Running VMs on RHEL
Running Virtual Machines on RHEL
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) provides a robust virtualization platform utilizing several tools that together create a powerful and flexible environment for running virtual machines. These tools include:
qemu
QEMU (Quick Emulator) is a hardware virtualization and emulation tool. It allows users to create and run virtual machines by emulating hardware components. QEMU is used for tasks requiring moderate performance, such as testing and development environments.
kvm
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a virtualization module in the Linux kernel that enables the kernel to function as a hypervisor. Unlike QEMU, KVM does not perform hardware emulation. Instead, it allows virtual machines to directly access the hardware of the host system, resulting in near-native performance. KVM is used in high-performance environments where efficient resource utilization is critical.
libvirt
Libvirt is a collection of software tools, including APIs and command-line utilities, designed to manage virtualized platforms. It provides a unified interface for managing various virtualization technologies, making it easier to create, modify, and monitor virtual machines.
OpenShift
Additionally, Red Hat offers OpenShift, a platform that integrates these tools to manage both virtual machines and containers. OpenShift is a commercially supported product that enhances the capabilities of the underlying virtualization technologies.
Not Installed by Default
In a standard RHEL installation, the virtualization clients are included, but the full virtualization platform is not installed by default.
Installation
To set up the required tools for virtualization, follow these steps:
First, install the necessary packages using the dnf package manager:
sudo dnf install -y qemu-kvm qemu-img libvirt virt-manager virt-install
After installation, you need to start the libvirt daemon (libvirtd), which will manage the QEMU and KVM processes. Enable the service to start at boot and start it immediately:
sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd
Check the status of the libvirtd service to ensure it is running correctly:
sudo systemctl status libvirtd
Graphical User Interface
RHEL provides two graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for managing virtual machines:
-
GNOME Boxes GNOME Boxes is a user-friendly interface for creating and managing virtual machines. It is designed for desktop users who need a simple way to set up virtual environments.
-
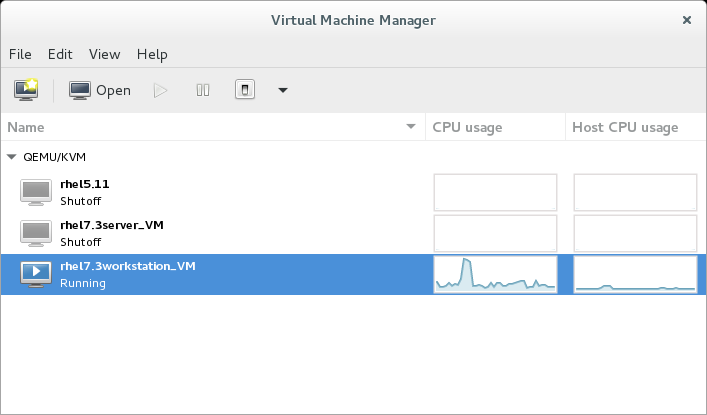
VirtManager VirtManager is a more advanced GUI for managing virtual machines. It offers a comprehensive set of tools for configuring and monitoring virtual environments, making it suitable for system administrators and power users.
Command-Line Interface
For users who prefer or require command-line tools, RHEL offers virt-install, a command-line utility for creating virtual machines. Here is an example command to create a virtual machine:
virt-install \
--name=webserver01 \
--ram=1024 \
--vcpus=1 \
--location=/var/lib/libvirt//img/docs/rhel-8.1-x86_64-dvd.iso \
--os-variant=rhel8 \
--graphics spice \
--disk path=/var/lib/libvirt//img/docs/webserver01.dsk,size=20 \
--extra-args='console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8 serial'