizes objects in images and videos
- Translates and summarizes text automatically
- Generates realistic conversations, images, and audio
These abilities make deep learning suitable for real-world, high-complexity problems.
Case Study: Box Office Revenue
Deep learning can be applied to real-world problems, like predicting the box office revenue of a movie based on various factors.
-
Simple Model Example
- Predict revenue from production budget
- Straight line shows relationship between budget and revenue
- Neural network uses budget as input to predict revenue
-
Adding More Data
- Include advertising spend, star power, and release timing
- Network becomes more complex and accurate
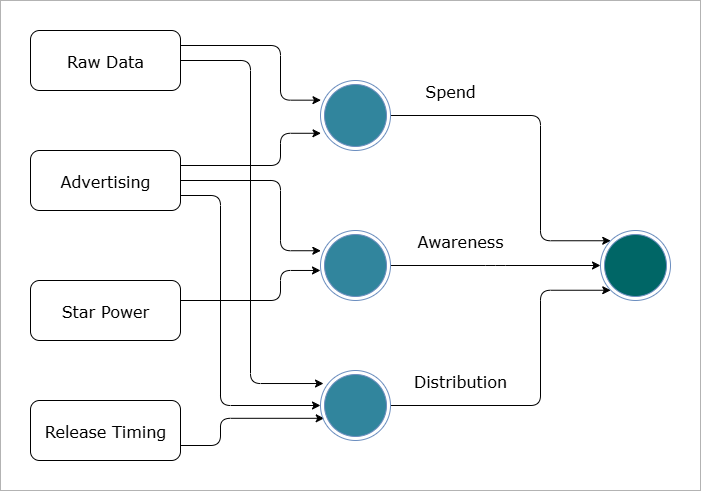
In a neural network, different neurons handle different aspects of the data.
- First Neuron: Estimates spend based on budget and advertising costs
- Second Neuron: Tracks awareness from advertising and star power
- Third Neuron: Considers distribution, timing, and combined factors
- Final Neuron: Takes outputs from previous neurons to estimate box office revenue
We can better understand this from the diagram below:
Training the Neural Network
Training a neural network involves feeding it data and allowing it to learn the relationships between different inputs and outputs.
- Input data is used to calculate relationships between neurons
- Network adjusts weights to improve predictions
- Accuracy increases with repeated testing and optimization
- Training allows the network to map inputs to outputs reliably.
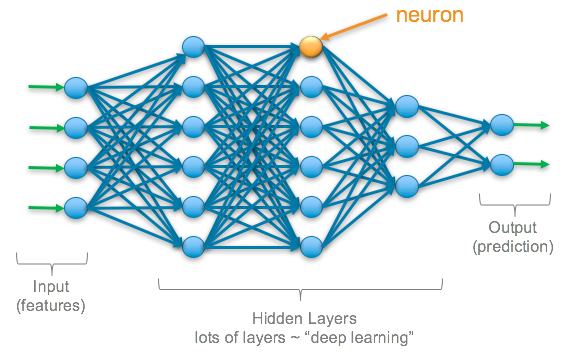
Deep Learning
Deep learning involves using much larger neural networks for computing very complex functions.
- Can contain thousands of neurons
- Stacked neurons compute very complex functions
- Provides accurate predictions for complicated tasks
 |
|---|
When to Use Deep Learning?
Deep learning is powerful but not always needed.
- Works best with large datasets
- Requires high-performance computing
- Finds features automatically when domain knowledge is limited
- Excels at computer vision, natural language processing, and other complex problems
Deep learning is most effective when the problem is complex, the data is large, and automated feature detection is valuable.