Automated Installations
Automated installations help streamline the deployment process by using predefined configurations, making it easier to manage and maintain multiple systems.
There are several solutions for performing automated installations:
- Vagrant is used for automatic deployment of virtual machines.
cloud-initand other templatees can be used in cloud environments.- Kickstart can be used with a PXE-boot server to provide instructions for automatic installation of RHEL.
A kickstart file contains all installation instructions to set up a RHEL instance. It can be used to easily reproduce installations.
Creating a Kickstart File
Kickstart files automate the installation of Red Hat-based systems by providing predefined answers to installation questions.
- AFter installation, a file
anaconda-ks.cfgis created on the root user home directory. - Edit this file manually to make any required changes.
The parameters used when booting the system can be found in the anaconda-ks.cfg file. Alternatively, you can use Red Hat's Kickstart Generator to create the kickstart configuration files.
To list existing kickstart files:
$ ll *.cfg
-rw-------. 1 root root 7194 May 4 2021 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-------. 1 root root 6940 May 4 2021 original-ks.cfg
ksvalidator
ksvalidator is a tool to check the syntax of your kickstart file. Note that it needs to be installed separately.
To install ksvalidator:
sudo yum install pykickstart -y
After installation, use the ksvalidator command followed by the kickstart file to validate it:
ksvalidator ./name-of-kickstart.cfg
Automatic Installations
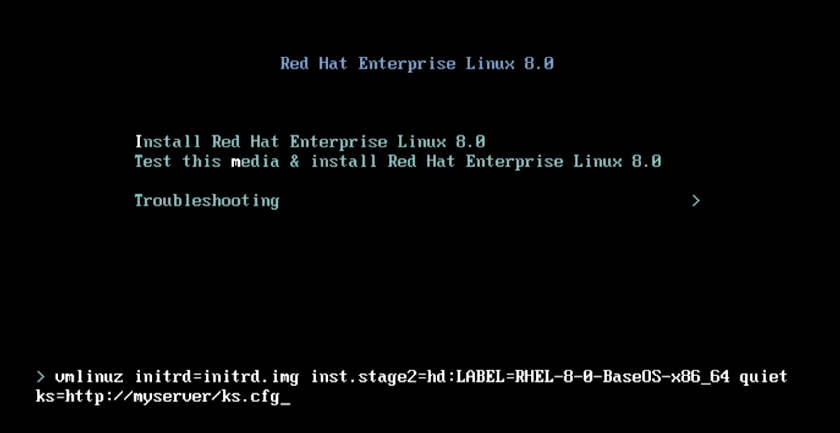
After modifying the kickstart file, you need to instruct the system to use it during the installation process. Beefore starting the installation, the client indicates where to get the Kickstart file from:
- Use `ks=http://location-of-the-file/ks.cfg
- You can also provide an interface from the installation program (via VM Manager),
During bootup, select the Install option and press the Tab key. This will prompt a command line at the bottom where you can provide the link to the kickstart file.
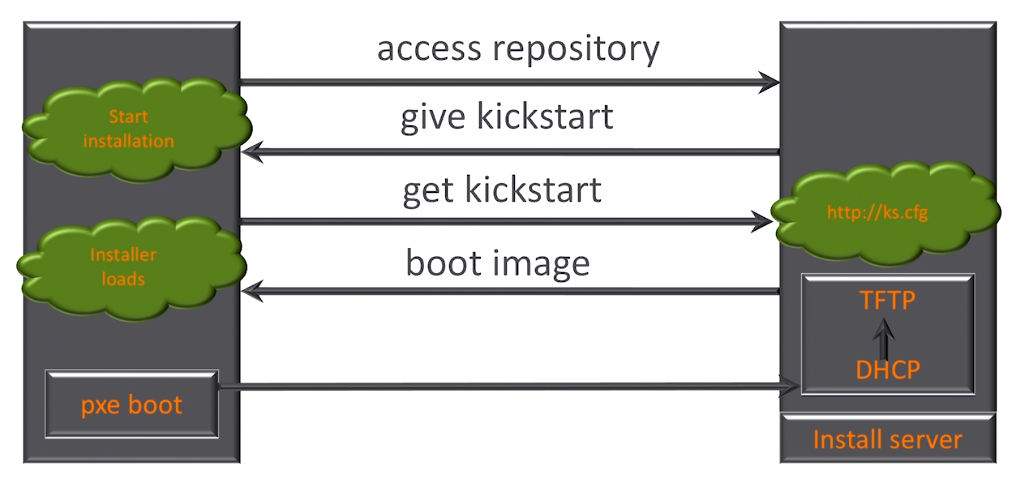
Fully Automated Datacenters
In a fully automated datacenter setup, an install-server hosts all the necessary files for automation and runs a DHCP server connected to a TFTP server.
The automated installation process involves:
- On the servers, initiate a pxeboot, prompting the server to reach out to the install-server-host.
- The host sends a boot image to the server.
- The server uses the boot image to load the configuration file and reaches out again to the host to get the kickstart file.
- The host sends the kickstart file, and the server begins the installation.
Using Vagrant to Set up VMs
Vagrant is a tool for building and managing virtual machine environments in a single workflow. It provides a simple way to create and configure lightweight, reproducible, and portable development environments.
- Vagrant works with a "box", which is a tar file that contains a VM image.
- Preconfigured boxes are available at vagrantcloud.com
- Administrators can also create their own boxes.
- Providers allow Vagrant to interface with the underlying host platform. Supported platforms: VirtualBox, VMware, Hyper-V, and KVM.
- Provisioners can be used to further configure a Vagrant-configured VM. Bash and Ansble are common provisioners.
- The Vagrantfile is a text file containinig the instructions for creating the Vagrant environment.
- Vagrant is not included in RHEL 8 and must be installed from EPEL.